Biology:Styphelia clelandii
| Styphelia clelandii | |
|---|---|

| |
| In the Big Desert Wilderness Park | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Ericales |
| Family: | Ericaceae |
| Genus: | Styphelia |
| Species: | S. clelandii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Styphelia clelandii (Cheel) J.H.Willis[1]
| |
| |
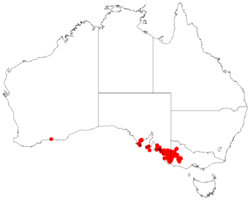
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
|
Leucopogon clelandii Cheel | |
Styphelia clelandii, commonly known as Cleland's bearded-heath,[2] is a species of flowering plant in the heath family Ericaceae and is endemic to the south-east of continental Australia. It is weak, open shrub with broadly egg-shaped leaves and white flowers arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils near the ends of the branches.
Description
Styphelia clelandii is a weak, open shrub that typically grows to a height of 15–30 cm (5.9–11.8 in) and branchlets that are sometimes covered with soft hairs. The leaves are broadly egg-shaped, 2.5–6 mm (0.098–0.236 in) long and 1.0–1.8 mm (0.039–0.071 in) wide and more or less sessile. The flowers are arranged singly or in pairs in leaf axils near the ends of branchlets, with round bracteoles about 1 mm (0.039 in) long. The sepals are oblong, 2–3 mm (0.079–0.118 in) long and glabrous, the petals white and joined at the base to form a cylindrical tube 0.9–1.6 mm (0.035–0.063 in) long, the lobes 1.7–2.3 mm (0.067–0.091 in) long. Flowering occurs from April to August and the fruit is an oval or elliptic drupe 2.2–3.5 mm (0.087–0.138 in) long.[2][3]
Taxonomy and naming
This species was first formally described in 1915 by Edwin Cheel in the Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of South Australia from specimens collected by John Burton Cleland near Coonalpyn in 1911.[4][5] In 1967, James Hamlyn Willis transferred the species to Styphelia as S. clelandii in the journal Muelleria.[1][6] The specific epithet (clelandii) honours Cleland.[5]
Distribution and habitat
Styphelia clelandii grows in mallee scrub and heath in the south-east of South Australia and to as far east as the Grampians in Victoria.[2][3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Styphelia clelandii". Plants of the World Online. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:325704-1#synonyms.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Leucopogon clelandii". State Herbarium of South Australia. http://www.flora.sa.gov.au/cgi-bin/speciesfacts_display.cgi?form=speciesfacts&name=Leucopogon_clelandii.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Walsh, Neville G.. "Styphelia clelandii". Royal Botanic Gardens Victoria. https://vicflora.rbg.vic.gov.au/flora/taxon/6bf3f1ae-1fc1-4e0b-9425-84cde04bead4.
- ↑ "Leucopogon clelandii". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/468339. Retrieved 26 May 2022.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Cheel, Edwin (1915). "On two new Species of Leucopogon". Transactions and Proceedings of the Royal Society of South Australia 39: 98–99. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/109513#page/116/mode/1up. Retrieved 26 May 2022.
- ↑ Willis, James H. (1967). "Systematic Notes on the Indigenous Australian Flora.". Muelleria 1 (3): 140. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/199349#page/28/mode/1up. Retrieved 24 September 2023.
Wikidata ☰ Q65949945 entry
 |

