Earth:Dabbahu Volcano
| Dabbahu Volcano | |
|---|---|
 Dabbahu volcano (background) and Manda-Hararo rift (foreground) in 2008 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,442 m (4,731 ft) [1] |
| Listing | List of volcanoes in Ethiopia |
| Coordinates | [ ⚑ ] 12°36′N 40°29′E / 12.6°N 40.48°E[1] |
| Geography | |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Stratovolcano |
| Last eruption | September 2005 |
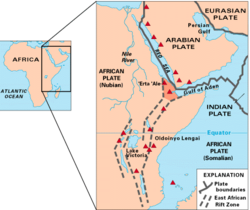
Dabbahu Volcano (also Boina, Boyna or Moina) is an active volcano located in the remote Afar Region of Ethiopia. This stratovolcano[2] is part of the Afar Triangle (Afar Depression), a highly active volcanic region which includes Erta Ale.[1] An eruption on September 26, 2005 created a large fissure in the ground, known as the Dabbahu fissure.[3]
2005 eruption
The only eruption of the volcano in recorded history occurred on September 26, 2005. Preceding the eruption, the ground swelled and an earthquake swarm consisting of over 130 events occurred.[2] Earthquakes measured 4.2 on the Richter scale.[4] The eruption began 5 kilometers northeast of the summit. Ash from the eruption darkened the area surrounding the volcano for nearly 3 days.
The eruption formed a 500 m long fissure ( [ ⚑ ] 12°39′01″N 40°31′10″E / 12.6502°N 40.5195°E) and a 30 m (98 ft) wide pumice cone at the fissure's southern end. Ash reached as far as the administrative center of Teru, located 40 km (25 mi) southwest of the volcano.
Plate tectonics
The volcano is located along the Somali Plate. Researchers predict that the land along this region, known as the East African Rift, will eventually break away, creating a new island consisting of eastern Ethiopia and Djibouti with a new sea in between.[5][6] Using seismic data from 2005, a research study predicted that this could occur in about one million years.[7]
Life
Scientists are studying the fissure for extremophiles.[8]
See also
- Erta Ale
- Geography of Ethiopia
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Dabbahu Volcano". http://www.volcanolive.com/dabbahu.html.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Dabbahu". Smithsonian Institution. https://volcano.si.edu/volcano.cfm?vn=221113.
- ↑ "Inside the Hottest Place on Earth". BBC News. 2009-03-19. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7950845.stm.
- ↑ "Quake triggers volcanic eruption in Ethiopia". http://friendsofethiopia.blogspot.com/2005/10/quake-triggers-volcanic-eruption-in.html.
- ↑ "Scientists: New Ocean Forming in Ethiopia". Fox News. 2005-12-10. http://www.foxnews.com/story/0,2933,178332,00.html.
- ↑ "Geologists have ringside seats for an ocean's birth". The Register. https://www.theregister.co.uk/2006/07/20/ocean_birth/.
- ↑ "Giant crack in Africa may create a new ocean". NBC News. http://www.nbcnews.com/id/33605604.
- ↑ "The Birth of an Ocean in the Hottest Desert on Earth". http://issuu.com/lightmediation/docs/birthofanocean?mode=embed&documentId=080419174234-ff3ffaf5e5a946daabe276d7b37ce6a1&layout=grey.
 |