Chemistry:Curtin–Hammett principle
The Curtin–Hammett principle is a principle in chemical kinetics proposed by David Yarrow Curtin and Louis Plack Hammett. It states that, for a reaction that has a pair of reactive intermediates or reactants that interconvert rapidly (as is usually the case for conformational isomers), each going irreversibly to a different product, the product ratio will depend both on the difference in energy between the two conformers and the energy barriers from each of the rapidly equilibrating isomers to their respective products. Stated another way, the product distribution reflects the difference in energy between the two rate-limiting transition states. As a result, the product distribution will not necessarily reflect the equilibrium distribution of the two intermediates.[1][2] The Curtin–Hammett principle has been invoked to explain selectivity in a variety of stereo- and regioselective reactions. The relationship between the (apparent) rate constants and equilibrium constant is known as the Winstein-Holness equation.
Definition
The Curtin–Hammett principle applies to systems in which different products are formed from two substrates in equilibrium with one another. The rapidly interconverting reactants can have any relationship between themselves (stereoisomers, constitutional isomers, conformational isomers, etc.). Product formation must be irreversible, and the different products must be unable to interconvert.[3]
For example, given species A and B that equilibrate rapidly while A turns irreversibly into C, and B turns irreversibly into D:
- [math]\ce{ \bf{C}\ \it <-[k_{\rm 1}] \bf{A} \it\ <=> [{K}]\ \bf{B}\ \it-> [k_{\rm 2}]\ \bf D }[/math]
K is the equilibrium constant between A and B, and k1 and k2 are the rate constants for the formation of C and D, respectively. When the rate of interconversion between A and B is much faster than either k1 or k2, then the Curtin–Hammett principle tells us that the C:D product ratio is not equal to the equilibrium A:B reactant ratio, but is instead determined by the relative energies of the transition states (i.e., difference in the absolute energies of the transition states). If reactants A and B were at identical energies, the product ratio would depend only on the activation barriers of the reactions leading to each respective product. However, in a real-world scenario, the two reactants are likely at somewhat different energy levels, although the barrier to their interconversion must be low for the Curtin–Hammett scenario to apply. In this case, the product distribution depends both on the equilibrium ratio of A to B and on the relative activation barriers going to the corresponding products C and D. Both factors are taken into account by the difference in the energies of the transition states (ΔΔG‡ in the figure below).
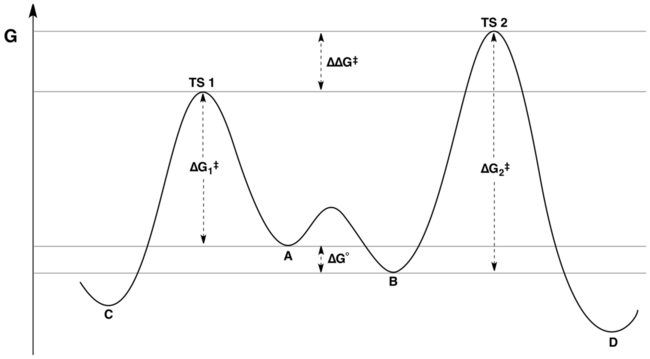
The reaction coordinate free energy profile of a typical reaction under Curtin-Hammett control is represented by the following figure:
The ratio of products only depends on the value labeled ΔΔG‡ in the figure: C will be the major product, because the energy of TS1 is lower than the energy of TS2. A common but false assertion is that the product distribution does not in any way reflect the relative free energies of substrates A and B; in fact, it reflects the relative free energies of the substrates and the relative activation energies.[3][4] This misunderstanding may stem from failing to appreciate the distinction between "the difference of energies of activation" and "the difference in transition state energies". Although these quantities may at first appear synonymous, the latter takes into account the equilibrium constant for interconversion of A and B, while the former does not.
Mathematically, the product ratio can be expressed as a function of K, k1, and k2 or in terms of the corresponding energies ΔG°, ΔG1‡, and ΔG2‡. By combining terms, the product ratio can be rewritten in terms of the quantity ΔΔG‡ alone, where ΔΔG‡ = (ΔG2‡ – ΔG1‡) + ΔG°. Inspection of the energy diagram (shown above) makes it apparent that ΔΔG‡ is precisely the difference in transition state energies.
Derivation
A generic reaction under Curtin–Hammett can be described by the following parameters:
- [math]\ce{ \bf{C}\ \it <-[k_{\rm 1}] \bf{A} \it\ <=> [{K}]\ \bf{B}\ \it-> [k_{\rm 2}]\ \bf D }[/math]
In order for rapid equilibration to be a good assumption, the rate of conversion from the less stable of A or B to the product C or D must be at least 10 times slower than the rate of equilibration between A and B.[5]
The rate of formation for compound C from A is given as
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d[\mathbf C]}{dt} = k_1[\mathbf A] }[/math],
and that of D from B as
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d[\mathbf D]}{dt} = k_2[\mathbf{B}] \approx k_2K[\mathbf A] }[/math],
with the second approximate equality following from the assumption of rapid equilibration. Under this assumption, the ratio of the products is then
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{[\mathbf D]}{[\mathbf C]}\approx\frac{d[\mathbf D]}{dt}\Big/\frac{d[\mathbf C]}{dt} = \frac{k_2[\mathbf B]}{k_1[\mathbf A]}\approx\frac{k_2K[\mathbf A]}{k_1[\mathbf A]} = \frac{k_2K}{k_1} }[/math].
In other words, because equilibration is fast compared to product formation, [math]\displaystyle{ [\mathbf B]/[\mathbf A]\approx K }[/math] throughout the reaction. As a result, [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d[\mathbf D]}{dt}\Big/\frac{d[\mathbf C]}{dt} }[/math] also remains roughly constant throughout the reaction. In turn, integration with respect to time implies that [math]\displaystyle{ [\mathbf D]/[\mathbf C] }[/math] likewise takes on an approximately constant value through the course of the reaction, namely [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{d[\mathbf D]}{dt}\Big/\frac{d[\mathbf C]}{dt} }[/math].
In terms of the ground state and transition state energies, the product ratio can therefore be written as:
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{[\mathbf D]}{[\mathbf C]}\approx \frac{k_2K}{k_1} = \frac{e^{-\Delta G_2^{\ddagger}/RT}e^{-\Delta G^\circ/RT} }{e^{-\Delta G_1^{\ddagger}/RT} }= \exp\big(-(\Delta G^{\Dagger}_2-\Delta G^{\Dagger}_1+\Delta G^\circ)/RT\big) }[/math].
Importantly, inspection of the energy diagram above allows us to identify
- [math]\displaystyle{ \Delta\Delta G^{\Dagger} =(\Delta G^{\Dagger}_2-\Delta G^{\Dagger}_1)+\Delta G^\circ }[/math]
with the energy difference of the transition states, giving us a simplified equation that captures the essence of the Curtin-Hammett principle:
Thus, although the product ratio depends on the equilibrium constant between A and B and the difference in energy between the barriers from A to C and from B to D, both of these factors are automatically taken into account by the energy difference of the transition states leading to the products, ΔΔG‡.
Classes of reactions under Curtin–Hammett control
Three main classes of reactions can be explained by the Curtin–Hammett principle: either the more or less stable conformer may react more quickly, or they may both react at the same rate.
Case I: More stable conformer reacts more quickly
One category of reactions under Curtin–Hammett control includes transformations in which the more stable conformer reacts more quickly. This occurs when the transition state from the major intermediate to its respective product is lower in energy than the transition state from the minor intermediate to the other possible product. The major product is then derived from the major conformer, and the product distribution does not mirror the equilibrium conformer distribution.
Example: piperidine oxidation
An example of a Curtin–Hammett scenario in which the more stable conformational isomer reacts more quickly is observed during the oxidation of piperidines. In the case of N-methyl piperidine, inversion at nitrogen between diastereomeric conformers is much faster than the rate of amine oxidation.[6] The conformation which places the methyl group in the equatorial position is 3.16 kcal/mol more stable than the axial conformation.[7] The product ratio of 95:5 indicates that the more stable conformer leads to the major product.[8]
Case II: Less stable conformer reacts more quickly
A second category of reactions under Curtin–Hammett control includes those in which the less stable conformer reacts more quickly. In this case, despite an energetic preference for the less reactive species, the major product is derived from the higher-energy species. An important implication is that the product of a reaction can be derived from a conformer that is at sufficiently low concentration as to be unobservable in the ground state.[3]
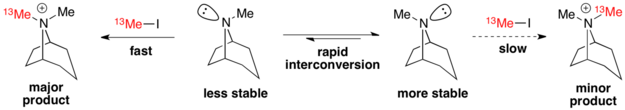
Example: tropane alkylation
The alkylation of tropanes with methyl iodide is a classic example of a Curtin–Hammett scenario in which a major product can arise from a less stable conformation.[3] Here, the less stable conformer reacts via a more stable transition state to form the major product.[9] Therefore, the ground state conformational distribution does not reflect the product distribution.
Case III: both conformers react at the same rate
It is hypothetically possible that two different conformers in equilibrium could react through transition states that are equal in energy. In this case, product selectivity would depend only on the distribution of ground-state conformers. In this case, both conformers would react at the same rate.
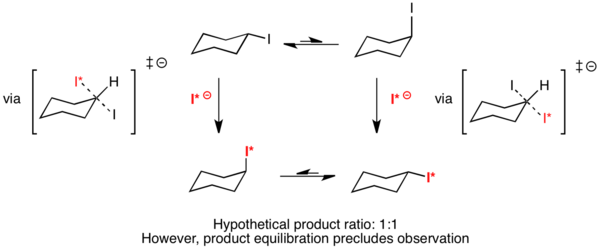
Example: SN2 reaction of cyclohexyl iodide
Ernest L. Eliel has proposed that the hypothetical reaction of cyclohexyl iodide with radiolabeled iodide would result in a completely symmetric transition state.[10] Because both the equatorial and axial-substituted conformers would react through the same transition state, ΔΔG‡ would equal zero. By the Curtin–Hammett principle, the distribution of products should then be 50% axial substituted and 50% equatorial substituted. However, equilibration of the products precludes observation of this phenomenon.[3]
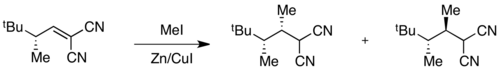
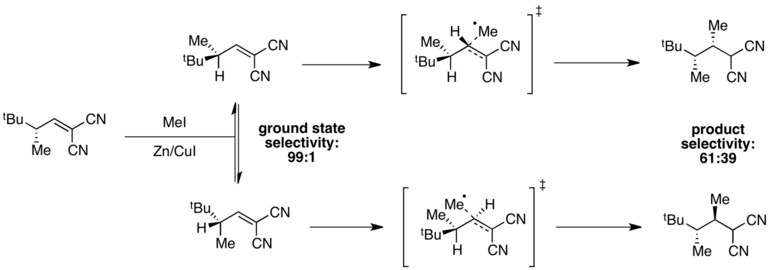
Example: radical methylation
When ground state energies are different but transition state energies are similar, selectivity will be degraded in the transition state, and poor overall selectivity may be observed. For instance, high selectivity for one ground state conformer is observed in the following radical methylation reaction.[11]
The conformer in which A(1,3) strain is minimized is at an energy minimum, giving 99:1 selectivity in the ground state. However, transition state energies depend both on the presence of A(1,3) strain and on steric hindrance associated with the incoming methyl radical. In this case, these two factors are in opposition, and the difference in transition state energies is small compared to the difference in ground state energies. As a result, poor overall selectivity is observed in the reaction.
Application to stereoselective and regioselective reactions
The Curtin–Hammett principle is used to explain the selectivity ratios for some stereoselective reactions.
Application to dynamic kinetic resolution
The Curtin–Hammett principle can explain the observed dynamics in transformations employing dynamic kinetic resolution, such as the Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation[12] and enantioselective lithiation.[13]
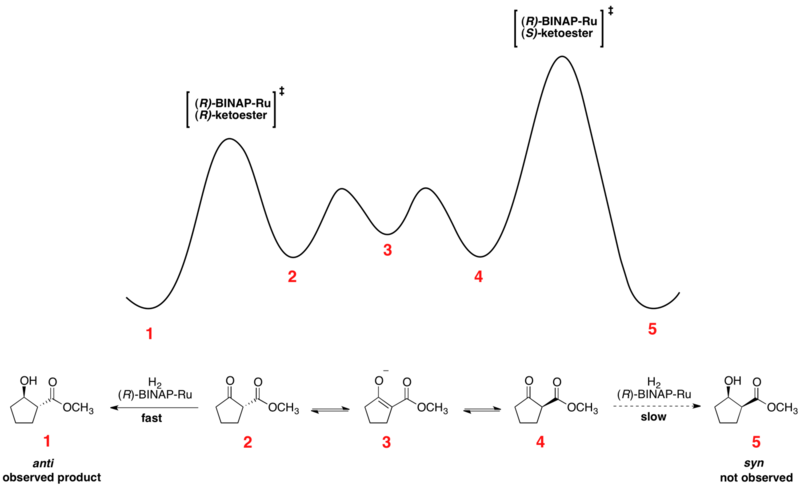
Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation
Rapid equilibration between enantiomeric conformers and irreversible hydrogenation place the reaction under Curtin–Hammett control. The use of a chiral catalyst results in a higher-energy and a lower-energy transition state for hydrogenation of the two enantiomers. The transformation occurs via the lower-energy transition state to form the product as a single enantiomer.[14] Consistent with the Curtin–Hammett principle, the ratio of products depends on the absolute energetic barrier of the irreversible step of the reaction, and does not reflect the equilibrium distribution of substrate conformers. The relative free energy profile of one example of the Noyori asymmetric hydrogenation is shown below:
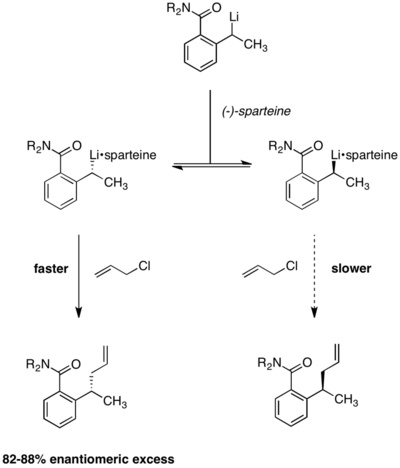
Enantioselective lithiation
Dynamic kinetic resolution under Curtin–Hammett conditions has also been applied to enantioselective lithiation reactions. In the reaction below, it was observed that product enantioselectivities were independent of the chirality of the starting material. The use of (−)-sparteine is essential to enantioselectivity, with racemic product being formed in its absence.[13] Equilibration between the two alkyllithium complexes was demonstrated by the observation that enantioselectivity remained constant over the course of the reaction. Were the two reactant complexes not rapidly interconverting, enantioselectivity would erode over time as the faster-reacting conformer was depleted.
Application to regioselective acylation
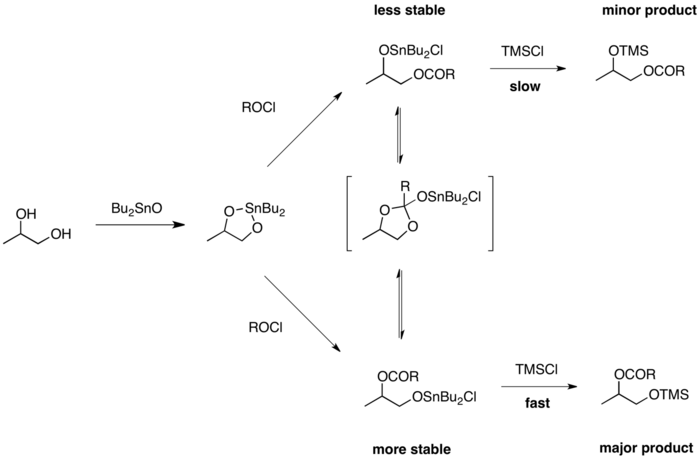
The Curtin–Hammett principle has been invoked to explain regioselectivity in the acylation of 1,2-diols. Ordinarily, the less-hindered site of an asymmetric 1,2-diol would experience more rapid esterification due to reduced steric hindrance between the diol and the acylating reagent. Developing a selective esterification of the most substituted hydroxyl group is a useful transformation in synthetic organic chemistry, particularly in the synthesis of carbohydrates and other polyhydroxylated compounds.[15] Stannylene acetals have been used to efficiently achieve this transformation.[16]
The asymmetric diol is first treated with a tin reagent to produce the dibutylstannylene acetal. This compound is then treated with one equivalent of acyl chloride to produce the stannyl monoester. Two isomers of the stannyl ester are accessible, and can undergo rapid interconversion through a tetrahedral intermediate. Initially, the less stable isomer predominates, as it is formed more quickly from the stannyl acetal. However, allowing the two isomers to equilibrate results in an excess of the more stable primary alkoxy stannane in solution. The reaction is then quenched irreversibly, with the less hindered primary alkoxy stannane reacting more rapidly. This results in selective production of the more-substituted monoester. This is a Curtin–Hammett scenario in which the more stable isomer also reacts more rapidly.
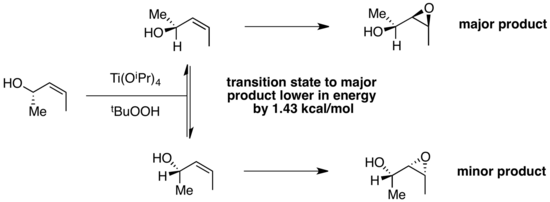
Application to asymmetric epoxidation
The epoxidation of asymmetric alkenes has also been studied as an example of Curtin–Hammett kinetics. In a computational study of the diastereoselective epoxidation of chiral allylic alcohols by titanium peroxy complexes, the computed difference in transition state energies between the two conformers was 1.43 kcal/mol.[17] Experimentally, the observed product ratio was 91:9 in favor of the product derived from the lower-energy transition state. This product ratio is consistent with the computed difference in transition state energies. This is an example in which the conformer favored in the ground state, which experiences reduced A(1,3) strain, reacts through a lower-energy transition state to form the major product.
Synthetic applications
Synthesis of AT2433-A1
The Curtin–Hammett principle has been invoked to explain selectivity in a variety of synthetic pathways. One example is observed en route to the antitumor antibiotic AT2433-A1, in which a Mannich-type cyclization proceeds with excellent regioselectivity. Studies demonstrate that the cyclization step is irreversible in the solvent used to run the reaction, suggesting that Curtin–Hammett kinetics can explain the product selectivity.[18]
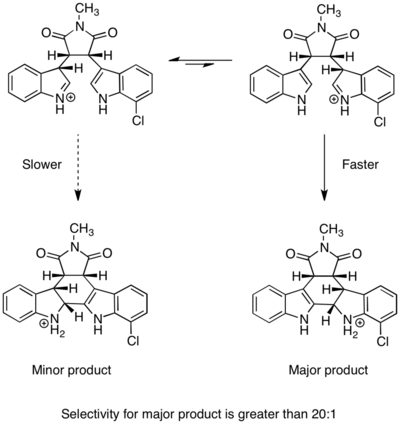
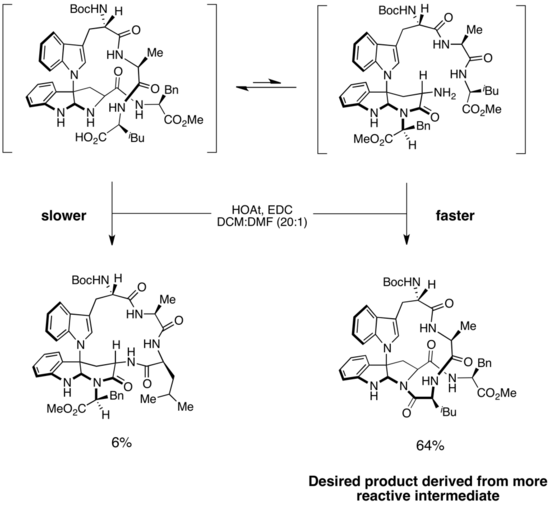
Synthesis of kapakahines B and F
A Curtin–Hammett scenario was invoked to explain selectivity in the syntheses of kapakahines B and F, two cyclic peptides isolated from marine sponges. The structure of each of the two compounds contains a twisted 16-membered macrocycle.[19] A key step in the syntheses is selective amide bond formation to produce the correct macrocycle. In Phil Baran’s enantioselective synthesis of kapakahines B and F, macrocycle formation was proposed to occur via two isomers of the substrate.[20] The more easily accessible, lower energy isomer led to the undesired product, whereas the less stable isomer formed the desired product. However, because the amide-bond-forming step was irreversible and the barrier to isomerization was low, the major product was derived from the faster-reacting intermediate. This is an example of a Curtin–Hammett scenario in which the less-stable intermediate is significantly more reactive than the more stable intermediate that predominates in solution. Because substrate isomerization is fast, throughout the course of the reaction excess substrate of the more stable form can be converted into the less stable form, which then undergoes rapid and irreversible amide bond formation to produce the desired macrocycle. This strategy provided the desired product in >10:1 selectivity. (I think there's an error in the Scheme. See Talk pages.)
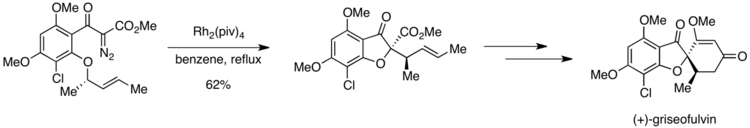
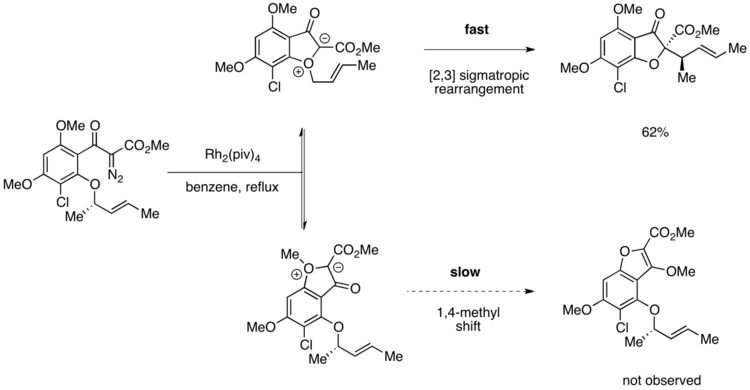
Synthesis of (+)-griseofulvin
In the first enantioselective synthesis of (+)-Griseofulvin, a potent antifungal agent,[21] a Curtin–Hammett situation was observed. A key step in the synthesis is the rhodium-catalyzed formation of an oxonium ylide, which then undergoes a [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement en route to the desired product.[22] However, the substrate contains two ortho-alkoxy groups, either of which could presumably participate in oxonium ylide generation.
Obtaining high selectivity for the desired product was possible, however, due to differences in the activation barriers for the step following ylide formation. If the ortho-methoxy group undergoes oxonium ylide formation, a 1,4-methyl shift can then generate an undesired product. The oxonium ylide formed from the other ortho-alkoxy group is primed to undergo a [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement to yield the desired compound. Pirrung and coworkers reported complete selectivity for the desired product over the product resulting from a 1,4-methyl shift. This result suggests that oxonium ylide formation is reversible, but that the subsequent step is irreversible. The symmetry-allowed [2,3] sigmatropic rearrangement must follow a pathway that is lower in activation energy than the 1,4-methyl shift, explaining the exclusive formation of the desired product.
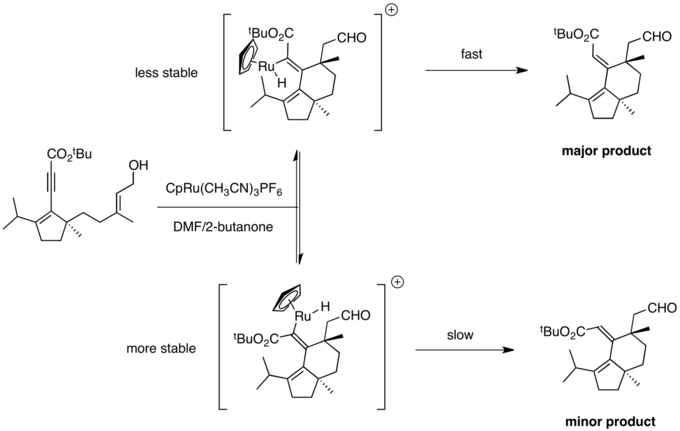
Synthesis of (+)-allocyathin B2
A potential Curtin-Hammett scenario was also encountered during the enantioselective total synthesis of (+)-allocyathin B2 by the Trost group.[23] The pivotal step in the synthesis was a Ru-catalyzed diastereoselective cycloisomerization. The reaction could result in the formation of two possible double bond isomers. The reaction provided good selectivity for the desired isomer, with results consistent with a Curtin-Hammett scenario. Initial oxidative cycloruthenation and beta-hydride elimination produce a vinyl-ruthenium hydride. Hydride insertion allows for facile alkene isomerization. It is unlikely that the reaction outcome mirrors the stability of the intermediates, as the large CpRu group experiences unfavorable steric interactions with the nearby isopropyl group. Instead, a Curtin–Hammett situation applies, in which the isomer favored in equilibrium does not lead to the major product. Reductive elimination is favored from the more reactive, less stable intermediate, as strain relief is maximized in the transition state. This produces the desired double bond isomer.
See also
References
- ↑ Carey, Francis A.; Sundberg, Richard J.; (1984). Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A Structure and Mechanisms (2nd ed.). New York N.Y.: Plenum Press. ISBN:0-306-41198-9
- ↑ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (1994) "Curtin–Hammett principle". doi:10.1351/goldbook.C01480
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Jeffrey I. Seeman (1983). "Effect of Conformational Change on Reactivity in Organic Chemistry. Evaluations, Application, and Extensions of Cutin–Hammett/Winstein–Holness Kinetics". Chemical Reviews 83 (2): 83–134. doi:10.1021/cr00054a001.
- ↑ Jeffrey I. Seeman (1986). "The Curtin–Hammett Principle and the Winstein–Holness Equation". Journal of Chemical Education 63 (1): 42–48. doi:10.1021/ed063p42. Bibcode: 1986JChEd..63...42S.
- ↑ Wzorek, Joseph (2009-12-18). "The Curtin-Hammett Principle and the Winstein-Holness Equation". http://evans.rc.fas.harvard.edu/pdf/smnr_2009_Wzorek_Joseph.pdf.
- ↑ P. J. Crowley; M. J. T. Robinson; M. G. Ward (1977). "Conformational effects in compounds with 6-membered rings-XII". Tetrahedron 33 (9): 915–925. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(77)80202-0.
- ↑ Luis Carballeira; Ignacio Pérez-Juste (1998). "Influence of calculation level and effect of methylation on axial/equatorial equilibria in piperidines". Journal of Computational Chemistry 19 (8): 961–976. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199806)19:8<961::AID-JCC14>3.0.CO;2-A.
- ↑ Y. Shvo; E.D. Kaufman (1972). "Configurational and conformational analysis of cyclic amine oxides". Tetrahedron 28 (3): 573–580. doi:10.1016/0040-4020(72)84021-3.
- ↑ Rodney D. Otzenberger; Kenneth B. Lipkowitz; Bradford P. Mundy (1974). "Quaternizations in the 8-azabicyclo[4.3.0]non-3-ene series". Journal of Organic Chemistry 39 (3): 319–321. doi:10.1021/jo00917a008.
- ↑ Eliel, Ernest L. (1962). Stereochemistry of Carbon Compounds. New York: McGraw–Hill. pp. 149–156, 234–239. https://archive.org/details/stereochemistryo0000elie.
- ↑ Giese, B.; Kopping, B.; Gobel, T.; Dickhaut, J.; Thoma, G.; Kulicke, K.; Trach, F. (2004). Organic Reactions.
- ↑ M. Kitamura; M. Tokunaga; R. Noyori (1993). "Quantitative expression of dynamic kinetic resolution of chirally labile enantiomers: stereoselective hydrogenation of 2-substituted 3-oxo carboxylic esters catalyzed by BINAP-ruthenium(II) complexes". Journal of the American Chemical Society 115 (1): 144–152. doi:10.1021/ja00054a020.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 Peter Beak; Amit Basu; Donald J. Gallagher; Yong Sun Park; S. Thayumanavan (1996). "Regioselective, Diastereoselective, and Enantioselective Lithiation−Substitution Sequences: Reaction Pathways and Synthetic Applications". Accounts of Chemical Research 29 (11): 552–560. doi:10.1021/ar950142b.
- ↑ Noyori, Ryōji; Ikeda, T.; Ohkuma, T.; Widhalm, M.; Kitamura, M.; Takaya, H.; Akutagawa, S.; Sayo, N. et al. (1989). "Stereoselective hydrogenation via dynamic kinetic resolution". Journal of the American Chemical Society 111 (25): 9134–9135. doi:10.1021/ja00207a038.
- ↑ Whistler, R. L.; Wolfrom, M. L (1963). Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry. Academic Press.
- ↑ Roelens, S. (1996). "Organotin-Mediated Monoacylation of Diols with Reversed Chemoselectivity". Journal of Organic Chemistry 61 (16): 5257–5263. doi:10.1021/jo960453f.
- ↑ Cui, M.; Adam, W.; Shen, J. H.; Luo, X. M.; Tan, X, J.; Chen, K. X.; Ji, R. Y.; Jiang, H. L. (2002). "A Density-Functional Study of the Mechanism for the Diastereoselective Epoxidation of Chiral Allylic Alcohols by the Titanium Peroxy Complexes". Journal of Organic Chemistry 67 (5): 1427–1435. doi:10.1021/jo016015c. PMID 11871869.
- ↑ Chisholm, J. D.; Van Vranken, D. L. (2000). "Regiocontrolled synthesis of the antitumor antibiotic AT2433-A1". Journal of Organic Chemistry 65 (22): 7541–7553. doi:10.1021/jo000911r. PMID 11076613.
- ↑ Nakao, Yoichi; Yeung, Bryan K. S.; Yoshida, Wesley Y.; Scheuer, Paul J.; Kelly-Borges, Michelle (1995). "Kapakahine B, a cyclic hexapeptide with an .alpha.-carboline ring system from the marine sponge Cribrochalina olemda". Journal of the American Chemical Society 117 (31): 8271–8272. doi:10.1021/ja00136a026. ISSN 0002-7863.
- ↑ Newhouse, T.; Lewis, C. A.; Baran, P. S. (2009). "Enantiospecific Total Syntheses of Kapakahines B and F". Journal of the American Chemical Society 131 (18): 6360–6361. doi:10.1021/ja901573x. PMID 19374357.
- ↑ Davies, R. R. (1980). Antifungal Chemotherapy. Wiley & Sons.
- ↑ Pirrung, M. C.; Brown, William, L.; Rege, S.; Laughton, P. (1991). "Total synthesis of (+)-griseofulvin". Journal of the American Chemical Society 113 (22): 8561–8562. doi:10.1021/ja00022a075.
- ↑ Trost, B. M.; Dong, L.; Schroeder, G. M. (2005). "Total synthesis of (+)-Allocyathin B2". Journal of the American Chemical Society 127 (9): 2844–2845. doi:10.1021/ja0435586. PMID 15740107.
External links
- https://web.archive.org/web/20111005191716/http://www.joe-harrity.staff.shef.ac.uk/meetings/CurtinHammettreview.pdf
- https://web.archive.org/web/20120402124752/http://evans.harvard.edu/pdf/smnr_2009_WZOREK_JOSEPH.pdf
 |