Biology:Unsuccessful transfer
From HandWiki
Short description: Failure of bacterial reproduction
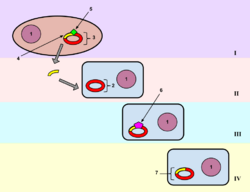
Unsuccessful transfer or abortive transfer is any bacterial DNA transfer from donor cells to recipient cells that fails to survive transduction and conjugation. In all cases, the transferred fragment could be diluted during the proliferation phase. Failures in the integration of the transferred DNA in the genetic material of the recipient cells may be due to:
- Failure of the incoming DNA to form a circular molecule;
- Post-circularisation, the circular molecule is wrong for maintenance, making this transfer occurs as plasmids. Genes that are located on the corresponding part of the DNA can express in the recipient cells.[1][2][3]
Dictionary definition
Rieger, Michaelis, and Green, in 1976 stated:
"'abortive transfer – any DNA transfer from bacterial donor to recipients cells that fails to establish the incoming DNA as part of the hereditary material of the recipient. A. t. has been observed following → transduction → transformation, and → conjugation. In all cases, the transmitted fragment is diluted out as the culture grows. Failure of integration of transferred DNA into the hereditary material of the recipient cell may be due to: 1. The failure of incoming DNA to form circular molecules; 2. circularization takes place, but the circular molecule fails to take up maintenance system. A. t. of the extrachromosomal elements (→ plasmids) as opposed to chromosomal fragments, is relatively uncommon elements since plasmids are genetic elements of autonomous survival in a bacterial cell. It is only when a mutation in the recipient or a resident plasmid makes the host component of the plasmid maintenance system inactive that a. t. of a plasmid occurs. Genes carried on abortive pieces of DNA may be expressed in the recipient cells.[1]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Rieger R. Michaelis A.; Green M. M. (1976). Glossary of genetics and cytogenetics: Classical and molecular. Heidelberg - New York: Springer-Verlag. ISBN 3-540-07668-9.
- ↑ King R. C.; Stransfield W. D. (1998). Dictionary of genetics. New York, Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 0-19-50944-1-7.
- ↑ Bajrović K., Jevrić-Čaušević A., Hadžiselimović R., Eds (2005). Uvod u genetičko inženjerstvo i biotehnologiju. Institut za genetičko inženjerstvo i biotehnologiju (INGEB) Sarajevo. ISBN 9958-9344-1-8.
 |