Social:Landslide victory
A landslide victory is an election result in which the victorious candidate or party wins by an overwhelming margin.[1] The term became popular in the 1800s to describe a victory in which the opposition is "buried",[1] similar to the way in which a geological landslide buries whatever is in its path. A landslide victory is the opposite of an electoral wipeout; a party which wins in a landslide typically inflicts a wipeout on its opposition.
What constitutes a landslide varies by the type of electoral system. Even within an electoral system, there is no consensus on what sized margin makes for a landslide.[1]
Notable examples
Australia
Local and mayoral elections:
- 2008 Brisbane City Council election – The Liberal Party won a landslide victory over the Labor Party. Campbell Newman was re-elected Lord Mayor of Brisbane with 66.1% of the two-party-preferred vote, with a swing of 13.7%.[2] The LNP won 16 of the 26 wards. Newman later became Premier of Queensland in a landslide victory at the 2012 state election.
- 2021 Mandurah City Council election – Rhys Williams was re-elected Mayor of Mandurah with 85% of the vote.[3]
State and territory elections:
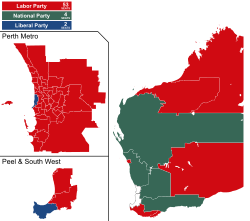
- 2021 Western Australian state election – Mark McGowan led the Labor Party to win 53 out of the 59 seats in the lower house. The Labor Party had a primary vote of 59.92% and a two-party-preferred vote of 69.68%. The National Party won 4 seats and the Liberal Party won 2 seats, making the National Party the official opposition, the first time they had held this status since the 1940s. To date, the election is the most decisive result at any Australian state or federal election since Federation, in terms of both percentage of lower house seats controlled by the governing party (89.8%) and two-party preferred margin.[4][5]
Fiji
- 1999 – the Fiji Labour Party, led by Mahendra Chaudhry, won a landslide victory,[6] winning 37 of the 71 seats in Parliament (gaining 30 seats). Chaudhry became the country's first Indo-Fijian Prime Minister. The incumbent, Sitiveni Rabuka (leader of Soqosoqo ni Vakavulewa ni Taukei), won just eight seats, losing 23. Five other parties also won a total of 26 seats and independents won eight seats.
- 2014 – FijiFirst, led by Frank Bainimarama, won a landslide victory[7][8] in the country's first elections since the 2006 Fijian coup d'état, led by Bainimarama. Bainimarama went on to serve a total of 16 years as Prime Minister, until losing the 2022 Fijian general election to Sitiveni Rabuka due to a hung parliament and the formation of a coalition between the three opposition parties (the People's Alliance, the National Federation Party and the Social Democratic Liberal Party).
Jamaica
- 2011 Jamaican general election – The People's National Party (PNP) led by Portia Simpson-Miller secured 42 seats to 21 for the Jamaica Labour Party.[9]
- 2020 Jamaican general election – The Jamaica Labour Party led by Andrew Holness was re-elected after winning a supermajority in Parliament.[10]
New Zealand
- Template:NZ election link – The Labour Party won 65 seats while the National Party won just 33 seats (the first time any party won an overall majority under MMP)[11]
Portugal
Legislative Elections
- 1987 – The centre-right Social Democratic Party led by Cavaco Silva won 148 out of the 250 seats and 50.2% of the popular vote. The second most voted party, the Socialist Party would receive just 22.2% of the total voting, falling 28 percentage points behind the winners.
- 1991 – Following the success attained in the previous legislative elections, the Social Democratic Party led by Cavaco Silva won 135 out of the 230 seats and 50.6% of the popular vote. The Socialist Party would also rise in voting, receiving 29.1% of the votes, but would still be far short of the Social Democrats.
Presidential Elections
- 1976 – António Ramalho Eanes, supported by the center-right and center-left political parties secured 61.6% of the total vote, while the second most voted candidate, FP-25 leader Otelo Saraiva de Carvalho, got 16.5% of the vote.
- 1991 – Incumbent president Mário Soares, supported by both the socialists and the social democrats achieved 70.3% of the total votes, while the second most voted candidate, Basilio Horta secured only 14.2% of the votes.
- 2006 – Aníbal Cavaco Silva, supported by the center-right parties, secured 50.5% of the votes in the first turn. Second most voted candidate, socialist Manuel Alegre would only secure 20.7%.
- 2011 – Incumbent president, Aníbal Cavaco Silva, supported by the center-right parties achieved 53% of the total voting, the second most voted candidate, socialist Manuel Alegre would only score 19.7%.
- 2016 — Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, supported by the center-right parties and benefiting from bigger media exposure than the rest of the candidates secured 52% of the votes in the first turn. Second most voted candidate António Sampaio da Nóvoa would only score 23% of voting.
- 2021 – Incumbent president, Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa, would renew his term receiving 60.6% of the total voting, whilst the second most voted candidate, socialist MEP Ana Gomes received only 13% of the votes. Rebelo de Sousa became the first presidential candidate to win in all the municipalities.
Azorean Regional Elections
- 1980 Azorean regional election (pt) – Social Democratic Party led by Mota Amaral took 30 of the 43 seats and 57.4% of the votes, the Socialist Party would only score 27.2%
- 1984 Azorean regional election (pt) – Social Democratic Party led by incumbent Azorean regional government president Mota Amaral took 28 of the 43 seats and 56.4% of the votes, the Socialist Party would only score 24.2%
Madeiran Regional Elections
Alberto João Jardim, member of the Social Democratic Party was the president of the Madeira region from 1978 to 2015. During this period of time, landslide victories for the Social Democrats were the norm.
| Year | % of votes for the Social Democratic Party | 2nd most voted party | % of votes for the 2nd most voted party | Margin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1976 Madeiran regional election (pt) | 59.6% | Socialist Party | 22.3% | 37.3 |
| 1980 Madeiran regional election (pt) | 65.3% | Socialist Party | 15.0% | 50.3 |
| 1984 Madeiran regional election (pt) | 67.8% | Socialist Party | 15.3% | 52.5 |
| 1988 Madeiran regional election (pt) | 62.3% | Socialist Party | 16.8% | 45.5 |
| 1992 Madeiran regional election (pt) | 56.9% | Socialist Party | 22.6% | 34.3 |
| 1996 Madeiran regional election | 56.9% | Socialist Party | 24.8% | 32.1 |
| 2000 Madeiran regional election | 56.0% | Socialist Party | 21.0% | 35.0 |
| 2004 Madeiran regional election | 53.7% | Socialist Party | 27.4% | 26.3 |
| 2007 Madeiran regional election | 64.2% | Socialist Party | 15.4% | 48.8 |
| 2011 Madeiran regional election | 48.6% | CDS – People's Party | 17.6% | 31.0 |
| 2015 Madeiran regional election | 44.4% | CDS – People's Party | 13.7% | 30.7 |
Samoa
- 2006 – The Human Rights Protection Party, led by Tuilaʻepa Saʻilele Malielegaoi, won a landslide victory, winning 33 seats, an increase of ten. The main opposition party, the new Samoa Democratic United Party, won 10 seats.[12]
- 2016 – The Human Rights Protection Party, led by Tuilaʻepa Saʻilele Malielegaoi, won by a landslide victory, winning 35 of the 49 seats in the Legislative Assembly, gaining six seats. The main opposition party, the Tautua Samoa Party (led by Palusalue Faʻapo II) only won two seats, losing 11 seats. Independents won 13 seats.[13]
Slovakia
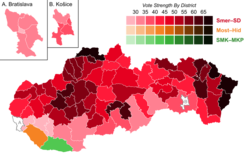
- 2012 – Direction – Social Democracy won an absolute majority of 83 out of 150 seats. It was the first time since the Velvet Revolution that a single party formed the government. The early elections followed the fall of Prime Minister Iveta Radičová's Slovak Democratic and Christian Union – Democratic Party-led coalition in October 2011 over a no confidence vote, which her government had lost because of its support for the European Financial Stability Fund.
Spain
- 1982 and 1986 – Felipe González's Spanish Socialist Workers' Party (PSOE) won two consecutive blowouts, with advantages of 22 and 18 percentage points over the second party, Manuel Fraga's right-wing People's Alliance, which scored just over one hundred seats and won only one region, Galicia. In 1982, PSOE won over 200 seats, the only time this has been achieved by a sole party.
- 2000 – Ruling José María Aznar's People's Party (PP) won by 10 percentage points to the PSOE.
- 2011 – local, regional and national elections were all landslide wins for the then-in opposition Mariano Rajoy's PP, winning the national election by a 16 percentage point margin to then-ruling PSOE.
Basque Country
- 2001 – Juan Jose Ibarretxe's Basque National Party-Basque Solidarity (PNV-EA) alliance won 33 seats and 42.2% of the share, 20 percentage points ahead of PP. The result is the best performance for the top voted list in a Basque regional election. With a record turnout of 79%, PNV-EA obtained more than 600,000 votes. PNV-EA also won more seats than PP (19) and PSE-EE (13) together, and was able to secure a working majority in parliament.
Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
A landslide victory in the elections of St. Vincent and the Grenadines involves a large swing from one party to another as well as one party winning a large majority in parliament. Landslide victories have usually occurred after a long period of government from one particular party and a change in the popular mood.
- 1989 – The New Democratic Party led by Prime Minister James Fitz-Allen Mitchell won all 15 seats in the House of Assembly and 66.3% of the popular vote.
Taiwan
- 1996 presidential election – As the first direct presidential election in Taiwan, the incumbent president Lee Teng-hui of Kuomintang won 54% of the votes while Peng Ming-min of the Democratic Progressive Party took only 21.1%.
- 2008 legislative election – Kuomintang won 81 seats while the Democratic Progressive Party won 27 seats.
- 2008 presidential election – Ma Ying-jeou of Kuomintang won 58.5% of the votes while Frank Hsieh took only 41.5%.
Presidential and Legislative Election held on the same day
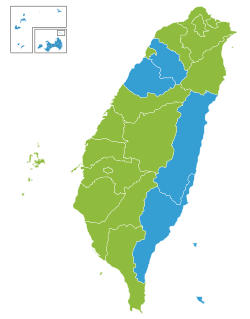
- 2016 – Tsai Ing-wen representing for the Democratic Progressive Party won 56.1% of the votes while Eric Chu of the Kuomintang took 31%. In the legislative election, Democratic Progressive Party won 68 seats while Kuomintang won 35 seats.
- 2020 – Tsai Ing-wen won a record 8.17 million votes for her second term, representing 57.1% of the popular vote, while Han Kuo-yu of Kuomintang took 38.6%. In the legislative election, the ruling party Democratic Progressive Party won 61 seats while Kuomintang won 38 seats.
Trinidad and Tobago
In Trinidad and Tobago's elections, a landslide victory involves a large swing from one party to another as well as one party winning a large majority in parliament. Landslide victories have usually occurred after a long period of government from one particular party and a change in the popular mood. Party politics and the political structure in Trinidad and Tobago has generally run along ethnic lines with most Afro-Trinidadians supporting the People's National Movement (PNM) and most Indo-Trinidadians supporting various Indian-majority parties, such as the current United National Congress (UNC) or its predecessors.
- 1971 – The People's National Movement led by Prime Minister Eric Williams won all 41 seats in the House of Representatives and 84.1% of the popular vote. Major opposition parties boycotted this election.
- 2010 – The People's Partnership led by Kamla Persad-Bissessar won 29 of the 41 seats in the House of Representatives. The election victory marked a change where the incumbent People's National Movement party led by Prime Minister Patrick Manning were voted out of power.
Tobago
- 2013 Tobago House of Assembly election – The Tobago Council of the People's National Movement led by Chief Secretary Orville London won all 12 seats in the Tobago House of Assembly and 61.4% of the popular vote.
Ukraine
- 2019 Ukrainian presidential election – Volodymyr Zelenskyy won all regions but one and 73.22% of the popular vote in the second round of the election, unseating incumbent Petro Poroshenko, who received 24.45% of the popular vote.
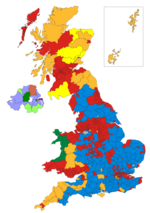
United Kingdom
In UK General Elections, a landslide victory involves winning a large majority in parliament and often goes with a large swing from one party to another as well. Landslide victories have usually occurred after a long period of government from one particular party and a change in the popular mood. In the past a majority of over 100 was regarded as the technical hurdle to be defined as a landslide, as that allows the government freedom to easily enact its policies in parliament. In more recent times, the label 'landslide' has been applied in numerous press articles to victories which would not previously have been regarded as such, for example the Conservative Party majority of 80 in 2019. Its current usage is more as political commentary rather than technical definition and is a reflection of the strength of the party's ability to put its programme through parliament.[14][15][16][17]
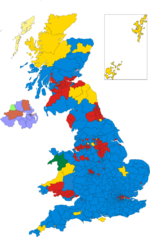
The largest landslide by any single party in the UK parliament, since universal suffrage was introduced, was the majority of 179 won by Tony Blair's Labour Party in 1997.
Notable landslide election results
- 1906 – Henry Campbell-Bannerman led his Liberal Party to victory over Arthur Balfour's Conservative Party who lost more than half their seats, including his own seat in Manchester East, as a result of the large national swing to the Liberal Party (The 5.4% swing from the Conservatives to Liberals was at the time the highest ever achieved). The Liberal Party won 397 seats (an increase of 214) while the Conservative Party were left with 156 seats (a decrease of 246).[18][19]
- 1945 – Clement Attlee led his Labour Party to victory over Winston Churchill's Conservative Party, a 12.0% swing from the Conservatives to Labour. Labour won 393 seats (an increase of 239) while the Conservative Party were left with 197 (a decrease of 190).[20]
- 1966 – Harold Wilson led the Labour Party to win 364 seats (an increase of 47) and gained an overall majority of 98 while the Conservative Party won 253 seats (a decrease of 51).
- 1983 – Margaret Thatcher won her second term in office with a landslide victory for the Conservatives gaining an overall majority of 144 by winning 397 seats (an increase of 38 seats) on 42.4% of the national vote and forcing her main opponent Michael Foot to resign after Labour won 209 seats.
- 1987 – Margaret Thatcher won her third term in office with a second landslide victory for the Conservatives gaining an overall majority of 102 by winning 376 seats (a decrease of 21 seats).
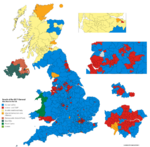
- 1997 – Tony Blair led the Labour Party to win 418 seats (an increase of 145) and gained an overall majority of 179 while the Conservative Party won 165 seats (a decrease of 178). The swing from the Conservatives to Labour was 10.2% and was the second biggest general election victory of the 20th Century after 1931.[21]
- 2001 – Tony Blair led the Labour Party win 412 seats (a decrease of 6) and gained an overall majority of 167 while the Conservative Party won 166 seats (an increase of 1). Making Tony Blair the first Labour Prime Minister to serve two consecutive full terms in office.[22]
- 2019 – Boris Johnson led the Conservative Party win a total of 365 seats (an increase of 48) and a majority of 80 seat, the party's largest majority since 1987. It left the Labour Party, who were led by Jeremy Corbyn, with 202 seats (a decrease of 60, their worst result since 1935). The election led to 54 Labour seats changing to Conservative predominantly in the Midlands and Northern England - some of which had been held by Labour since the first half of the 20th century.[23]
Scotland
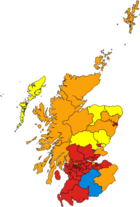
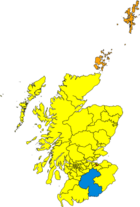
- 2011 Scottish Parliament Election – Alex Salmond led the Scottish National Party to a second term in Scottish Government with unprecedented success when they became the first party in Scotland to win an overall majority under an electoral system which was supposed to prevent such a result winning 69 seats and led to the holding of the 2014 Scottish independence referendum. The Scottish Labour Party only lost 7 seats overall however lost 22 constituency seats to the SNP in their worst result in Scotland for almost thirty years.
- 2015 UK General Election (Scotland) – The Scottish National Party led by First Minister Nicola Sturgeon who took over from Alex Salmond following the 2014 Scottish independence referendum won 56 out of 59 Westminster parliamentary constituency seats in Scotland, an increase of 50. The SNP, additionally, achieved 50% of the total votes in Scotland, 30% higher than the previous election. The Scottish Labour Party were reduced to one seat, from 41. The overall swing in Scotland was 23.9% from Labour to the SNP.
See also
- Wipeout (elections)
- Realigning election
- Wave elections in the United States
- Blowout (sports)
- Landslide (board game)
- Paper candidate
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Murse, Tom (8 October 2020). "Landslide Victory: Definition in Elections". ThoughtCo. https://www.thoughtco.com/definition-of-a-landslide-election-3367585.
- ↑ "Newman wins Brisbane election landslide". ABC News. 15 March 2008. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2008-03-15/newman-wins-brisbane-election-landslide/1074230.
- ↑ "The Mayor that was re-elected in a landslide, collecting 85 per cent of the votes". 20 October 2021. https://www.6pr.com.au/the-mayor-that-was-re-elected-in-a-landslide-collecting-85-per-cent-of-the-votes/.
- ↑ "Biggest State Election Landslides" (in en-AU). 2021-03-12. https://armariuminterreta.site/2021/03/12/biggest-state-election-landslides/.
- ↑ "Mark McGowan claims WA election victory as Liberals all but wiped out". The New Daily. 14 March 2021. https://thenewdaily.com.au/news/state/wa/2021/03/14/west-australian-election-labor-landslide/.
- ↑ "Fiji's military strongman voted out in landslide to the Labour Party". 19 May 1999. https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/1999/05/fji-m19.html.
- ↑ Fiji coup leader sworn in as PM Herald Sun. 22 September 2014. Retrieved 9 March 2023
- ↑ "Fiji's Military Ruler Wins Landslide Election Victory (2014)". https://youtube.com/watch?v=N-_XZroodeM.
- ↑ "Dominating victory in Jamaica elections even surprises winning opposition side". Washington Post. 30 December 2011. https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/americas/dominating-victory-in-jamaica-elections-even-surprises-winning-opposition-side/2011/12/30/gIQA6aZ8QP_story.html. Retrieved 31 December 2011.
- ↑ "Political Tsunami turns Jamaica green with massive JLP victory" (in en-US). https://www.myvuenews.com/political-tsunami-turns-jamaica-green-with-massive-jlp-victory/.
- ↑ "New Zealand election: Jacinda Ardern's Labour Party scores landslide win" (in en-GB). BBC News. 17 October 2020. https://www.bbc.com/news/world-asia-54519628.
- ↑ "Elections in 2006". Inter-Parliamentary Union. http://archive.ipu.org/parline-e/reports/arc/2351_06.htm.
- ↑ "Legislative Assembly (Fono)". Inter-Parliamentary Union. http://archive.ipu.org/parline-e/reports/2351_E.htm.
- ↑ Bush, Stephen (2021-06-08). "Despite all reports, the election wasn't a landslide – and Johnson may be about to discover that reality" (in en-US). https://www.newstatesman.com/politics/uk-politics/2019/06/despite-all-reports-election-wasn-t-landslide-and-johnson-may-be-about-discover.
- ↑ "Election results 2019: Boris Johnson returns to power with big majority" (in en-GB). BBC News. 2019-12-12. https://www.bbc.com/news/election-2019-50765773.
- ↑ Holder, Josh; Voce, Antonio; Barr, Caelainn; Holder, Josh; Voce, Antonio; Barr, Caelainn. "How did Boris Johnson achieve his landslide victory? A visual guide" (in en-GB). The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. https://www.theguardian.com/politics/ng-interactive/2019/dec/13/boris-johnson-achieves-landslide-victory-visual-guide.
- ↑ "Inside the landslide: Thatcher's personal papers for 1983 opened to the public" (in en). 2013-10-10. https://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/inside-the-landslide-thatchers-personal-papers-for-1983-opened-to-the-public.
- ↑ "1906: The Liberal landslide". 9 February 2006. http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/programmes/bbc_parliament/4694864.stm.
- ↑ Liberal Landslide: The General Election of 1906.
- ↑ Labour Landslide, July 5-19, 1945.
- ↑ Labour's Landslide: The British General Election 1997.
- ↑ "The rise and fall of New Labour" (in en-GB). BBC News. 2010-08-03. https://www.bbc.com/news/uk-politics-10518842.
- ↑ "Boris Johnson must fulfil his One Nation pledge". Financial Times. 13 December 2019. https://www.ft.com/content/007bff64-1c40-11ea-97df-cc63de1d73f4. Retrieved 2019-12-14.
 |