Cybersquatting
Cybersquatting (also known as domain squatting) is the practice of registering, trafficking in, or using an Internet domain name, with a bad faith intent to profit from the goodwill of a trademark belonging to someone else.
The term is derived from "squatting", which is the act of occupying an abandoned or unoccupied space or building that the squatter does not own, rent, or otherwise have permission to use.
Terminology
In popular terms, "cybersquatting" is the term most frequently used to describe the deliberate, bad faith abusive registration of a domain name in violation of trademark rights. However, precisely because of its popular currency, the term has different meanings to different people. Some people, for example, include "warehousing", or the practice of registering a collection of domain names corresponding to trademarks with the intention of selling the registrations to the owners of the trademarks, within the notion of cybersquatting, while others distinguish between the two terms.[1] In the former definition, the cybersquatter may offer to sell the domain to the person or company who owns a trademark contained within the name at an inflated price.
Similarly, some consider "cyberpiracy" to be interchangeable with "cybersquatting", whereas others consider that the former term relates to violation of copyright in the content of websites, rather than to abusive domain name registrations.[1]
Because of the various interpretations of the term, World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), in a 1999 report, approved by its member states, considered it as the abusive registration of a domain name.[2][3]
Legal resolution
International
Since 1999, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) has provided an administrative process wherein a trademark holder can attempt to claim a squatted site.
Trademark owners in 2021 filed a record 5,128 cases under the Uniform Domain-Name Dispute-Resolution Policy (UDRP) with World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO)'s Arbitration and Mediation Center, eclipsing the 2020 level by 22%. The surge pushed WIPO cybersquatting cases to almost 56,000 and the total number of domain names covered past the 100,000 mark.[4] As a matter of comparison, in 2006, there were 1823 complaints filed with WIPO, which was a 25% increase over the 2005 rate.[5]
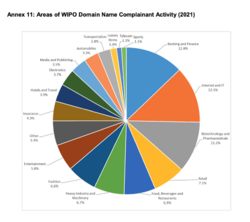
The accelerating growth in cybersquatting cases filed with the WIPO Center has been largely attributed by the WIPO Center[6] to trademark owners reinforcing their online presence to offer authentic content and trusted sales outlets, with a greater number of people spending more time online, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic. Representing 70% of WIPO's Generic top-level domain (gTLD) cases, .com demonstrated its continuing primacy.
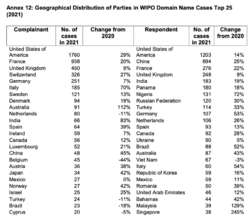
WIPO UDRP cases in 2021 involved parties from 132 countries. The top three business areas were Banking and Finance (13%), Internet and IT (13%), and Biotechnology and Pharmaceuticals (11%).[7] The U.S., with 1,760 cases filed, France (938), the U.K. (450), Switzerland (326), and Germany (251) were the top five filing countries.[8]
In 2007 it was stated that 84% of the claims made since 1999 were decided in the complaining party's favor.[5]
In the United States of America
Some countries have specific laws against cybersquatting beyond the normal rules of trademark law. For example, according to the United States federal law known as the Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act (ACPA), cybersquatting is registering, trafficking in, or using an Internet domain name with bad faith intent to profit from the goodwill of a trademark belonging to someone else. The United States adopted the U.S. Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act in 1999. This expansion of the Lanham (Trademark) Act (15 U.S.C.) is intended to provide protection against cybersquatting for individuals as well as owners of distinctive trademarked names. However, some notable personalities, including actor Kevin Spacey, failed to obtain control of their names on the internet because the US ACPA considers ownership of a website name "fair use" for which no permission is needed, unless there is an attempt to profit from the domain name by putting it up for sale.[9]
Jurisdiction is an issue, as shown in the case involving Kevin Spacey, in which Judge Gary A. Feess, of the United States District Court of the Central District of California, ruled that the actor would have to file a complaint in a Canadian court, where the current owner of kevinspacey.com resided. Spacey later won the domain through FORUM (formerly known as the National Arbitration Forum).
In Spain
In relation to cybersquatting, the Spanish Supreme Court issued the first sentence on this practice, relating it to the crime of misappropriation (STS 358/2022, of April 7). An unprecedented fact that established the legal fit of this computer crime in Spanish jurisprudence.
The case revolves around four members of the religious association Alpha Education for Comprehensive Health. They created a web page (the Internet domain of which was www.alfatelevision.org) and opened a bank and PayPal account for donations made to the association.
Some time later, there were some disagreements between the members of the association and the four defendants who opened a new website, changed the internet domain and changed the password of the accounts, which redirected all the donations from the followers. Later, the association dismissed the four members.
The general secretary of the association denounced the four members for a crime of misappropriation and they were sentenced by the Provincial Court of Guadalajara, understanding that the internet domain was an asset of the association.
This resolution was appealed to the Supreme Court through an appeal, which was upheld by the court. Finally, the Supreme Court acquitted the four accused, understanding that the proven facts do not fit the crime of misappropriation. In this sense, it highlights that there are elements that did not concur in this case and that the actions carried out by these individuals (creation of another domain, change of passwords...) occurred prior to their termination and that, therefore, they were in willingness to do it.
In addition, the sentence reflects cases in which cybersquatting could have criminal relevance. In the first place, if the conduct sought to harm the rights of a brand, it could constitute a crime against industrial or intellectual property. Secondly, if the intention was to use the domain name in a deceitful way to cause an error in the transfer of assets, the accused could face a crime of fraud. Finally, if cybersquatting were used to attack a domain name, the accused would be facing a crime of computer sabotage.[10]
Notable cases
With litigation
- Jethro Tull vs. Denny Hammerton,[11] 2000 (WIPO Case)
- Madonna vs. Parisi,[12] 2000 (WIPO Case)
- Primedia Magazine Finance Inc. (Tiger Beat) vs Next Level Productions (Benny Doro).[13]
- People for the Ethical Treatment of Animals v. Doughney, 2001
- Lamparello v. Falwell, 2005
- Lufthansa v. Future Media Architects, 2008[14]
- Microsoft vs. MikeRoweSoft
- Dennis Toeppen v. Panavision[15]
- Nissan Motors vs. Nissan Computer
- Van Cleef & Arpels, S.A. v. Nexperian Holding Limited[16]
- Aviva Brands Limited v. Nexperian Holding Limited[17]
- Swiss Arabian Perfumes Ind. Ltd. v. Nexperian Holding Limited[18]
- Mou Limited v. Nexperian Holding Limited[19]
- Planned Parenthood Federation of America, Inc. v. Bucci
- Satyam Infoway Ltd. v. Sifynet Solutions Pvt. Ltd.
Without litigation
- The White House against Whitehouse.com and Whitehouse.org
Accused of cybersquatting
- The personal website of a NASA engineer, gail.com, could be accused of cybersquatting on a typo for Gmail. However, gail.com claims that the site was created after Gail's husband bought her the URL in 1996, eight years before Gmail was introduced, and Gail does not appear to profit from the site.[20]
Social media
With the rise of social media websites such as Facebook and Twitter, a new form of cybersquatting involves registering trademark-protected brands or names of public figures on popular social media websites. Such cases may be referred to as "username squatting".
On June 5, 2009, Tony La Russa, the manager of the St. Louis Cardinals, filed a complaint against Twitter, accusing Twitter of cybersquatting.[21] The dispute centered on a Twitter profile that used La Russa's name, had a picture of La Russa, and had a headline that said "Hey there! Tony La Russa is now using Twitter." The profile encouraged users to "join today to start receiving Tony La Russa's updates." According to La Russa, the status updates were vulgar and derogatory. La Russa argued that the author of the profile intended, in bad faith, to divert Internet traffic away from La Russa's website and make a profit from the injury to La Russa's mark.[21] On June 26, 2009, La Russa filed a notice of voluntary dismissal after the parties settled the case.[22]
Efforts to curtail cybersquatting in social media
Social networking websites have attempted to curb cybersquatting, making cybersquatting a violation of their terms of service.
Twitter's name squatting policy forbids the cybersquatting as seen in many domain name disputes, like "username for sale" accounts: "Attempts to sell or extort other forms of payment in exchange for usernames will result in account suspension."[23] Additionally, Twitter has an "Impersonation Policy" that forbids non-parody impersonation. An account may be guilty of impersonation if it confuses or misleads others; "accounts with the clear intent to confuse or mislead may be permanently suspended." Twitter's standard for defining parody is whether a reasonable person would be aware that the fake profile is a joke.[24]
Soon after the La Russa suit was filed, Twitter took another step to prevent "identity confusion" caused by squatting by unveiling Twitter verification.[25] Usernames stamped with the "verified account" insignia is intended to indicate that the accounts are real and authentic. However, after the acquisition of Twitter by Elon Musk the verification system was changed to make it easier for individuals to get verified through the Twitter Blue program,[26] giving accounts "Profile Labels" instead – identifying ownership information such as whether the account is an individual, business, or a government.[27]
Facebook reserves the right to reclaim usernames on the website if they infringe on a trademark.[28] Trademark owners are responsible for reporting any trademark infringement on a username infringement form Facebook provides. Furthermore, Facebook usernames require "mobile phone authentication".[28] In order to obtain a username, the individual needs to verify the account by phone.
Sources
![]() This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC-BY-4.0 2021 WIPO's Global Intellectual Property Filing Services, WIPO. To learn how to add open license text to HandWiki articles, please see this how-to page. For information on reusing text from HandWiki, please see the terms of use.
This article incorporates text from a free content work. Licensed under CC-BY-4.0 2021 WIPO's Global Intellectual Property Filing Services, WIPO. To learn how to add open license text to HandWiki articles, please see this how-to page. For information on reusing text from HandWiki, please see the terms of use.
See also
- Brandjacking
- Domain name front running
- Domain Name System
- Domain sniping
- Domain tasting
- Taubman Sucks, a short documentary about a precedent-setting intellectual property lawsuit.
- Top-level domain
- Typosquatting
- Uniform Resource Locator (URL)
- Michael Urvan
- John Zuccarini, convicted of violating the Truth in Domain Names Act
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "WIPO Internet Domain Name Process" (in en). April 30, 1999. https://www.wipo.int/amc/en/processes/process1/report/finalreport.html.
 Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Text was copied from this source, which is available under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
- ↑ "The management of internet names and addresses: intellectual property issues. Final report.". 30 April 1999. https://www.wipo.int/export/sites/www/amc/en/docs/report-final1.pdf.
- ↑ "Administrative Panel Decision". 2000. https://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/html/2000/d2000-0662.html.
- ↑ "Total Number of WIPO Domain Name Cases and Domain Names by Year". World Intellectual Property Organization. 10 February 2022. p. 9. https://www.wipo.int/export/sites/www/pressroom/en/documents/pr_2022_886_annexes.pdf#page=9.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "U.N: Cybersquatting complaints rise". Yahoo! News. March 12, 2007. https://news.yahoo.com/s/ap/20070312/ap_on_hi_te/un_cybersquatting_2.
- ↑ "Innovative Activity Overcomes Pandemic Disruption - WIPO's Global Intellectual Property Filing Services Reach Record Levels". World Intellectual Property Organization. 10 February 2022. https://www.wipo.int/pressroom/en/articles/2022/article_0002.html.
- ↑ "Areas of WIPO Domain Name Complainant Activity (2021)". 10 February 2022. https://www.wipo.int/export/sites/www/pressroom/en/documents/pr_2022_886_annexes.pdf#page=12.
- ↑ "Geographical Distribution of Parties in WIPO Domain Name Cases Top 25 (2021)". 10 February 2022. https://www.wipo.int/export/sites/www/pressroom/en/documents/pr_2022_886_annexes.pdf#page=13.
- ↑ "Kevin Spacey loses pivotal cybersquatting court case". https://www.theregister.co.uk/2001/11/26/kevin_spacey_loses_pivotal_cybersquatting/. "In the Anticybersquatting Consumer Protection Act 1999, US Congress accepted that as long as there is no attempt to sell on a "personal name" Web site for profit, then it is an example of "fair use" and permission is not needed from the individual in question."
- ↑ "El Tribunal Supremo se pronuncia por primera vez sobre el delito de apropiación indebida de un dominio de internet". April 25, 2022. https://www.poderjudicial.es/cgpj/es/Poder-Judicial/Noticias-Judiciales/El-Tribunal-Supremo-se-pronuncia-por-primera-vez-sobre-el-delito-de-apropiacion-indebida-de-un-dominio-de-internet.
- ↑ "A hit for Jethro Tull in domain name dispute". The Independent. 2000-07-31. https://www.independent.co.uk/news/business/analysis-and-features/a-hit-for-jethro-tull-in-domain-name-dispute-709779.html.
- ↑ "Madonna wins cybersquatting case.". Internet Business News. Oct 17, 2000. http://www.allbusiness.com/technology/technology-services/651746-1.html.
- ↑ Arbitration and Mediation Center. "Administrative Panel Decision Primedia Magazine Finance Inc. v. Next Level Productions". WIPO. http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/html/2001/d2001-0616.html.
- ↑ "Deutsche Lufthansa AG v Future Media Architects, Inc". http://www.adrforum.com/domains/decisions/1153492.htm.
- ↑ "Panavision Int'l, L.P. v. Toeppen | Internet Trademark Case Summaries". http://www.finnegan.com/Panavision-Intl-LP-v-Toeppen-01-01-1998/.
- ↑ Arbitration and Mediation Center. "WIPO Domain Name Decision: D2017-0441". http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/text/2017/d2017-0441.html.
- ↑ Arbitration and Mediation Center. "WIPO Domain Name Decision: D2017-0730". http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/text/2017/d2017-0730.html.
- ↑ Arbitration and Mediation Center. "WIPO Domain Name Decision: D2017-0872". http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/text/2017/d2017-0872.html.
- ↑ Arbitration and Mediation Center. "WIPO Domain Name Decision: D2017-1079". http://www.wipo.int/amc/en/domains/decisions/text/2017/d2017-1079.html.
- ↑ Nowicki, Cole. "A Good Place: The happy accident of mistakenly logging onto gail.com" (in en). https://theoutline.com/post/7676/the-happy-accident-of-mistakenly-logging-onto-gail-com.
- ↑ 21.0 21.1 "seeLa Russa Complaint, La Russa v. Twitter, Inc., No. CGC-09-488101, 2009 WL 1569936". Citmedialaw.org. http://www.citmedialaw.org/threats/la-russa-v-twitter-inc.
- ↑ "seeLa Russa Notice of Voluntary Dismissal, La Russa v. Twitter, Inc., No. CGC-09-488101, 2009 WL 1569936". Citmedialaw.org. http://www.citmedialaw.org/threats/la-russa-v-twitter-inc.
- ↑ "Twitter Support: Name Squatting Policy". Help.twitter.com. http://help.twitter.com/forums/26257/entries/18370.
- ↑ "Twitter Support: Impersonation Policy". Help.twitter.com. http://help.twitter.com/forums/26257/entries/18366.
- ↑ "About verified accounts | Twitter Help Center". Twitter. https://twitter.com/help/verified.
- ↑ "Twitter Verification requirements - how to get the blue check" (in en). https://help.twitter.com/en/managing-your-account/about-twitter-verified-accounts.
- ↑ "About profile labels" (in en). Twitter. https://help.twitter.com/en/rules-and-policies/profile-labels.
- ↑ 28.0 28.1 "Help Center, FACEBOOK". Facebook.com. http://www.facebook.com/help/usernames.
External links
 |