Sabin (unit)
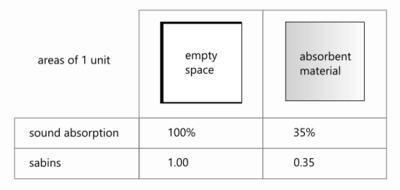
In acoustics, the sabin (or more precisely the square foot sabin) is a unit of sound absorption, used for expressing the total effective absorption for the interior of a room. Sound absorption can be expressed in terms of the percentage of energy absorbed compared with the percentage reflected. It can also be expressed as a coefficient, with a value of 1.00 representing a material which absorbs 100% of the energy, and a value of 0.00 meaning all the sound is reflected.[1]
The concept of a unit for absorption was first suggested by American physicist Wallace Clement Sabine, the founder of the field of architectural acoustics. He defined the "open-window unit" as the absorption of 1 square foot (0.093 m2) of open window.[1] The unit was renamed the sabin after Sabine, and it is now defined as "the absorption due to unit area of a totally absorbent surface".[1]
Sabins may be calculated with either imperial or metric units. One square foot of 100% absorbing material has a value of one imperial sabin, and 1 square metre of 100% absorbing material has a value of one metric sabin.
The total absorption A in metric sabins for a room containing many types of surface is given by [math]\displaystyle{ A = S_1 \alpha_1 + S_2 \alpha_2 + \ldots + S_n \alpha_n = \sum S_i \alpha_i , }[/math] where S1, S2, ..., Sn are the areas of the surfaces in the room (in m2), and α1, α2, ..., αn are the absorption coefficients of the surfaces.
Sabins are used in calculating the reverberation time of concert halls, lecture theatres, and recording studios.[2]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Moore 1979, p. 35.
- ↑ Davis & Davis 1975, p. 168.
Sources
- Davis, Don; Davis, Caroline (1975). Sound System Engineering (2nd ed.). Indianapolis: H. W. Sams. ISBN 978-0-672-21156-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=aaLcAwAAQBAJ&q=davis+Sound+System+Engineering.
- Moore, John Edwin (1979). Design for Good Acoustics and Noise Control. London: Macmillan. ISBN 978-03332-4-293-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=RD5dDwAAQBAJ.
External links
- Understanding sabins from NetWell Noise Control
 |