Biology:Acacia salicina
| Acacia salicina | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. salicina
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia salicina Lindl.[1]
| |
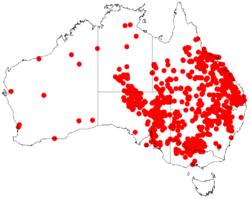
| |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Acacia salicina is a thornless species of Acacia tree native to Australia .
It is a large shrub or small evergreen[2] tree growing up to 13.7m (45 feet) tall. Fast grower dropping lots of leaf litter. It has a life span of about 10–50 years. In the Northern Hemisphere, Acacia salicina flowers primarily from October to January and the seed pods are often visible from April to July.[3] The tree's seeds are shiny, black and have a crimson appendage-like aril.[4] Acacia salicina is "closely related" to Acacia ligulata[5] and Acacia bivenosa.[6]
Common names
Common names include cooba, native willow, willow wattle, Broughton willow, sally wattle, black sallee and black wattle. The Wiradjuri people of New South Wales use the name Guba.[7]
Chemical compounds
Wood
- (−)-7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavanone[8]
- 7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxydihydroflavonol[8]
- 7,8,3',4'-tetrahydroxyflavonol[8]
Natural growing conditions
Acacia salicina is found throughout Australia , with the plant itself found growing in regions receiving in excess of 1500mm annually in northern Queensland and as low as 100mm annually in central Australia. Its natural altitude range is from 50-300m above sea level.[4] It does well in full sun exposure and it tolerates frosts down to -6.7 deg. C (-20 deg. F).[2]
Uses
Erosion management
Acacia salicina can be used to help stabilize riverbanks and other areas.[9]
Fodder
The tree's foliage and seed pods are important fodder for livestock during dry periods, since the tree can withstand drought quite well.[9] Its foliage and pods compare quite poorly to other fodders with regard to digestibility by livestock. This affects its available nutritional value.[10] The 1889 book 'The Useful Native Plants of Australia’ records that "The leaves are eaten by stock. This is another tree which is rapidly becoming scarce, owing to the partiality of stock to it."[11]
Food
The seeds are edible.[9]
Landscaping
Acacia salicina is excellent for landscaping in dry areas.[9]
Tannin
The bark has a high tannin content.[9]
Wood
The wood is very hard and it is used in making fine furniture.[9] At one time, the tree's wood was used in the manufacture of axles for wagon wheels. Acacia salicina's wood burns nicely and makes good fuel.[9] Its calorific content is 18900kJ/kg dry mass.[10] The tree produces seed and timber for woodworking in as little as five years after planting.[12]
Other uses
The bark has been traditionally put to use by Indigenous Australians as a toxin for fishing.[9] The leaves of A. salicina are thought to be psychoactive, since indigenous Australians "burn its leaves and smoke the ash to obtain a state of inebriation."[13]
The 1889 book, The Useful Native Plants of Australia, records that common names included "Native Willow" and "Broughton Willow" near the Broughton River in South Australia. It also records it was called "Cooba" or "Kooba" by Indigenous people in Western New South Wales and "Motherumba" by those on the Castlereagh River, New South Wales.[11]
Weed status
Acacia salicina spreads widely through seed dispersal, and individual trees can rapidly form thickets through production of adventitious shoots from the root system. The species has become a significant weed over some of its native,[10][14] and introduced range.[15]
References
- ↑ "ILDIS LegumeWeb (version 10)". http://www.ildis.org/LegumeWeb/?version~10.01&LegumeWeb&tno~16286&genus~Acacia&species~salicina.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Gardens At Carefree Town Center - Plant Identification List
- ↑ PDF Ursula K. Schuch and Margaret Norem, Growth of Legume Tree Species Growing in the Southwestern United States, University of Arizona.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Species Bank Treatment for Acacia Salicina". http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/species-bank/sbank-treatment2.pl?id=2006.
- ↑ "Fact Sheet for Acacia ligulata". http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/cgi-bin/texhtml.cgi?form=speciesfacts&keyname=Acacia+ligulata.
- ↑ "Acacia ligulata - WATTLE". http://www.worldwidewattle.com/speciesgallery/ligulata.php.
- ↑ Williams, Alice; Sides, Tim, eds (2008). Wiradjuri Plant Use in the Murrumbidgee Catchment. Murrumbidgee Catchment Management Authority. p. 10. ISBN 978-0-7347-5856-9.
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Clark-Lewis, J. W.; Nair, V. (15 March 1964). "Flavan derivatives. X. 7,8,3',4'-Tetrahydroxyflavanone and 7,8,3',4'- Tetrahydroxydihydroflavonol from Acacia species". Australian Journal of Chemistry 17 (10): 1164–1169. doi:10.1071/ch9641164. https://www.publish.csiro.au/ch/ch9641164. Retrieved 15 March 2022.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 9.3 9.4 9.5 9.6 9.7 Acacia Salicina, Csu.edu.au
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 "Acacia Search". http://www.worldwidewattle.com/infogallery/utilisation/acaciasearch/pdf/salicina.pdf.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 J. H. Maiden (1889). The useful native plants of Australia : Including Tasmania. Turner and Henderson, Sydney. https://primo-slnsw.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/primo-explore/fulldisplay?docid=SLNSW_ALMA21105097830002626&context=L&vid=SLNSW&search_scope=EEA&tab=default_tab&lang=en_US.
- ↑ Victorian Landcare & Catchment Management, Autumn 2003 Issue 27 p. 8
- ↑ Yaniv, Zohara; Bachrach, Uriel (25 July 2005). Handbook of Medicinal Plants. CRC Press. p. 183. ISBN 9781560229957. https://books.google.com/books?id=QN78GmmPGBQC&dq=acacia+alkaloids&pg=PA183. Retrieved 15 March 2022.
- ↑ "Listed invasive native species by Catchment Management Authority". http://www.nativevegetation.nsw.gov.au/p/fact_sheet_9_list.pdf.
- ↑ "Invasive Plants Database". http://invasive.m-fuukei.jp/sdetail.php?g=Acacia&s=salicina.
Wikidata ☰ Q2709212 entry
 |




