Biology:Hydrocotyle bonariensis
From HandWiki
Short description: Species of flowering plant
| Hydrocotyle bonariensis | |
|---|---|

| |
| Largeleaf pennywort | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Araliaceae |
| Genus: | Hydrocotyle |
| Species: | H. bonariensis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hydrocotyle bonariensis Lam.[1]
| |
| |
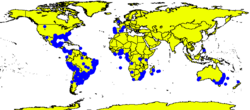
| Occurrence data from GBIF | |
| Synonyms | |
|
Hydrocotyle bonariensis Comm. ex Lam. | |
Hydrocotyle bonariensis, the largeleaf pennywort,[1] once a member of the family Apiaceae, now in the family Araliaceae[4] and of the genus Hydrocotyle, is a hairless and creeping[5] perennial.[6]
Description
- Flowers
- This plant has numerous white[5] to creamy-yellow[6] flowers, and the flower stalks can be 30 centimetres (12 in) in height.[5]
- Fruits and reproduction
- The stems creep and root at the nodes; the plant spreads by rhizomes. Dollar Weed produces a dry dehiscent fruit that, at maturity, splits into two or more parts each with a single seed.[6]
- Habitat
- This plant lives in sandy areas of somewhat extreme conditions: very dry lands that are flooded sometimes.
- Community species
- Co-dominate species
- Imperata brasiliensis
- Bacopa monnieri[8]
Distribution
This species colonizes sandy ground[5] and disturbed foreshore sites, estuaries, coastline, sand dunes and ponds.[6] H. bonariensis has also displayed a tendency to prefer, and be stronger at, higher elevations.[9]
- Native[10]
- Afrotropic:
- West-Central Tropical Africa: Cameroon
- West Tropical Africa: Côte d'Ivoire, Ghana, Liberia, Nigeria, Senegal
- South Tropical Africa: Angola, Mozambique
- Southern Africa: South Africa
- Western Indian Ocean: Madagascar , Mauritius, Réunion
- Nearctic:
- Southeastern United States: Alabama, Florida, Georgia, Louisiana, Mississippi, North Carolina, South Carolina
- South-Central United States: Texas
- Neotropic:
Neighbors
- Colombian communities
- In a remote sensing project for rapid ecological evaluation, H. bonariensis was found in Colombia inhabiting several of the evaluated areas; the last two communities are considered exceptional for the diversity.[11]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Natural Resources Conservation Service (NRCS). "PLANTS Profile, Hydrocotyle bonariensis". The PLANTS Database. United States Department of Agriculture. http://plants.usda.gov/java/profile?symbol=HYBO.
- ↑ Tropicos. "Hydrocotyle bonariensis Lam.". Missouri Botanical Garden. http://www.tropicos.org/Name/01702251.
- ↑ "Hydrocotyle bonariensis Lam. record n° 27212". African Plants Database. South African National Biodiversity Institute, the Conservatoire et Jardin botaniques de la Ville de Genève and Tela Botanica.. http://www.ville-ge.ch/cjb/bd/africa/details.php?langue=an&id=27212.
- ↑ "genus Hydrocotyle". Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) online database. https://npgsweb.ars-grin.gov/gringlobal/taxonomygenus.aspx?id=5898.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Aluka. "Hydrocotyle bonariensis Lam. [family UMBELLIFERAE"]. African Plants. Ithaka Harbors, Inc. http://www.aluka.org/action/showCompilationPage?doi=10.5555/AL.AP.COMPILATION.PLANT-NAME-SPECIES.HYDROCOTYLE.BONARIENSIS.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 "Ecology of Cumberland Plain Woodland *Hydrocotyle bonariensis". Hot Science topics. Department of Environment and Climate Change, Botanic Gardens Trust. http://www.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/science/hot_science_topics/Ecology_of_Cumberland_Plain_Woodland/woodland_plants/hydrocotyle_bonariensis.
- ↑ Klein, Alecsandro Schardosim; Vanilde Citadini-Zanette; Robson Santos (September 2007). "Florística e estrutura comunitária de restinga herbácea no município de Araranguá, Santa Catarina" (in es). Biotemas 20 (3): 15–26. – 1643. http://www.biotemas.ufsc.br/pdf/volume203/p15a26.pdf. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
- ↑ "HABITATS DE PRAIAS DO ATLÂNTICO" (in pt). DESCRIÇÃO DO SITE. BRAZILIAN LONG TERM ECOLOGICAL RESEARCH (PELD). http://www.peld.furg.br/portugues/habitates_de_praias_do_oceno.htm.
- ↑ Knight, Tiffany M.; Thomas E. Miller (2004). "Local adaptation within a population of Hydrocotyle bonariensis". Evolutionary Ecology Research (6): 103–114. http://www.biology.wustl.edu/faculty/knight/knightandmiller.pdf. Retrieved 2008-04-25.
- ↑ {{citation | mode = cs1 | title = Hydrocotyle bonariensis | work = Germplasm Resources Information Network (GRIN) | url = | publisher = [[Organization:Agricultural Research ServAgricultural Research Service (ARS), United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) | access-date = 2008-04-25 }}
- ↑ Berlinc, Christian Niel; Rosario Beyhaut (17–23 October 2004). "RAPID ECOLOGICAL EVALUATION FOR THE PROJECT ON THE USE OF REMOTE SENSING TECHNOLOGIES FOR ECOSYSTEM MANAGEMENT TREATIES". Remote Sensing Technologies for Ecosystem Management Treaties. Bureau of Oceans and International Environmental and Scientific Affairs and United States Department of State. http://sedac.ciesin.columbia.edu/rs-treaties/papers/LM_October2004fieldreport_english.pdf.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q5954749 entry
 |



