Biology:Celoporthe
From HandWiki
Short description: Genus of fungi
| Celoporthe | |
|---|---|
| |
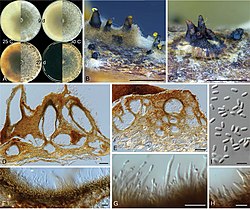
| Celoporthe hawaiiensis | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Subdivision: | |
| Class: | |
| Subclass: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Celoporthe Nakab., Gryzenh., Jol.Roux & M.J.Wingf. (2006)
|
| Type species | |
| Celoporthe dispersa Nakab., Gryzenh., Jol.Roux & M.J.Wingf. (2006)
| |
| Species | |
|
C. dispersa | |
Celoporthe is a genus of ascomycete fungi within the family Cryphonectriaceae. It was circumscribed in 2006 to contain the type species Celoporthe dispersa, which was found in South Africa growing on trees in the Myrtales.[2] In 2011, several species were described from China and Indonesia: C. eucalypti, C. guangdongensis, C. indonesiensis, and C. syzygii.[3] Molecular analysis of DNA sequences revealed an additional two species from South Africa in 2013, C. fontana and C. woodiana[4] and in 2020 three more species from Hawaii were added to the genus.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Roux, Jolanda; Kamgan Nkuekam, Gilbert; Marincowitz, Seonju; Van Der Merwe, Nicolaas A.; Uchida, Janice; Wingfield, Michael J.; Chen, Shuaifei (2020). "Cryphonectriaceae associated with rust-infected Syzygium jambos in Hawaii". MycoKeys 76: 49–79. doi:10.3897/mycokeys.76.58406. PMID 33505197.
- ↑ "Celoporthe dispersa gen. et sp. nov. from native Myrtales in South Africa". Studies in Mycology 55: 255–68. 2006. doi:10.3114/sim.55.1.255. PMID 18490984.

- ↑ "Novel species of Celoporthe from Eucalyptus and Syzygium trees in China and Indonesia". Mycologia 103 (6): 1384–410. 2011. doi:10.3852/11-006. PMID 21700641.
- ↑ "Species delineation in the tree pathogen genus Celoporthe (Cryphonectriaceae) in southern Africa". Mycologia 105 (2): 297–311. 2013. doi:10.3852/12-206. PMID 23233512. https://repository.up.ac.za/bitstream/2263/21554/1/Vermeulen_Species%282013%29.pdf.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q5058420 entry
 |

