Biology:Manihot carthaginensis subsp. glaziovii
| Tree cassava | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Malpighiales |
| Family: | Euphorbiaceae |
| Genus: | Manihot |
| Species: | |
| Subspecies: | M. c. subsp. glaziovii
|
| Trinomial name | |
| Manihot carthaginensis subsp. glaziovii Allem
| |
| Synonyms [1] | |
| |
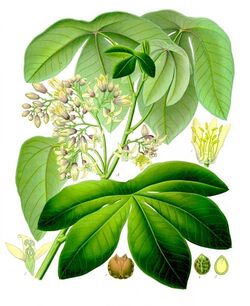
Manihot carthaginensis subsp. glaziovii, also known as Manihot glaziovii, the tree cassava or Ceara rubber tree, is a species of deciduous flowering plant in the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, that is native to eastern Brazil .
Description
- Leaves - palmipartite, peltate; lobes broadly ovate to obovate; green above, glaucous beneath.[2]
- Flowers - show branched inflorescence. Unisexual flowers are greenish-white or pale yellow with reddish markings.[3]
- Fruit - globose.
Common names
- French - manioc de ceara, maniçoba, ceara, caouchouc de ceara
- Portuguese - maniçoba
- Swahili - mpira
- Yoruba - gbaguda
Uses
The tree cassava was used a source of rubber, instead of Hevea brasiliensis throughout the world. The plant is introduced largely in the world, but now it is classified as one of the highly invasive plant of the world.[4]
This species is useful in cassava breeding because it is a wild relative.[5] Several quantitative trait loci (QTLs) are known to be usable or in use for introgression into cultivated cassava.[5] This includes those for cassava brown streak disease resistance found by Abaca et al., 2013 and four found by Nzuki et al., 2017.[5]
Invasiveness
The species is invasive in New Caledonia.[6]
References
- ↑ "Manihot carthaginensis subsp. Glaziovii (Müll.Arg.) Allem — the Plant List". http://www.theplantlist.org/tpl/record/kew-119757.
- ↑ "Manihot glaziovii". 2009. http://www.worldagroforestry.org/treedb2/AFTPDFS/Manihot_glaziovii.PDF.
- ↑ "Flora of Zimbabwe: Species information: Manihot glaziovii". https://www.zimbabweflora.co.zw/speciesdata/species.php?species_id=135510.
- ↑ "Manihot glaziovii in Flora of China @ efloras.org". http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=2&taxon_id=242331575.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2
- Tomlinson, Katie R.; Bailey, Andy M.; Alicai, Titus; Seal, Sue; Foster, Gary D. (2017). "Cassava brown streak disease: historical timeline, current knowledge and future prospects". Molecular Plant Pathology (John Wiley & Sons, Inc.) 19 (5): 1282–1294. doi:10.1111/mpp.12613. ISSN 1464-6722. PMID 28887856.
- This review cites this research.
- Nzuki, Inosters; Katari, Manpreet S.; Bredeson, Jessen V.; Masumba, Esther; Kapinga, Fortunus; Salum, Kasele; Mkamilo, Geoffrey S.; Shah, Trushar et al. (2017). "QTL Mapping for Pest and Disease Resistance in Cassava and Coincidence of Some QTL with Introgression Regions Derived from Manihot glaziovii". Frontiers in Plant Science (Frontiers Media SA) 8: 1168. doi:10.3389/fpls.2017.01168. ISSN 1664-462X. PMID 28785268.
- ↑ Hequet, Vanessa (2009) (in fr). Les espèces exotiques envahissantes de Nouvelle-Calédonie. pp. 17. http://horizon.documentation.ird.fr/exl-doc/pleins_textes/divers12-08/010052239.pdf.
Further reading
- History of Manihot glaziovii
- An acid phosphatase from Manihot glaziovii as an alternative to alkaline Phosphatase for molecular cloning experiments.
- Characterisation and evaluation of a novel feedstock, Manihot glaziovii, Muell. Arg, for production of bioenergy carriers: Bioethanol and biogas.
Wikidata ☰ Q20164643 entry
 |


