Chemistry:Corey–Kim oxidation
| Corey-Kim oxidation | |
|---|---|
| Named after | Elias James Corey Choung Un Kim |
| Reaction type | Organic redox reaction |
| Identifiers | |
| Organic Chemistry Portal | corey-kim-oxidation |
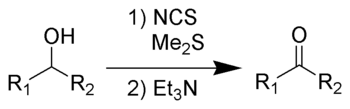
The Corey–Kim oxidation is an oxidation reaction used to synthesise aldehydes and ketones from primary and secondary alcohols.[1][2][3][4][5] It is named for American chemist and Nobel Laureate Elias James Corey and Korean-American chemist Choung Un Kim.
Although the Corey–Kim oxidation possesses the distinctive advantage over Swern oxidation of allowing an operation above –25 °C, it is not so commonly used due to issues with selectivity in substrates susceptible to chlorination by N-chlorosuccinimide.
Reaction mechanism
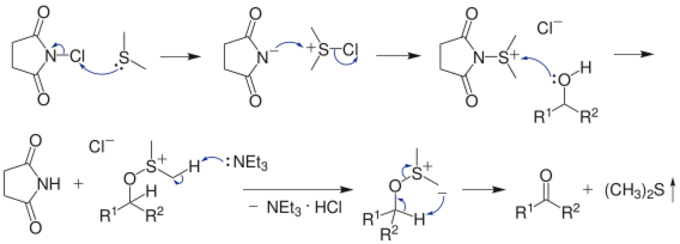
Dimethyl sulfide (Me2S) is treated with N-chlorosuccinimide (NCS), resulting in formation of an "active DMSO" species that is used for the activation of the alcohol. Addition of triethylamine to the activated alcohol leads to its oxidation to aldehyde or ketone and generation of dimethyl sulfide. In variance with other alcohol oxidation using "activated DMSO," the reactive oxidizing species is not generated by reaction of DMSO with an electrophile. Rather, it is formed by oxidation of dimethyl sulfide with an oxidant (NCS).
Under Corey–Kim conditions allylic and benzylic alcohols have a tendency to evolve to the corresponding allyl and benzyl chlorides unless the alcohol activation is very quickly followed by addition of triethylamine. In fact, Corey–Kim conditions —with no addition of triethylamine— are very efficient for the transformation of allylic and benzylic alcohols to chlorides in presence of other alcohols.
Variations
Substituting dimethyl sulfide with something less noxious has been the goal of several research projects. Ohsugia et al.[6] substituted a long-chain sulfide, dodecyl methyl sulfide, for dimethyl sulfide. Crich et al.[7] utilized fluorous technology in a similar manner.
See also
References
- ↑ E. J. Corey; C. U. Kim (1972). "New and highly effective method for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carbonyl compounds". Journal of the American Chemical Society 94 (21): 7586–7587. doi:10.1021/ja00776a056.
- ↑ E. J. Corey; C. U. Kim (1974). "A method for the oxidation of sec,tert-1,2-diols to α-hydroxy ketones without carbon-carbon cleavage". Tetrahedron Letters 15 (3): 287–290. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(01)82195-X.
- ↑ S. Katayama; K. Fukuda; T. Watanabe; M. Yamauchi (1988). "Synthesis of 1,3-Dicarbonyl Compounds by the Oxidation of 3-Hydroxycarbonyl Compounds with Corey–Kim Reagent". Synthesis 1988 (3): 178–183. doi:10.1055/s-1988-27506.
- ↑ T. T. Tidwell (1990). "Oxidation of Alcohols by Activated Dimethyl Sulfoxide and Related Reactions: An Update". Synthesis 1990 (10): 857–870. doi:10.1055/s-1990-27036.
- ↑ J. T. Pulkkinen; J. J. Vepsäläinen (1996). "3-Unsubstituted 1,5-Diaryl-2,4-pentanediones and -4-methoxy-2-pentanones: Synthesis via Corresponding 3-Hydroxy Ketones Generated from 2-Isoxazolines". Journal of Organic Chemistry 61 (24): 8604–8609. doi:10.1021/jo960887a.
- ↑ Ohsugia, S.-I.; Nishidea, K.; Oonob, K.; Okuyamab, K.; Fudesakaa, M.; Kodamaa, S.; Node, M. Tetrahedron 2003, 59, 8393–8398.
- ↑ Crich, D.; Neelamkavil, S. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 3865–3870.
External links
 |