Software:Emergent
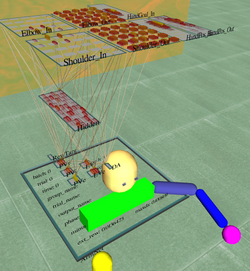 A robotics simulation utilizing the Open Dynamics Engine | |
| Original author(s) | Carnegie Mellon University |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | University of Colorado at Boulder |
| Stable release | 8.2.0 / September 7, 2017
|
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Type | Neural network software |
| License | GPL |
| Website | Emergent homepage |
Emergent (formerly PDP++) is a neural simulation software that is primarily intended for creating models of the brain and cognitive processes. Development initially began in 1995 at Carnegie Mellon University, and (As of 2014), continues at the University of Colorado at Boulder. The 3.x release of the software, which was known as PDP++, is featured in the textbook Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience.
Features
Emergent features a modular design, based on the principles of object-oriented programming. It runs on Microsoft Windows, Darwin / macOS and Linux. C-Super-Script (variously, CSS and C^C), a built-in C++-like interpreted scripting language, allows access to virtually all simulator objects and can initiate all the same actions as the GUI, and more. Version 4 and upward features a full 3D environment for visualizations, based on Qt and Open Inventor. Robotics simulations are made possible by integration with the Open Dynamics Engine. A plugin system allows for expanding the software in many ways. Version 5 introduced parallel threading support, numerous speed improvements, a help browser featuring an interface to the project's Wiki and auto-generated documentation, undo and redo using diffs and a definable undo depth. In addition, 5.0.2 introduced a built-in plugin source code editor, and plugins can now be compiled from the main interface, enabling full development of plugins within Emergent.
Emergent also provides an implementation of Leabra which was developed by Randall C. O'Reilly in his PhD thesis.[1]
See also
- David Rumelhart[clarification needed]
- Randall C. O'Reilly
- James McClelland (psychologist)[clarification needed]
- Biologically inspired computing
- Computational neuroscience
- Leabra
Bibliography
- "The Emergent neural modeling system". Neural Networks 21 (8): 1146–1152. October 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neunet.2008.06.016. ISSN 0893-6080. PMID 18684591. http://psych.colorado.edu/~oreilly/papers/AisaMingusOReilly08.pdf.
- O'Reilly, Randall; Munakata, Yuko (2000). Computational Explorations in Cognitive Neuroscience: Understanding the Mind by Simulating the Brain. The MIT Press. ISBN 978-0-262-65054-0.
References

