Biology:Oxypolis rigidior
| Oxypolis rigidior | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Oxypolis |
| Species: | O. rigidior
|
| Binomial name | |
| Oxypolis rigidior (L.) Raf.
| |
Oxypolis rigidior, known as cowbane, common water dropwort,[1] stiff cowbane,[2] or pig-potato, is a species of flowering plant in the carrot family native to eastern North America. It is a perennial wildflower found in wet habitats.[3][4][5] Oxypolis rigidior is poisonous to mammals.
Description
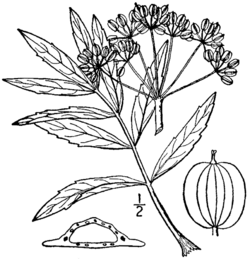
Oxypolis rigidior is 2–6 foot tall perennial herb of eastern North America. Its leaves are compound, odd-pinnate with 7-11 leaflets, and have variable shape. Umbels of 3 mm white flowers appear August to October. Flat fruits with conspicuous "wings" appear October through November.[5][3]
The variable leaf shape may make identification challenging. Water hemlock, a related very poisonous species, which sometimes even shares the common name "cowbane", is similar, as is the closely related Savanna cowbane (Oxypolis ternata).[5][3]
Taxonomy
Two varieties have been described, O. rigidior var. rigidior and O. rigidior var. ambigua.[5]
Toxicity
Both roots and top parts are reported as poisonous to mammals.[6][7]
Interestingly, however, they are also considered edible and safe by some.[8][9] Thayer calls them Cherokee swamp potato in reference to their use in Cherokee cuisine and states that “the tubers can used as a potato-like vegetable…fantastic in any way you’d use a potato”.[9] However, he also states that the plant should be gathered with “great caution” due to its resemblance to another plant, water hemlock, which shares the name cowbane.
References
- ↑ "Oxypolis rigidior" (in en). Minnesota Wildflowers. https://www.minnesotawildflowers.info/flower/cowbane. Retrieved 21 August 2020.
- ↑ "Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center - The University of Texas at Austin". https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=OXRI.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 Peterson, Roger Tory; McKenny, Margaret (1968). A Field Guide to Wildflowers Northeastern and Northcentral North America. New York, NY, USA: Houghton Mifflin. p. 52. https://archive.org/details/fieldguidetowild00pete_483.
- ↑ "Oxypolis rigidior (L.) Raf.". USDA. http://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=oxri. Retrieved July 21, 2015.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 Weakley, Alan S. (May 2015). Flora of the Southern and Mid-Atlantic States. Chapel Hill, NC, USA: The University of North Carolina Herbarium. p. 1236. http://www.herbarium.unc.edu/FloraArchives/WeakleyFlora_2015-05-29.pdf. Retrieved 8 July 2015.
- ↑ Dr. John Hilty. "Cowbane (Oxypolis rigidior)". illinoiswildflowers.info/. http://www.illinoiswildflowers.info/wetland/plants/cowbane.htm. Retrieved July 21, 2015.
- ↑ Cowbane at the Encyclopædia Britannica
- ↑ "BRIT - Native American Ethnobotany Database". http://naeb.brit.org/uses/species/2714/.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Thayer, Samuel (2023) (in English). Sam Thayer’s Field Guide to Edible Wild Plants. United States: Forager’s Harvest. pp. 424-425. ISBN 978-0-9766266-4-0.
Wikidata ☰ Q17134564 entry
 |