Software:OpenSync
| File:Opensync logo.png | |
| Developer(s) | The OpenSync Project |
|---|---|
| Stable release | 0.22
/ 28 October 2007 |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Synchronization |
| License | GNU Lesser General Public License |
OpenSync is an obsolete (or at least years-dormant)[1] software library framework used for synchronization of PIM data (contacts, calendar, tasks, and notes) between personal computers and mobile devices. It is derived from MultiSync. OpenSync is plugin based and its product-specific plugins allow support for a wide variety of different synchronization endpoints (PIM applications, mobile phones, personal digital assistants, groupware servers, and Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directories). Its design and implementation would allow other synchronization uses as well.
OpenSync has been selected to be KDE's main synchronization framework. It is cross-platform software that can be run on Microsoft Windows and various Unix-like systems, including Linux and Mac OS X.
OpenSync is free and open source software, released under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
Features
OpenSync has an ambitious goal to solve all possible PIM synchronization needs. Regardless of its current shortcomings, its feature list is extensive:
- Cross-platform software, implemented in C programming language
- Plugin based
- Uses threads
- Two or more members in one synchronization (group)
- Capabilities detection
- Object merger
- Object type filtering
- Supported formats are defined in external XML file
- Multiple graphical user interfaces for different environments
- Command-line user interface
- Bindings to other languages (Python)
- vCard 2.1, 3.0 support
- vEvent 1.0, 2.0 support
- vNote 1.1 support
- vTodo 1.0, 2.0 support
- SyncML 1.1 and partial SyncML 1.2, WBXML support
- IrMC support
- Bluetooth support
- USB support
- HTTP support
- LDAP support
- Only SyncML server support
(Note: vEvent 1.0 is the same as vCalendar 1.0, and vEvent 2.0 is the same as vCalendar 2.0 or iCalendar, which all are supported as well.)
OpenSync synchronization takes place in groups which can have two or more different type of members supporting different set of object attributes. Development version also has a sync engine that is able to merge attributes from same object changed on different endpoints.
Architecture
Virtual formats
Before synchronizing anything, OpenSync converts data coming from members into internal XML-based formats, which are:
- xmlformat-contact
- xmlformat-event
- xmlformat-note
- xmlformat-todo
This conversion is implemented in VFormat plugin. Format descriptions are in XML format, allowing more frequent updates to those without modifying and recompiling the actual program code.
Capabilities
OpenSync is able to automatically configure some products for synchronized attribute settings (for supported attributes and data formats).
Merger
OpenSync is able to merge different attribute changes of same object since last synchronization between different group members. This reduces significantly manual conflict resolutions and user attention to actual synchronization process.
Supported platforms
Since OpenSync is written in C and libraries it uses are openly available, it can be compiled to almost any platform where C compiler is available. Currently known working platforms are:
- Linux i386 and x86-64
- Solaris SPARC, i386, x86-64
- FreeBSD, i386, x86-64
- Microsoft Windows (only file plugin is usable) i386, x86-64
Supported devices
Support is based on general features and may vary depending on features of particular device, OpenSync bugs, or connection method used (Bluetooth, USB, IRDA).
Motorola
The Motorola plugin is written in Python.
Nokia
Generally, devices supporting SyncML 1.1 or 1.2 over Bluetooth, USB, or IP-protocol are supported. Nokia 770, N800, and N810 Internet Tablets using GPE suite are supported.
Sony Ericsson
Sony Ericsson devices supporting SyncML or IrMC.
User interfaces
Msynctool
Msynctool is the command-line interface that comes with OpenSync. Its name comes from the term "MultiSync", but it has been decided to change the name to something closer to the project name. Msynctool supports all features that OpenSync itself supports, and is thus considered to be the reference user interface.
Mototool
Mototool is the command-line interface for Motorola's devices, and is also written in Python.
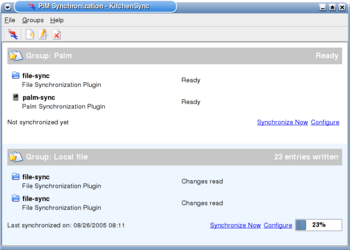
KitchenSync
KitchenSync is the GUI frontend for the K Desktop Environment. It synchronizes KDE PIM-suite applications like Kaddressbook (contacts), KOrganizer (calendar), and Knotes (notes). Mail synchronization is not supported. In future versions KitchenSync will be ported to KDE Akonadi. KitchenSync is written with C++-language, Qt- and KDE toolkits.
KDE PIM applications can also be combined into Kontact framework, where they appear as a single application with tighter integration. As applications are the same, Kontact is also a supported application.
Gnome-Sync
Gnome-Sync was a GUI frontend for GNOME desktop environment, now discontinued.[2] It was written in C and used the GTK+ toolkit.
Plugins
Some of the plugins available for OpenSync are:
- vformat – Internal virtual format
- python – Python programming language API
- file – File plugin syncing vcard, vevent, and vnote files in directory
- kdepim – K Desktop Environment – KDE PIM suite
- evolution2 – GNOME Evolution PIM suite
- irmc – IrMC Infrared Mobile Communications
- syncml – SyncML
- moto – Motorola
- ldap – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
- palm – Palm OS
- synce – SynCE, Windows CE/Windows Mobile
- gpe – GPE Palmtop Environment
- google-calendar – Google Calendar
- gnokii – Gnokii (Nokia)
- jescs – Sun Java Enterprise System Calendar Server (JESCS)
- sunbird – Mozilla Sunbird
- opie – Open Palmtop Integrated Environment (OPIE)
Current status
The OpenSync codebase has not been updated since 2012, but no stable release has been made since 2007. That stable release is 0.22, and as the codebase will be its last 0.2x release (although some fixes have been added). Main development efforts now focus on the current versions. Development versions (0.31 through 0.39) have gone through major architectural changes including capabilities and merging support, but a stable 0.40 release has proved elusive.
Shortcomings
These are current challenges that developers are aware of and trying to address in the future releases.[citation needed]
- Older versions do not work in many cases.
- Due to recent heavy modifications and rare releases, compiling it manually is currently recommended.
- Most platforms ship the latest releases, which are laborious to compile manually.
- Configuring current versions is difficult for normal users.
- Lack of a Microsoft Windows PIM-suite plugin limits the community.
- SyncML support is only for servers.
- The architecture is not very suitable for binary data synchronization (music, pictures, etc.).
See also
- ActiveSync
- HotSync
- Intellisync
- iSync
- Kdepim
- Nokia PC Suite
- Z-push
References
External links