Organization:International Maritime Security Construct
التحالف الدولي لأمن وحماية حرية الملاحة البحرية (Arabic) Script error: The function "transl" does not exist. | |
 | |
 | |
| Motto | Vigilance, Surveillance, Assurance |
|---|---|
| Formation | September 16, 2019 |
| Type | Military alliance |
| Headquarters | Manama, Bahrain |
Region | Persian Gulf |
Membership | 8 states
|
Official language | English |
| Remarks | Capture of the Stena Impero |
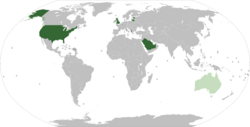
The International Maritime Security Construct (IMSC) is a consortium of countries officially tasked with maintaining order and security in the Persian Gulf and the Gulf of Oman, particularly regarding the oil supply.[1] It was formed on 16 September 2019 in Bahrain, by the United Kingdom , Australia , Albania, Saudi Arabia, Bahrain, Lithuania, the United Arab Emirates, and the United States , which leads the initiative.[2][3][4][5][6]
The IMSC's primary tasks will be monitoring the waters of the region, specifically to ensure the freedom of navigation of merchant vessels plying their trade in the area. The security construct was formed after multiple oil tankers and merchant ships were attacked which were widely blamed on Iran as well to deter Iran's seizure of tankers in the region's waters."[3]
Formation
Earlier in summer 2019 near the Strait of Hormuz, a Norway tanker and a Japan ese tanker were attacked, and the British tanker Stena Impero was seized.[4] Several Gulf states signed on in mid-September in the wake of attacks on the Abqaiq facility.[5]
Shortly thereafter, the ISMC was formed "in support of regional and international efforts to deter and counter threats to maritime navigation and global trade in order to secure freedom of navigation in the gulf amid heightened regional tensions... after attacks on oil tankers that were widely blamed on Iran, as well as to address Iran's seizure of tankers in the region."[3]
U.S. Air Force General Paul Selva, vice chairman of the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff, describes the purpose of the IMSC as protecting the freedom of navigation in the waters of the region, while the commander of U.S. Naval Forces in the Middle East defines its role as strictly defensive.[1]
Lithuania joined the coalition in March 2020.[7]
Command
The IMSC command is shared between alliance countries. Posts last around three months.
On January 30, 2020, Royal Navy Commodore James Parkin (the Commander of the UK Littoral Strike Group) took over command of the consortium from US Navy Rear Admiral Alvin "Bull" Holsey (the Commander of US Carrier Strike Group ONE).[8][9] Parkin handed over command to Commodore Robert Bellfield in May 2020.[10]
| Name | Service | Photo | Term began | Term ended | Notes | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Rear Admiral Alvin "Bull" Holsey |  |
November 7, 2019[11] | January 30, 2020 | ||
| 2. | Commodore James Parkin |  |
January 30, 2020 | April 30, 2020[12] | ||
| 3. | Commodore Robert Bellfield | April 30, 2020[12] | Incumbent |
External links
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Maritime coalition launched to protect Gulf shipping after Iran attacks" (in en). 2019-11-07. https://www.arabnews.com/node/1580576/middle-east.
- ↑ "Iran, Russia and China Plan Joint Naval Drill in Gulf of Oman". The Maritime Executive, LLC. 23 September 2013. https://www.maritime-executive.com/article/iran-russia-and-china-plan-joint-drill-in-gulf-of-oman.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Saudi Arabia joins international maritime security alliance". Al Arabiya English. 18 September 2019. http://english.alarabiya.net/en/News/gulf/2019/09/18/Saudi-Arabia-joins-International-Maritime-Security-Construct.html.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "UAE joins naval security coalition in the Gulf". Defense News. Sightline Media Group. 20 September 2019. https://www.defensenews.com/news/your-military/2019/09/20/uae-joins-naval-security-coalition-in-the-gulf/.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "UAE Agrees To Join U.S.-Led Maritime Coalition To Protect Gulf Shipping". National Public Radio. 19 September 2019. https://www.npr.org/2019/09/19/762225417/uae-agrees-to-join-u-s-led-maritime-coalition-to-protect-gulf-shipping.
- ↑ "U.S. Central Command welcomes Albania's participation in the International Maritime Security Construct (IMSC)". 1 November 2019. https://www.centcom.mil/MEDIA/STATEMENTS/Statements-View/Article/2005518/us-central-command-welcomes-albanias-participation-in-the-international-maritim/. Retrieved 1 November 2019.
- ↑ "Lithuania Joins the International Maritime Security Construct". https://www.cusnc.navy.mil/Media/News/Display/Article/2125964/lithuania-joins-the-international-maritime-security-construct/.
- ↑ "British Officer takes command of Gulf maritime security mission" (in en). https://www.gov.uk/government/news/british-officer-takes-command-of-gulf-maritime-security-mission.
- ↑ Lamothe, Dan (January 30, 2020). "Allies hesitated to join a U.S.-led task force protecting ships from Iran. Now a British officer is in charge.". The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/national-security/2020/01/30/allies-hesitated-join-us-led-task-force-protecting-ships-iran-now-british-officer-is-charge/.
- ↑ IMSC [@IMSC_Sentinel] (3 May 2020). "Welcome aboard Commodore Robert Bellfield as the new @IMSC_Sentinel Commander! Great things ahead for this multinational coalition. #FreedomOfNavigation #GulfSecurity". https://twitter.com/IMSC_Sentinel/status/1256927874545844225.
- ↑ "New Commander Opens IMSC Command Center". https://www.centcom.mil/MEDIA/NEWS-ARTICLES/News-Article-View/Article/2011371/.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 "IMSC Holds Virtual Change of Command Ceremony". https://www.centcom.mil/MEDIA/NEWS-ARTICLES/News-Article-View/Article/2176451/imsc-holds-virtual-change-of-command-ceremony/.

