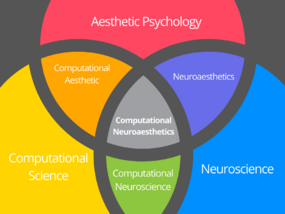
Computational neuroaesthetics
Computational neuroaesthetics is the discipline that connects neuromarketing, psychology and computer science.[1] It represents the evolution of neuroaesthetics and computational aesthetics and investigates the brain processes of human beings involved during the aesthetic experience.
In pursuing this research objective it uses a methodology that integrates the methods and techniques which are typical of neuroscience with those typical of computational science. The visual stimuli observed by people, such as images, are computationally processed to obtain a numerical value of the aesthetic features, such as brightness and hues, which are related to the brain processes of the subjects. In doing so, computational neuroaesthetics overcomes the limits of computational aesthetics, which uses only classical measuring instruments, such as self report scales, to assess the positive emotions experienced by individuals.
Areas of application
The results that emerge from computational neuroaesthetics research can be applied in several areas. The privileged one is the field of marketing and communication, since it is possible to know which aesthetic characteristics an advertising stimulus should have to be appreciated at a deep and implicit level by consumers. These positive reactions are a factor that influences the orientation of people towards the products and the brands that are promoted.[2][3]
Another area of application is design and user experience design. In fact, the aesthetics of products and phygital interfaces is a fundamental component for user experience. Computational neuroaesthetics offers useful knowledge to develop a design that respects those aesthetic parameters which are able to improve user experience. Products and services with good UX levels are perceived as better and easier to use by consumers.[4]
In the fields of health and well-being psychology, the knowledge of this discipline represents a potential tool able to build positive and transformative aesthetic experiences which could promote patients' engagement.
Origins
Aesthetics is a discipline that, within the psychological field, has been studied over the decades by different approaches, including the gestalt and cognitivist ones. In 2005, Chatterjee,[5] stressed the need to use a research approach able to integrate neuroaesthetics with an analytical description of the features of visual stimuli in order to obtain quantifiable parameters.
References
- ↑ Martone, Mattia (2020). Computational Neuroaesthetics: innovation in Digital Marketing. ISBN 979-8577902698. https://www.academia.edu/44511803.
- ↑ Fennis, Bob M.; Stroebe, Wolfgang (2010). The Psychology of Advertising.
- ↑ Schwarz, Norbert; Clore, Gerald L.. "Mood as Information: 20 Years Later". Psychological Inquiry 14: 3&4. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229060100.
- ↑ Norman, Donald A. (2005). Emotional Design: Why We Love (or Hate) Everyday Things.
- ↑ Chatterjee, Anjan (2011). "Neuroaesthetics: A Coming of Age Story". Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 23 (1): 53–62. doi:10.1162/jocn.2010.21457. PMID 20175677. http://dx.doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2010.21457.
 |