Software:Diff-Text
| Developer(s) | DiffEngineX LLC |
|---|---|
| Initial release | Oct 29, 2012 |
| Written in | C-sharp |
| Operating system | Any |
| Type | Data comparison |
| License | Closed Source |
| Website | diff-text.com |
Diff-Text is a web-based software tool that identifies differences between two blocks of plain text. It operates on a closed-source model and offers a donation or pay-what-you-want payment option.[1][2] To be compared, text is pasted directly into the web-page. Diff-Text was developed by DiffEngineX LLC and uses improved algorithms originally developed for the spreadsheet compare tool DiffEngineX. It allows the user to choose between comparing on the level of paragraphs, whole lines, words, or characters. If comparing whole lines, only the line that is not a part of the other block will be reported. Diff Text considers a paragraph to be any line ending with a Windows, Macintosh or Unix line terminator.
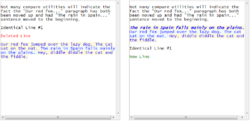
The website can combine the original and modified text blocks into one pane with all differences highlighted. Alternatively, the marked-up original and modified text blocks can be displayed in individual panes. Navigation from one difference to the next is supported.
All of the above features are not unique and can be found in other text comparison tools. The software can display just the differences, the differences with a variable amount of context on either side or the whole marked-up text. The website supports the use of SSL ("https") so confidential text can be compared. The algorithm used by Diff-Text is used by Selection Diff Tool, which is an app for Microsoft Word and Excel 2013.[3][better source needed]
Limitations of using the longest common subsequence algorithm
Diff-Text has the ability to spot text that has either been moved up or down in the document and placed into a new context. To avoid spurious similarities being flagged, the software allows the user to specify the minimum number of adjacent words or characters to be reported as a move. Text movements are reported such that the number of individual edits to transform the original text into the modified text are at a minimum.
The vast majority of text comparison software based on the longest common subsequence problem algorithm incorrectly report moved text as unlinked additions and deletions. The algorithm only reports the longest in-order run of text between two documents. Text moved out of the longest run of similarities is missed.
Heuristics are not used. Any similarity between the two documents above the specified minimum will be reported (if detecting moves is selected). This is the main difference between Diff-Text and most other text comparison algorithms. Diff-Text will always match up significant similarities even if contained within non-identical or moved lines. It never resorts to guessing or the first match that happens to be found, which may result in non-optimal matches elsewhere.
Diff-Text can spot sentence re-ordering within a paragraph. To indicate this, the background color of the text changes to light blue and yellow.
If the user specifies text movements should not be detected, its algorithm runs in (m log n) time, which is an improvement from the standard quadratic time often seen in software of this type. m and n refer to the sizes of the original and modified texts.
References
- ↑ HVG Weekly [1], 2 November 2012. Retrieved on 8 December 2012.
- ↑ "diffenginex / Diff Text / wiki / Home — Bitbucket". https://bitbucket.org/diffenginex/diff-text/wiki/Home.
- ↑ Office.Microsoft.com [2], 26 November 2012. Retrieved on 8 December 2012.
External links