Google matrix
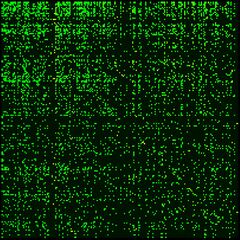
A Google matrix is a particular stochastic matrix that is used by Google's PageRank algorithm. The matrix represents a graph with edges representing links between pages. The PageRank of each page can then be generated iteratively from the Google matrix using the power method. However, in order for the power method to converge, the matrix must be stochastic, irreducible and aperiodic.
Adjacency matrix A and Markov matrix S
In order to generate the Google matrix G, we must first generate an adjacency matrix A which represents the relations between pages or nodes.
Assuming there are N pages, we can fill out A by doing the following:
- A matrix element [math]\displaystyle{ A_{i, j} }[/math] is filled with 1 if node [math]\displaystyle{ j }[/math] has a link to node [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math], and 0 otherwise; this is the adjacency matrix of links.
- A related matrix S corresponding to the transitions in a Markov chain of given network is constructed from A by dividing the elements of column "j" by a number of [math]\displaystyle{ k_j=\Sigma_{i=1}^N A_{i,j} }[/math] where [math]\displaystyle{ k_j }[/math] is the total number of outgoing links from node j to all other nodes. The columns having zero matrix elements, corresponding to dangling nodes, are replaced by a constant value 1/N. Such a procedure adds a link from every sink, dangling state [math]\displaystyle{ a }[/math] to every other node.
- Now by the construction the sum of all elements in any column of matrix S is equal to unity. In this way the matrix S is mathematically well defined and it belongs to the class of Markov chains and the class of Perron-Frobenius operators. That makes S suitable for the PageRank algorithm.
Construction of Google matrix G

Then the final Google matrix G can be expressed via S as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ G_{ij} = \alpha S_{ij} + (1-\alpha) \frac{1}{N} \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; (1) }[/math]
By the construction the sum of all non-negative elements inside each matrix column is equal to unity. The numerical coefficient [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] is known as a damping factor.
Usually S is a sparse matrix and for modern directed networks it has only about ten nonzero elements in a line or column, thus only about 10N multiplications are needed to multiply a vector by matrix G.[2][3]
Examples of Google matrix
An example of the matrix [math]\displaystyle{ S }[/math] construction via Eq.(1) within a simple network is given in the article CheiRank.
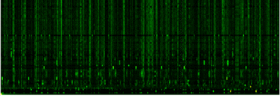
For the actual matrix, Google uses a damping factor [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] around 0.85.[2][3][4] The term [math]\displaystyle{ (1-\alpha) }[/math] gives a surfer probability to jump randomly on any page. The matrix [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] belongs to the class of Perron-Frobenius operators of Markov chains.[2] The examples of Google matrix structure are shown in Fig.1 for Wikipedia articles hyperlink network in 2009 at small scale and in Fig.2 for University of Cambridge network in 2006 at large scale.
Spectrum and eigenstates of G matrix

For [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \lt \alpha \lt 1 }[/math] there is only one maximal eigenvalue [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda =1 }[/math] with the corresponding right eigenvector which has non-negative elements [math]\displaystyle{ P_i }[/math] which can be viewed as stationary probability distribution.[2] These probabilities ordered by their decreasing values give the PageRank vector [math]\displaystyle{ P_i }[/math] with the PageRank [math]\displaystyle{ K_i }[/math] used by Google search to rank webpages. Usually one has for the World Wide Web that [math]\displaystyle{ P \propto 1/K^{\beta} }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ \beta \approx 0.9 }[/math]. The number of nodes with a given PageRank value scales as [math]\displaystyle{ N_P \propto 1/P^\nu }[/math] with the exponent [math]\displaystyle{ \nu = 1+1/\beta \approx 2.1 }[/math].[6][7] The left eigenvector at [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda =1 }[/math] has constant matrix elements. With [math]\displaystyle{ 0 \lt \alpha }[/math] all eigenvalues move as [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_i \rightarrow \alpha \lambda_i }[/math] except the maximal eigenvalue [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda =1 }[/math], which remains unchanged.[2] The PageRank vector varies with [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha }[/math] but other eigenvectors with [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda_i \lt 1 }[/math] remain unchanged due to their orthogonality to the constant left vector at [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda = 1 }[/math]. The gap between [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda = 1 }[/math] and other eigenvalue being [math]\displaystyle{ 1 - \alpha \approx 0.15 }[/math] gives a rapid convergence of a random initial vector to the PageRank approximately after 50 multiplications on [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] matrix.
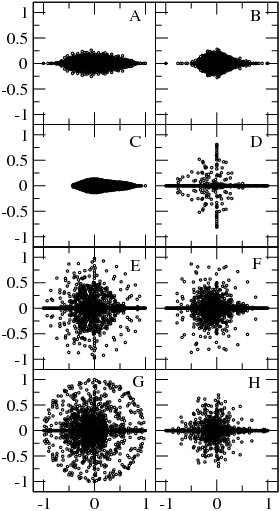
At [math]\displaystyle{ \alpha=1 }[/math] the matrix [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] has generally many degenerate eigenvalues [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda =1 }[/math] (see e.g. [6][8]). Examples of the eigenvalue spectrum of the Google matrix of various directed networks is shown in Fig.3 from [5] and Fig.4 from.[8]
The Google matrix can be also constructed for the Ulam networks generated by the Ulam method [8] for dynamical maps. The spectral properties of such matrices are discussed in [9,10,11,12,13,15].[5][9] In a number of cases the spectrum is described by the fractal Weyl law [10,12].
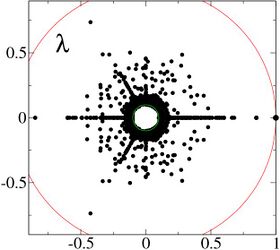
The Google matrix can be constructed also for other directed networks, e.g. for the procedure call network of the Linux Kernel software introduced in [15]. In this case the spectrum of [math]\displaystyle{ \lambda }[/math] is described by the fractal Weyl law with the fractal dimension [math]\displaystyle{ d \approx 1.3 }[/math] (see Fig.5 from [9]). Numerical analysis shows that the eigenstates of matrix [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] are localized (see Fig.6 from [9]). Arnoldi iteration method allows to compute many eigenvalues and eigenvectors for matrices of rather large size [13].[5][9]
Other examples of [math]\displaystyle{ G }[/math] matrix include the Google matrix of brain [17] and business process management [18], see also.[1] Applications of Google matrix analysis to DNA sequences is described in [20]. Such a Google matrix approach allows also to analyze entanglement of cultures via ranking of multilingual Wikipedia articles abouts persons [21]
Historical notes
The Google matrix with damping factor was described by Sergey Brin and Larry Page in 1998 [22], see also articles on PageRank history [23],[24].
See also
- CheiRank
- Arnoldi iteration
- Markov chain
- Transfer operator
- Perron–Frobenius theorem
- Web search engines
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Ermann, L.; Chepelianskii, A. D.; Shepelyansky, D. L. (2011). "Towards two-dimensional search engines". Journal of Physics A 45 (27): 275101. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/45/27/275101. Bibcode: 2012JPhA...45A5101E.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Google's PageRank and Beyond. Princeton University Press. 2006. ISBN 978-0-691-12202-1.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Austin, David (2008). "How Google Finds Your Needle in the Web's Haystack". AMS Feature Columns. http://www.ams.org/samplings/feature-column/fcarc-pagerank.
- ↑ Law, Edith (2008-10-09). "PageRank Lecture 12". https://www.cs.cmu.edu/~elaw/pagerank.pdf.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Frahm, K. M.; Georgeot, B.; Shepelyansky, D. L. (2011-11-01). "Universal emergence of PageRank". Journal of Physics A 44 (46): 465101. doi:10.1088/1751-8113/44/46/465101. Bibcode: 2011JPhA...44T5101F.
- ↑ Donato, Debora; Laura, Luigi; Leonardi, Stefano; Millozzi, Stefano (2004-03-30). "Large scale properties of the Webgraph". European Physical Journal B 38 (2): 239–243. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2004-00056-6. Bibcode: 2004EPJB...38..239D. http://www.cosinproject.eu/publications/donato-epjb38-2004.pdf.
- ↑ Pandurangan, Gopal; Ranghavan, Prabhakar; Upfal, Eli (2005). "Using PageRank to Characterize Web Structure". Internet Mathematics 3 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1080/15427951.2006.10129114. http://cs.brown.edu/research/pubs/pdfs/2005/Pandurangan-2005-UPC.pdf.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Georgeot, Bertrand; Giraud, Olivier; Shepelyansky, Dima L. (2010-05-25). "Spectral properties of the Google matrix of the World Wide Web and other directed networks". Physical Review E 81 (5): 056109. doi:10.1103/PhysRevE.81.056109. PMID 20866299. Bibcode: 2010PhRvE..81e6109G.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 Ermann, L.; Chepelianskii, A. D.; Shepelyansky, D. L. (2011). "Fractal Weyl law for Linux Kernel Architecture". European Physical Journal B 79 (1): 115–120. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2010-10774-7. Bibcode: 2011EPJB...79..115E.
- Serra-Capizzano, Stefano (2005). "Jordan Canonical Form of the Google Matrix: a Potential Contribution to the PageRank Computation". SIAM J. Matrix Anal. Appl. 27 (2): 305. doi:10.1137/s0895479804441407.
- Ulam, Stanislaw (1960). A Collection of Mathematical Problems. Interscience Tracts in Pure and Applied Mathematics. New York: Interscience. p. 73.
- Froyland G.; Padberg K. (2009). "Almost-invariant sets and invariant manifolds—Connecting probabilistic and geometric descriptions of coherent structures in flows". Physica D 238 (16): 1507. doi:10.1016/j.physd.2009.03.002. Bibcode: 2009PhyD..238.1507F.
- Shepelyansky D.L.; Zhirov O.V. (2010). "Google matrix, dynamical attractors and Ulam networks". Phys. Rev. E 81 (3): 036213. doi:10.1103/physreve.81.036213. PMID 20365838. Bibcode: 2010PhRvE..81c6213S.
- Ermann L.; Shepelyansky D.L. (2010). "Google matrix and Ulam networks of intermittency maps". Phys. Rev. E 81 (3): 036221. doi:10.1103/physreve.81.036221. PMID 20365846. Bibcode: 2010PhRvE..81c6221E.
- Ermann L.; Shepelyansky D.L. (2010). "Ulam method and fractal Weyl law for Perron-Frobenius operators". Eur. Phys. J. B 75 (3): 299–304. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2010-00144-0. Bibcode: 2010EPJB...75..299E.
- Frahm K.M.; Shepelyansky D.L. (2010). "Ulam method for the Chirikov standard map". Eur. Phys. J. B 76 (1): 57–68. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2010-00190-6. Bibcode: 2010EPJB...76...57F.
- Chepelianskii, Alexei D. (2010). "Towards physical laws for software architecture". arXiv:1003.5455 [cs.SE].
- Shepelyansky D.L.; Zhirov O.V. (2010). "Towards Google matrix of brain". Phys. Lett. A 374 (31–32): 3206. doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2010.06.007. Bibcode: 2010PhLA..374.3206S.
- Abel M.; Shepelyansky D.L. (2011). "Google matrix of business process management". Eur. Phys. J. B 84 (4): 493. doi:10.1140/epjb/e2010-10710-y. Bibcode: 2011EPJB...84..493A.
- Kandiah, Vivek; Shepelyansky, Dima L. (2013). "Google Matrix Analysis of DNA Sequences". PLOS ONE 8 (5): e61519. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0061519. PMID 23671568. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...861519K.
- Eom, Young-Ho; Shepelyansky, Dima L. (2013). "Highlighting Entanglement of Cultures via Ranking of Multilingual Wikipedia Articles". PLOS ONE 8 (10): e74554. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074554. PMID 24098338. Bibcode: 2013PLoSO...874554E.
- Brin S.; Page L. (1998). "The anatomy of a large-scale hypertextual Web search engine". Computer Networks and ISDN Systems 30 (1–7): 107. doi:10.1016/s0169-7552(98)00110-x.
- Massimo, Franceschet (2010). "PageRank: Standing on the shoulders of giants". arXiv:1002.2858 [cs.IR].
- Vigna, Sebastiano (2010). "Spectral Ranking". http://vigna.di.unimi.it/ftp/papers/SpectralRanking.pdf.
External links
- Google matrix at Scholarpedia
- Google PR Shut Down
- Video lectures at IHES Workshop "Google matrix: fundamental, applications and beyond", Oct 2018
 |

