Biology:Neochloris
| Neochloris | |
|---|---|
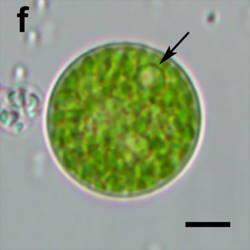
| |
| Neochloris aquatica | |
| Scientific classification | |
| (unranked): | Viridiplantae |
| Division: | Chlorophyta |
| Class: | Chlorophyceae |
| Order: | Sphaeropleales |
| Family: | Neochloridaceae |
| Genus: | Neochloris Starr, 1955 |
| Type species | |
| Neochloris aquatica | |
| Species[1] | |
| |
Neochloris is a genus of green algae in the family Neochloridaceae.[1] It is found in freshwater aquatic and terrestrial soil habitats.[2]
Description
Neochloris consists of spherical cells that are solitary or sometimes found in small clusters. The cell wall is thin and smooth. Cells are multinucleate (with multiple nuclei).[3] Each cell has a single parietal chloroplast with one to several pyrenoids.[2]
Neochloris reproduces asexually. Reproduction occurs via aplanospores or zoospores. Zoospores bear two flagella; upon spore germination, the zoospore loses its flagella and becomes spherical.[4]
Taxonomy
Neochloris was first described by Richard C. Starr in 1955 with a single species Neochloris aquatica, with more species being added by later authors. However, the genus in this circumscription was polyphyletic.[3] Species once placed in Neochloris have now been placed in two segregate genera, Ettlia and Parietochloris.[3]
Ettlia and Parietochloris differ from Neochloris in being uninucleate while Neochloris sensu stricto contains multinucleate cells.[3] Additional features of the flagellar apparatus are visible in ultrastructure as well. The basal bodies of the zoospore flagella in Neochloris are arranged directly opposite to each other,[3] those of Ettlia are arranged in a clockwise orientation, and those of Parietochloris are arranged in a counterclockwise orientation.[3]
Ecology
The species Neochloris aquatica may have potential as a biological control agent against mosquitoes, specifically Culex quinquefasciatus.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Genus: Neochloris taxonomy browser". AlgaeBase version 4.2 World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway. 2007. http://www.algaebase.org/browse/taxonomy/#id=6996. Retrieved 2023-09-21.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Bicudo, Carlos E. M.; Menezes, Mariângela (2006). Gêneros de Algas de Águas Continentais do Brasil: chave para identificação e descrições (2 ed.). RiMa Editora. pp. 508. ISBN 857656064X.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 Deason, T. R.; Silva, P. C.; Watanabe, S.; Floyd, G. L. (1991). "Taxonomic status of the species of the green algal genus Neochloris". Plant Systematics and Evolution 177 (3–4): 213–219. doi:10.1007/BF00937958.
- ↑ Shubert, Elliot; Gärtner, Georg (2014). "Chapter 7. Nonmotile Coccoid and Colonial Green Algae". Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification (2 ed.). Elsevier Inc.. ISBN 978-0-12-385876-4.
- ↑ Gil, M. Florencia; Fassolari, Marisol; Battaglia, Marina E.; Berón, Corina M. (2021). "Culex quinquefasciatus larvae development arrested when fed on Neochloris aquatica". PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases 15 (12): e0009988. doi:10.1371/journal.pntd.0009988. PMID 34860833.
Wikidata ☰ Q6992123 entry
 |

