Chemistry:Metal-catalyzed σ-bond rearrangement
From HandWiki
Revision as of 11:36, 26 October 2020 by imported>Scavis2 (update)
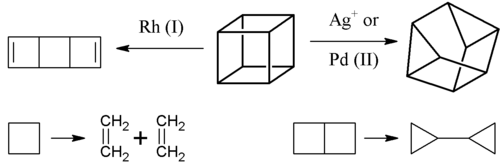
The metal ion-catalyzed σ-bond rearrangement is a collection of chemical reactions that occur with highly strained organic compounds are treated with metal ions like Ag+, Rh(I), or Pd(II) based reagents.[1] [2+2] ring openings are sometimes observed:
These rearrangements proceed via oxidative addition of strained rings. Such processes are related to the activation of cyclopropanes by transition metals.
See also
References
 |