Chemistry:Turmerone
From HandWiki
Tumerones are a group of related chemical compounds of the sesquiterpene class. They are found in turmeric (Curcuma longa),[1] from which they derive their name, as well as other related plants such as Curcuma caesia.[2] There are multiple structural types of turmerones which differ in the number and placement of double bonds including α-tumerone, β-turmerone (also known as curlone), and ar-turmerone. Each of these types consists of multiple stereoisomers. A number of in vitro biological activities of turmerones have been reported, including antiinflammatory, immunomodulatory, antiproliferative, and antifungal activities.[3][4][5]
Example chemical structures
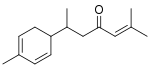 α-turmerone
|
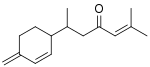 β-turmerone
|
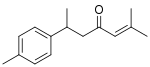 ar-turmerone
|
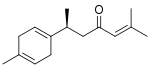 (S)-turmerone
|
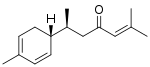 (S)-α-turmerone
|
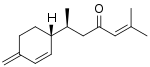 (+)-β-turmerone
|
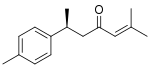 (S)-ar-turmerone
|
References
- ↑ Xiang, Hongping; Zhang, Lanyue; Xi, Lu; Yang, Yan; Wang, Xiaowei; Lei, Dehua; Zheng, Xi; Liu, Xiaoxuan (2018). "Phytochemical profiles and bioactivities of essential oils extracted from seven Curcuma herbs". Industrial Crops and Products 111: 298–305. doi:10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.035.
- ↑ Dosoky, Noura; Setzer, William (2018). "Chemical Composition and Biological Activities of Essential Oils of Curcuma Species". Nutrients 10 (9): 1196. doi:10.3390/nu10091196. PMID 30200410.
- ↑ Takemoto, Yuki; Kishi, Chihiro; Ehira, Hinano; Matsui, Nobutaka; Yamaguchi, Taichi; Yoshioka, Yuri; Matsumura, Shinichi; Moriyama, Tatsuya et al. (2022). "Inhaled turmerones can be incorporated in the organs via pathways different from oral administration and can affect weight-gain of mice". Scientific Reports 12 (1): 11039. doi:10.1038/s41598-022-15168-9. PMID 35773461. Bibcode: 2022NatSR..1211039T.
- ↑ Obulesu, Magisetty (2021). "Health benefits of turmeric: Emphasis on anticancer activity". Turmeric and Curcumin for Neurodegenerative Diseases. pp. 3–18. doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-822448-9.00006-6. ISBN 9780128224489.
- ↑ Kuttan, Ramadasan; Liju, Vijayastelterb; Jeena, Kottarapat (2011). "An evaluation of antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antinociceptive activities of essential oil from Curcuma longa. L". Indian Journal of Pharmacology 43 (5): 526–531. doi:10.4103/0253-7613.84961. PMID 22021994.
 |

