Organization:Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa
Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA)
| |
|---|---|
Anthem: "People of Africa"[1] | |
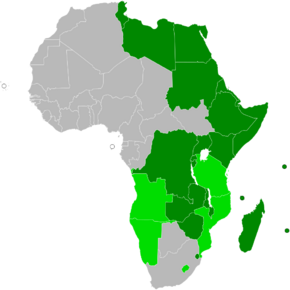 Map of Africa indicating COMESA membership. Current members Former members | |
| Secretariat | |
| Official languages | |
| Type | Trade bloc |
| Membership | 21 member states |
| Leaders | |
• Secretary General | Chileshe Mpundu Kapwepwe |
| Establishment | Agreement |
• Signed | 5 November 1993 |
• Ratified | 8 December 1994 |
Website www | |
The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is a regional economic community in Africa with twenty-one member states stretching from Tunisia to Eswatini. COMESA was formed in December 1994, replacing a Preferential Trade Area which had existed since 1981. Nine of the member states formed a free trade area in 2000 (Djibouti, Egypt, Kenya, Madagascar , Malawi, Mauritius, Sudan, Zambia and Zimbabwe), with Rwanda and Burundi joining the FTA in 2004, the Comoros and Libya in 2006, Seychelles in 2009 and Tunisia and Somalia in 2018.
COMESA is one of the pillars of the African Economic Community.
In 2008, COMESA agreed to an expanded free-trade zone including members of two other African trade blocs, the East African Community (EAC) and the Southern Africa Development Community (SADC). COMESA is also considering a common visa scheme to boost tourism.[2]
Membership
Current members
| Country | Joined |
|---|---|
| Horn of Africa countries | |
| 21 Dec 1981 | |
| 1994 | |
| 21 Dec 1981 | |
| 21 Dec 1981 (PTA) / 19 Jul 2018 (COMESA)[3] | |
| North African countries | |
| 6 Jan 1999 | |
| 3 Jun 2005[n 1] | |
| 21 Dec 1981 | |
| 18 Jul 2018[3] | |
| Indian Ocean | |
| 21 Dec 1981 | |
| " | |
| " | |
| 2001 | |
| African Great Lakes | |
| 21 Dec 1981 | |
| " | |
| " | |
| " | |
| " | |
| Southern Africa | |
| 21 Dec 1981[n 2] | |
| " | |
| " | |
| Central Africa | |
| 21 Dec 1981[n 3] |
Former members
| Country | Left |
|---|---|
| 1997 | |
| 1997 | |
| 2 Sep 2000 | |
| 2 May 2004 | |
| 2007 [n 4] |
Organs
According to the treaties, the following organs have decision-making power:
- The COMESA Authority, composes of Heads of States or Government and is COMESA's supreme policy-making organ. The Authority is headed by a Chairman elected for an agreed period; the current chairperson from November 2021 is Egyptian President Fattah El Sisi.[4] The Authority is tasked with the general policy direction and controlling the overall performance of the executive functions of COMESA. The COMESA Authority meets once a year at Summits which are held in different member States. The hosting government and the COMESA Secretariat bear joint responsibility for their organization. Whilst the hosting country assumes the chairmanship of the Authority for the year, an Extraordinary Summit can be held at the request of any member of the Authority; so long as one-third of the members of the Authority support such a request.[5] The Authority meetings are held in closed sessions and usually decisions are taken by consensus. The session leaders have to issue a communiqué, recording any decisions made. These directives and decisions taken by the Authority are binding on all member States and the other organs to which they are addressed.
- The COMESA Council of Ministers
- The COMESA Court of Justice decisions have precedence over any decisions of national courts. The Court of Justice may receive cases not only from member States, but also from natural and legal persons, against the council to determine the legality of any act towards the directive's, regulation or decision made. The Persons are also permitted under the Treaty to sue a member State in the COMESA Court; the legality under the Treaty of any act, directive regulation, or decision of such member State.
In the event that a member State's court is reviewing the application or interpretation of the Treaty, it may request the Courts' opinion on the matter. If the national court is a court from which there is no appeal or remedy, then court is required to refer the question to the COMESA court. The national remedies must be exhausted before a person can bring a matter to the COMESA CJ. The COMESA Court has jurisdiction over suits brought by COMESA employees and third parties against COMESA or its institutions. It also may act as an arbitrary tribunal on any matter arising from a contract to which COMESA or any of its institutions is a party. Further the Court can adjudicate any dispute between member States who agree to bring the dispute before it. Unlike the Statute of the International Court, the treaty does not state the sources of law to be applied by the Court. The Treaty and any COMESA issued legal instruments, will make the initial law to be applied, but municipal law and international law may also be determined applicable by the Court.
While the jurisdiction of the COMESA Court provides multiple avenues for the creation of standard interpretation of the Treaty, there is no specific provision of an avenue for the settlement of disputes between the institutions of the Common Market. The Court is not given the power to interpret the statutes of the other COMESA institutions. Finally, the Treaty does not specify that the Court will have jurisdiction over human rights issues within the context of Community
Due to its varying jurisdictions of the Court, the Eighth Meeting of Ministers of Justice and Attorneys General recommended to the Council of Ministers and the Authority that the Treaty be amended to provide for two divisions in the Court, the Court of First Instance and the Appellate Division. The proposal was adopted and the Court was expanded in June 2005 with the appointment of seven judges in the Court of First Instance and five judges in the Appellate Division. The work of the Court was then suspended until the Appellate Division judges were appointed and the Rules of Court for the Appellate Division were drawn up and adopted. During this reformation of the Court, the previously fully independent Court was made subject to the review of any proposed Rules of Court by the Ministers of Justice and Attorneys-General. The Court was established under the 1994 Treaty, the first set of judges was not appointed until 1998.
Unlike other African regional courts, the COMESA Court continues to receive cases. However, due to lack of funds the Court is unable to hear all its cases at certain times. Funding is only done for one session of the Court per year, these has contributed greatly to piling of cases. The backlog of cases will most certainly increase with the current growth in trade disputes in the region.[6]
- The Committee of Governors of Central Banks
The following lower policy organs make recommendations to the above:
- The Inter-governmental Committee
- The Twelve Technical Committees
- The Consultative Committee of the Business Community and other Interest Groups
- The COMESA Secretariat
Other COMESA institutions created to promote development are:
- The PTA Bank (Eastern and Southern African Trade and Development Bank) in Bujumbura, Burundi
- The COMESA Clearing House in Harare, Zimbabwe
- The COMESA Association of Commercial Banks in Harare, Zimbabwe
- The COMESA Leather Institute in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
- The COMESA Re-Insurance Company (ZEP-RE) in Nairobi, Kenya
- The Regional Investment Agency in Cairo, Egypt
- COMTEL Project, aimed at creating regional telecommunications infrastructure
Comparison with other regional blocs
See also
- Rules of Origin
- Market access
- Free-trade area
- Tariffs
- Trade bloc
- East African Community (EAC)
- Economic Community of Central African States (ECCAS)
- Southern African Development Community (SADC)
- Southern African Customs Union (SACU)
- Southern African Confederation of Agricultural Unions (SACAU)
- Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS)
- Arab Maghreb Union (UMA)
- Intergovernmental Authority on Development (IGAD)
- Greater Arab Free Trade Area (GAFTA)
- Yellow card system, the COMESA motor insurance scheme.
Notes
- ↑ 10th COMESA summit, as Libyan Arab Jamahiriya
- ↑ As Swaziland
- ↑ As Zaire
- ↑ Self-suspension:
- "SADC, COMESA and the EAC: Conflicting regional and trade agendas". Institute for Global Dialogue. October 2008. http://www.igd.org.za/publications/occasional-papers/item/download/32.
- "African integration is great but has its hurdles". New Vision. 26 May 2010. http://www.newvision.co.ug/D/8/20/720784.
References
- ↑ "Comesaweb – Comesa anthem". Comesa.int. http://about.comesa.int/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=16&Itemid=34.
- ↑ Writer, eTN Staff (27 April 2010). "Apple files patent for iTravel - eTurboNews (eTN)". http://www.eturbonews.com/30789/comesa-countries-considering-single-travel-visa.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 "Tunisia, Somalia Joins COMESA". Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa. 2018-07-19. http://www.comesa.int/tunisia-joins-comesa-as-20th-member-state/.
- ↑ Gakunga, Mwangi (24 November 2021). "Egypt Takes Over COMESA Leadership – Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa" (in en-US). https://www.comesa.int/the-21st-comesa-summit-gets-underway-in-cairo/.
- ↑ "About COMESA". The Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA). http://about.comesa.int/index.php?option=com_content&view=article&id=56&Itemid=116.
- ↑ "Court of Justice of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa". http://www.aict-ctia.org/courts_subreg/comesa/comesa_home.html.
External links
 |

