Biology:Cycas thouarsii
| Cycas thouarsii Madagascar cycad | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Gymnospermae |
| Division: | Cycadophyta |
| Class: | Cycadopsida |
| Order: | Cycadales |
| Family: | Cycadaceae |
| Genus: | Cycas |
| Species: | C. thouarsii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cycas thouarsii | |
| |
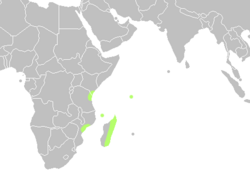
| Range of Cycas thouarsii[2] | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Cycas thouarsii, the Madagascar cycad, is an evergreen arborescent cycad in the genus Cycas. It is named after a French botanist Louis-Marie Aubert du Petit-Thouars (1758—1831).
Description
The stem of this cycad resembles that of a palm, and grows 4–10 meters tall and up to 45 cm in diameter. The large photosynthetic leaves have spiral arrangement on the stem and are interspersed with many brown, hairy, triangular scale-like leaves. The photosynthetic leaves are pinnate, dark-green, somewhat glossy, and usually 150—300 centimeters long, with 60-120 leaflets per side. The leaflets are c. 17 cm long, lanceolate, with a slightly bent margin, and a midrib that is more prominent on the paler lower surface. The leaf-stalk is 40–50 cm long, and has two rows of spines along almost its whole length. The emerging leaves are hairy and show involute vernation; and the young leaves have a distinct bluish tint, which distinguishes it from its relatives C. rumphii and C. circinalis. The pollen cone is spindle-shaped, 30–60 cm high and 10–15 cm in diameter, and varies in color from orange to pale brown. The pollen cone scales have a sharp apical spine. The ovulate cones are composed of overlapping, yellow, hairy megasporophylls, each 29—32 centimeters long, with 5-13 marginal teeth per side, and bearing 4-10 ovules along their edges. The seeds are ovoid, 50—60 millimeters in size with a red-brown fleshy seed coat, and a spongy endocarp. This spongy endocarp is characteristic of this species, and allows the seeds to float.[3][2]
Coralloid roots: these contain nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria
Habitat, ecology and conservation status
The Madagascar cycad is found on Madagascar and the nearby islands of Comoros, Mayotte and the Seychelles. It is also found along the coasts of Kenya, Mozambique, and Tanzania.[1] According to de Laubenfels and Adema, the plant is also found in Sri Lanka, but this may be confusion with the closely related Cycas circinalis.[2] The tree grows 200 meters above sea level, in light forests and their borders, or near coastal sites on sandy soil or coral formations. These areas have annual precipitations varying from 1000 to 3000 millimeters per year.[citation needed]
The plant is quite rare both as an individual and in group communities, and populations were impacted by collectors, the growth of the seaside resorts and agriculture development[citation needed]. However, there is no immediate threat to this species, and it is classified as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List.
Cultivation
As a relatively fast-growing cycad, Cycas thouarsii is occasionally grown in horticulture as a specimen plant. It requires moist but well-drained soil, and will tolerate shade, partial shade, and sun (with sufficient humidity). It is hardy to only a very light frost but can tolerate brief exposure to temperatures down to −3.9 °C (25 °F - USDA hardiness zone 9b) but this results in leaf scorching.[4]
Use as Food
Although toxic, the seeds are eaten on the Comorian island of Ngazidja, particularly in the regions of Hamahame and Washili, where the plant, known as ntsambu, has cultural significance. The cyanotoxins are removed from the seeds by a process of repeated washing, fermentation and drying, which renders them edible.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Golding, J.; Hurter, J. (2010). "Cycas thouarsii". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2010: e.T41940A10606292. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2010-3.RLTS.T41940A10606292.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/41940/10606292. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 de Laubenfels, D. J.; Adema, F. (1998). "A taxonomic revision of the genera Cycas and Epicycas Gen. Nov. (Cycadaceae)". Blumea 43: 351–400.
- ↑ "Cycas thouarsii". http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/cycadpg?taxname=Cycas+thouarsii.
- ↑ "Cycas thouarsii at San Marco growers". https://www.smgrowers.com/products/plants/plantdisplay.asp?plant_id=3418.
- ↑ Walker, iain. (2012). "Ntsambu, the foul smell of home: Food, commensality and identity in the Comoros and in the diaspora". Food and Foodways 20 (3–4): 187–210. doi:10.1080/07409710.2012.715962.
Wikidata ☰ Q1063758 entry
 |








