Organization:Economy of the Arab League
Template:Life in the Arab LeagueThe economy of the Arab League is the economy of the member states of the Arab League. The economy has traditionally been dependent on exports of oil and natural gas; however, the tourism sector has grown rapidly, becoming the fastest-growing sector in the region. The Greater Arab Free Trade Area, founded in 1997, is the league's free trade area which removed customs taxes on 65% of trade between counties in the Arab World.
Members of the Arab League are among the richest and poorest of the world, and there is a great disparity in the economic development of members of the league. There is a significant difference imbalance in wealth between the Gulf states, which include Qatar, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia and war-torn nations within the league, such as Somalia, Sudan and Yemen.
Free trade agreements
GDP and GDP per capita of member states

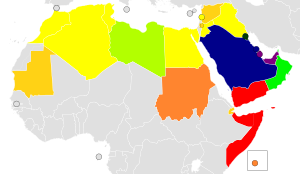
| >$70,000 $60,000 - $70,000 $50,000 – $60,000 $40,000 – $50,000 | $30,000 – $40,000 $20,000 – $30,000 $10,000 – $20,000 $5,000 – $10,000 | $2,500 – $5,000 $1,000 – $2,500 <$1,000 No data |
Based on latest figures and estimates, the Arab League has a GDP of approximately US$3.5 trillion at nominal values and $8.4 trillion at purchasing power parity (PPP). The member states with the largest nominal GDP are Saudi Arabia at US$1.07 trillion, followed by the UAE at $509.18 billion and Egypt at $389.4 billion. The member states with the highest GDP (PPP) are Saudi Arabia at US$2.25 trillion, followed by Egypt at $1.81 trillion and the UAE at $895.17 billion.
The member state with the smallest nominal GDP is Comoros at US$1.36 billion, followed by the Djibouti at $3.87 billion and Mauritania at $10.36 billion. The member state with the smallest GDP (PPP) is Comoros at US$3.43 billion, followed by the Djibouti at $7.19 billion and Somalia at $32.08 billion.[1][2]
The member state with the highest nominal GDP per capita is Qatar at US$81,968.34, followed by the UAE at $50,602.33 and Saudi Arabia at $32,586.17. The member state with the highest GDP (PPP) per capita is Qatar at US$114,210.45, followed by the UAE at $88,961.77 and Saudi Arabia at $68,452.85. The member state with the lowest nominal GDP per capita is Sudan at US$533.85, followed by the Yemen at $617.67 and Somalia at $717.41. The member state with the lowest GDP (PPP) per capita is Somalia at $1998.47, followed by the Yemen at $2053.45 and Comoros at $3463.63.[3][4]
List
| Country/Territory | GDP (nominal, billions) | GDP (PPP, billions) | GDP per capita (nominal) | GDP per capita (PPP) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 224.11 | 628.99 | 4,874.71 | 13,681.62 | (2023, est.) | |
| 44.99 | 95.97 | 28,464.17 | 60,715.02 | (2023, est.) | |
| 1.36 | 3.43 | 1,377.02 | 3,463.63 | (2023, est.) | |
| 3.87 | 7.19 | 3,761.24 | 6,985.11 | (2023, est.) | |
| 398.40 | 1,809.43 | 3,770.13 | 17,123.03 | (2023, est.) | |
| 254.99 | 508.97 | 5,882.89 | 11,742.40 | (2023, est.) | |
| 50.02 | 132.09 | 4,850.66 | 12,809.17 | (2023, est.) | |
| 159.69 | 256.59 | 32,215.03 | 51,764.83 | (2023, est.) | |
| 21.78 | 78.23 | 3,283.41 | 11,793.82 | (2022, est.) | |
| 40.19 | 166.89 | 5,872.22 | 24,381.73 | (2023, est.) | |
| 10.36 | 33.41 | 2,337.91 | 7,542.41 | (2023, est.) | |
| 147.34 | 385.34 | 3,979.87 | 10,408.31 | (2023, est.) | |
| 108.28 | 200.30 | 21,265.63 | 39,336.14 | (2023, est.) | |
| 18.11 | 36.39 | 3,464.38 | 6,642.34 | 2021 | |
| 235.5 | 328.13 | 81,968.34 | 114,210.45 | (2023, est.) | |
| 1,069.44 | 2,246.54 | 32,586.17 | 68,452.85 | (2023, est.) | |
| 11.52 | 32.08 | 717.41 | 1,998.47 | (2023, est.) | |
| 25.57 | 172.65 | 533.85 | 3,604.78 | (2023, est.) | |
| 60.043 | 136.36 | 2,806.69 | 6,374.06 | 2010 | |
| 51.271 | 162.10 | 4,190.60 | 13,248.95 | (2023, est.) | |
| 509.18 | 895.17 | 50,602.33 | 88,961.77 | (2023, est.) | |
| 21.05 | 69.96 | 617.67 | 2,053.45 | (2023, est.) | |
| 3,467.06 | 8,386.21 | 7,594.49 | 18,369.71 |
References
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook, April 2022: War Sets Back The Global Recovery" (in en). https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/Issues/2022/04/19/world-economic-outlook-april-2022.
- ↑ "Arab world - GDP by country 2022" (in en). https://www.statista.com/statistics/806135/gdp-of-the-arab-world/.
- ↑ "Pressure on Egypt’s economy mounts after downgrade" (in en). https://www.aljazeera.com/economy/2023/10/6/egypts-bonds-spiral-lower-after-moodys-downgrade-over-economic-woes.
- ↑ "These Are The 5 Largest Arab Economies In 2021, Led By Saudi Arabia" (in en-US). https://www.forbesmiddleeast.com/industry/economy/saudi-maintains-on-top-of-five-largest-arab-economies-in-2021-ahead-of-uae-and-egypt.
- ↑ "World Economic Outlook Database". IMF. October 2023. https://www.imf.org/en/Publications/WEO/weo-database/2023/October/weo-report?c=612,419,632,611,469,433,439,443,446,672,682,686,449,453,456,726,732,463,744,466,487,474,&s=NGDPD,PPPGDP,NGDPDPC,PPPPC,&sy=2010&ey=2025&ssm=0&scsm=1&scc=0&ssd=1&ssc=0&sic=0&sort=country&ds=.&br=1.
- ↑ "Here Are the Richest Countries in the MENA Region 2021". https://www.uaemoments.com/here-are-the-richest-countries-in-the-mena-region-2021-405506.html.
- ↑ Suneson, Grant (7 July 2019). "These are the 25 richest countries in the world". https://www.usatoday.com/story/money/2019/07/07/richest-countries-in-the-world/39630693/.
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080506173842/
- http://www.amf.org.ae/venglish [1]
- Full text of the Agadir Agreement (English version)
- The Agadir Agreement and Open regionalism by Steffen Wippel
 |

