Earth:Waituna
A waituna is a freshwater coastal lagoon on a mixed sand and gravel (MSG) beach, formed where a braided river meets a coastline affected by longshore drift.[1][2] This type of waterbody is neither a true lake, lagoon nor estuary.[2]
This classification differentiates it from hapua, a type of river mouth lagoon. Both waituna and hapua are rare globally but common in New Zealand, where they are considered ecologically significant as sites of traditional Māori food-gathering as well as for their diversity of fish and bird species.[3]
Waitnua form an interlinked chain of habitats which run the length of the east coast of the South Island: from Wairua Lagoon and Lake Grassmere / Kapara Te Hau in Marlborough, through Lake Ellesmere / Te Waihora and Coopers Lagoon / Muriwai in central Canterbury, and Washdyke Lagoon and Wainono Lagoon in South Canterbury, to Waituna Lagoon in Southland.[1] Waituna Lagoon is one of the finest examples.[4][5]
The name translates as “water of eels”.
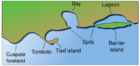
Difference between a hapua and a waituna
Both waituna and hapua are fed by small rivers flowing out to an MSG beach, on an eroding wave-dominated coast, with strong longshore drift.
Hapua are long-lived river mouth lagoons, whereas waituna are ephemeral coastal "lakes" that do not persist over geological time.
Hapua persist because the river mouth turns sideways and carves out cliffs on a daily basis, whereas waituna form when gravel creates a barrier that impedes the drainage of freshwater. Natural openings through the barrier are rare, although artificial openings are common. Over geological time, provided natural coastal processes are able to operate unimpeded, the "lake" floods and infills, or the barrier disappears with coastal erosion.[3]
Waituna characteristics
Waituna are low in salt, high in water that lies around for a long time, and shallow – typically less than 3 metres (9.8 ft) deep. They are tideless and the water is not well mixed by wind. The barrier prevents flushing by rainfall events. All this is evident in the green colour of water in above photo.
Waituna case study
Te Waihora / Lake Ellesmere is an outstanding natural feature. It is a wetland of international importance and an area of immense cultural significance to Ngāi Tahu.[6]
The waituna is fed by two small rivers, Selwyn River / Waikirikiri and Irwell River. These bring it a, comparatively, low volume of water, along with loads of silt and sand.
At the coast, in an area known as Canterbury Bight, a current runs parallel to the shore from south to north. This strong current brings with it sand and gravel sourced from the Rakaia River. The bight is chronically eroding because its beaches are starved of sediment. The Rakaia River, incidentally, has a hapau at its mouth.
Over geological time, a spit grew, drift-aligned to the current. It was, initially, as to be expected, wide the southern end where it receives the most sand and gravel, and narrow at the northern end. However, as it grew, it bumped into Banks Peninsula. This stopped it growing, but the sediment kept coming, so it no longer fits the rules of a spit. It's now wider at the proximal end and narrower at the distal end. It's become a barrier. Approximately 5000 years ago, it swung around, hinged at the point near Wairewa marae on the shores of Lake Forsyth / Waiwera.
The barrier, named Kaitorete Spit, even though it's a barrier not a spit, prevents the Selwyn / Waikirikiri and Irwell rivers from draining into the sea, and hence, a waituna sits behind the barrier.
Its natural lake level is 4 metres (13 ft) above sea level.
Photographs
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Kirk, R.M; Lauder, G.A (2000). "Significant coastal lagoon systems in the South Island, New Zealand". Department of Conservation. https://www.doc.govt.nz/globalassets/documents/science-and-technical/sfc146.pdf.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Single, M.B. and Hemmingson, M.A. (2001). "Mixed sand and gravel barrier beaches of South Canterbury, New Zealand". Ecology and Geomorphology of Coastal Shinge: 261–276.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hart, Deirdre (2008). "Chapter 20 Canterbury Coastal Systems". in Winterbourne, Michael (in English). The natural history of Canterbury (3rd ed.). Christchurch, NZ: Canterbury University Press. ISBN 9781877257575.
- ↑ Environment Southland (2022). "Waituna Lagoon". https://www.waituna.org.nz/about-waituna/waituna-lagoon.
- ↑ Department of Conservation. "Awarua-Waituna Wetlands". https://www.doc.govt.nz/our-work/freshwater-restoration/arawai-kakariki-wetland-restoration/sites/awarua-waituna-wetlands/.
- ↑ Christchurch City Council (12 November 2014). "Christchurch District Plan: Site of Ecological Significance". https://districtplan.ccc.govt.nz/Images/DistrictPlanImages/Site%20of%20Ecological%20Significance/SES%20E%201.pdf.
 |