Biology:Glossary of leaf morphology
The following terms are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple (a single leaf blade or lamina) or compound (with several leaflets). The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.
The terms listed here all are supported by technical and professional usage, but they cannot be represented as mandatory or undebatable; readers must use their judgement. Authors often use terms arbitrarily, or coin them to taste, possibly in ignorance of established terms, and it is not always clear whether because of ignorance, or personal preference, or because usages change with time or context, or because of variation between specimens, even specimens from the same plant. For example, whether to call leaves on the same tree "acuminate", "lanceolate", or "linear" could depend on individual judgement, or which part of the tree one collected them from. The same cautions might apply to "caudate", "cuspidate", and "mucronate", or to "crenate", "dentate", and "serrate."
Another problem is to establish definitions that meet all cases or satisfy all authorities and readers. For example, it seems altogether reasonable to define a mucro as "a small sharp point as a continuation of the midrib", but it may not be clear how small is small enough, how sharp is sharp enough, how hard the point must be, and what to call the point when one cannot tell whether the leaf has a midrib at all. Various authors or field workers might come to incompatible conclusions, or might try to compromise by qualifying terms so vaguely that a description of a particular plant practically loses its value.
Use of these terms is not restricted to leaves, but may be applied to morphology of other parts of plants, e.g. bracts, bracteoles, stipules, sepals, petals, carpels or scales. Some of these terms are also used for similar-looking anatomical features on animals.
Leaf structure
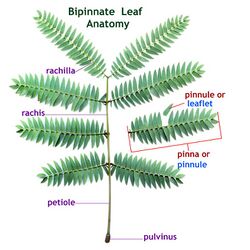
Leaves of most plants include a flat structure called the blade or lamina, but not all leaves are flat, some are cylindrical. Leaves may be simple, with a single leaf blade, or compound, with several leaflets. In flowering plants, as well as the blade of the leaf, there may be a petiole and stipules; compound leaves may have a rachis supporting the leaflets. Leaf structure is described by several terms that include:[citation needed]
thumb|A ternate compound leaf with a petiole but no rachis (or rachillae)
| Image | Term | Latin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
 |
bifoliolate | Having two leaflets[1] | |
| geminate | |||
| jugate | |||
 |
bigeminate | Having two leaflets, each leaflet being bifoliolate | |
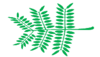 |
bipinnate | bipinnatus | The leaflets are themselves pinnately-compound; twice pinnate |
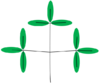 |
biternate | With three components, each with three leaflets | |
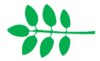 |
imparipinnate | With an odd number of leaflets, pinnate with a terminal leaflet (the opposite of paripinnate) | |
| odd-pinnate | |||
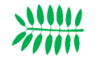 |
paripinnate | Pinnate with an even number of leaflets, lacking a terminal leaflet (the opposite of imparipinnate) | |
| even-pinnate | |||
 |
palmately compound | palmatus | Consisting of leaflets all radiating from one point |
| pinnately compound | pinnatus | Having two rows of leaflets on opposite sides of a central axis, see imparipinnate and paripinnate | |
| simple | Leaf blade in one continuous section, without leaflets (not compound) | ||
 |
ternate | ternatus | With three leaflets |
| trifoliate | trifoliatus | ||
| trifoliolate | trifoliolatus | ||
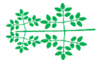 |
tripinnate | tripinnatus | Pinnately compound in which each leaflet is itself bipinnate |
Leaf and leaflet shapes
Being one of the more visible features, leaf shape is commonly used for plant identification. Similar terms are used for other plant parts, such as petals, tepals, and bracts.

| Image | Term | Latin | Refers principally to | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| acicular | acicularis | whole leaf | Slender and pointed, needle-like | |
| acuminate | acuminatus | leaf tip | Tapering to a long point in a concave manner | |
| acute | leaf tip or base | Pointed, having a short sharp apex angled less than 90° | ||
 |
apiculate | apiculatus | leaf tip | Tapering and ending in a short, slender point |
| aristate | aristatus | leaf tip | Ending in a stiff, bristle-like point | |
| asymmetrical | whole leaf | With the blade shape different on each side of the midrib | ||
 |
attenuate | attenuatus | leaf base | Having leaf tissue taper down the petiole to a narrow base and always having some leaf material on each side of the petiole |
 |
auriculate | auriculatus | leaf base | Having ear-shaped appendages reaching beyond the attachment to the petiole or stem (in case of a seated leaf) |
 |
caudate | caudatus | leaf tip | Tailed at the apex |
| cirrus, cirrate | leaf tip | Having a rachis that extends beyond the leaf blade or leaflets into a long whip-like extension or cirrus (common in climbing palms); antonym: ecirrate | ||
 |
cordate, cordiform | cordatus | whole leaf or base | Heart-shaped, with the petiole or stem attached to the notch |
| cuneate | cuneatus | leaf base | Triangular, wedge-shaped, stem attaches to point | |
| cuneiform | whole leaf | Narrowly triangular, widest on the opposite end from the stem, with the corners at that end rounded | ||
 |
cuspidate | cuspidatus | leaf tip | With a sharp, elongated, rigid tip; tipped with a cusp |
 |
deltoid, deltate | deltoideus | whole leaf | Shaped like the Greek letter delta; triangular with stem attached to side |
 |
digitate | digitatus | whole leaf | A palmately compound leaf with leaflets, similar to palmate[2] |
| ecirrate | leaf tip | Without a cirrus; antonym: cirrate | ||
| elliptic | ellipticus | whole leaf | Shaped like an ellipse (widest at mid-blade and with similar convex tapering towards apex and base), with a short or no point | |
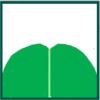 |
emarginate | emarginatus | leaf tip | Slightly indented at the tip |
| ensiform | ensiformis | whole leaf | Shaped like a sword; long and narrow with a sharp pointed tip | |
| falcate | falcatus | whole leaf | Sickle-shaped | |
| fenestrate | fenestratus | leaf surface features | Large openings through the leaf; see perforate; sometimes used to describe leaf epidermal windows | |
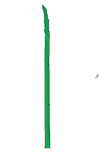 |
filiform | filiformis | whole leaf | Thread- or filament-shaped |
 |
flabellate | flabellatus | whole leaf | Semi-circular or fan-like |
| hastate | hastatus | whole leaf or base | Spear-shaped: pointed, with barbs, shaped like a spear point, with flaring pointed lobes at the base | |
 |
laciniate | lacinatus | whole leaf | Very deeply lobed with the lobes being very drawn out and often making the leaf look somewhat like a branch or a pitchfork |
| laminar | 3-D shape | Flat (like most leaves) | ||
| lanceolate | lanceolatus | whole leaf | Long, wider in the middle, shaped like a lance tip | |
| linear | linearis | whole leaf | Long and very narrow like a blade of grass | |
 |
lobed | lobatus | whole leaf | Being divided by clefts; may be pinnately lobed or palmately lobed |
| lorate | loratus | whole leaf | Having the form of a thong or strap | |
| lyrate | lyratus | whole leaf | Shaped like a lyre, pinnately lobed leaf with an enlarged terminal lobe and smaller lateral lobes. See also List of lyrate plants. | |
 |
mucronate | mucronatus | leaf tip | Ending abruptly in a small sharp point as a continuation of the midrib[3] |
 |
multifid | multi + findere | whole leaf | Cleft into many parts or lobes |
| obcordate | obcordatus | whole leaf | Heart-shaped, stem attaches at the tapering end | |
| oblanceolate | oblanceolatus | whole leaf | Much longer than wide and with the widest portion near the tip; reversed lanceolate | |
| oblique | leaf base | Asymmetrical leaf base, with one side lower than the other | ||
| oblong | oblongus | whole leaf | Having an elongated form with slightly parallel sides; roughly rectangular | |
| obovate | obovatus | whole leaf | Teardrop-shaped, stem attaches to the tapering end; reversed ovate | |
| obtrullate | whole leaf | Reversed trullate; the longer sides meet at the base rather than the apex. | ||
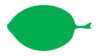 |
obtuse | obtusus | leaf tip or base | Blunt, forming an angle > 90° |
 |
orbicular | orbicularis | whole leaf | Circular |
 |
ovate | ovatus | whole leaf | Egg-shaped, with a tapering point and the widest portion near the petiole |
 |
palmate | palmatus | whole leaf | Palm-shaped, i.e. with lobes or leaflets stemming from the leaf base[4] |
 |
palmately lobed | palmatus | whole leaf | Lobes spread radially from a point[5] |
 |
palmatifid | palma + findere | whole leaf | Palm-shaped, having lobes with incisions that extend less than halfway toward the petiole |
 |
palmatipartite | palma + partiri | whole leaf | Having palmate lobes with incisions that extend over halfway toward the petiole |
 |
palmatisect | palma + secare | whole leaf | Having palmate lobes with incisions that extend almost up, but not quite to the petiole. |
 |
pandurate | panduratus | whole leaf | Fiddle-shaped; obovate with a constriction near the middle. |
 |
pedate | pedatus | whole leaf | Palmate, with cleft lobes[6] |
 |
peltate | peltatus | stem attachment | A round leaf where the petiole attaches near the center, e.g. a lotus leaf |
 |
perfoliate | perfoliatus | stem attachment | With the leaf blade surrounding the stem such that the stem appears to pass through the leaf |
| perforate | perforatus | leaf surface features | Many holes, or perforations, on leaf surface. Compare with fenestrate. | |
 |
pinnately lobed | pinna + lobus | whole leaf | Having lobes pinnately arranged on the central axis |
 |
pinnatifid | pinna + findere | whole leaf | Having lobes with incisions that extend less than halfway to the midrib |
 |
pinnatipartite | pinnatus + partiri | whole leaf | Having lobes with incisions that extend more than halfway to the midrib |
 |
pinnatisect | pinnatus + sectus | whole leaf | Having lobes with incisions that extend almost to, or up to, the midrib |
 |
plicate | plicatus | 3-D shape | Folded into pleats, usually lengthwise, serving the function of stiffening a large leaf |
 |
reniform | reniformis | whole leaf | Shaped like a kidney, with an inward curve on one side |
 |
retuse | leaf tip | With a shallow notch in a round apex | |
 |
rhomboid, rhombic | rhomboidalis | whole leaf | Diamond-shaped |
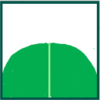 |
rounded | rotundifolius | leaf tip or base | Circular, no distinct point |
| semiterete | 3-D shape | Rounded on one side and flat on the other | ||
 |
sinuate | sinuatus | 3-D shape | Circularly-lobed leaves |
| sagittate | sagittatus | whole leaf | Arrowhead-shaped with the lower lobes folded, or curled downward | |
| spatulate | spathulatus | whole leaf | Spoon-shaped; having a broad flat end which tapers to the base | |
| spear-shaped | hastatus | whole leaf | See hastate. | |
 |
subobtuse | subobtusus | leaf tip or base | Somewhat blunted; neither blunt nor sharp |
| subulate | subulatus | leaf tip | Awl-shaped with a tapering point | |
 |
terete | 3-D shape | Cylindrical with a circular or distorted circular cross-section and a single surface wrapping around it with no grooves or ridges. Subterete means the leaves are not completely terete, as seen in various lichens and succulents. | |
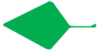 |
trullate | whole leaf | Shaped like a masonry trowel | |
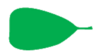 |
truncate | truncatus | leaf tip or base | With a squared-off end |
| undulate | undulatus | 3-D shape | Wave-like | |
| unifoliate | unifoliatus | compound leaves | With a single leaflet; it is distinct from a simple leaf by the presence of two abscission layers and often by petiolules and stipels. |
Edge
Leaf margins (edges) are frequently used in visual plant identification because they are usually consistent within a species or group of species, and are an easy characteristic to observe. Edge and margin are interchangeable in the sense that they both refer to the outside perimeter of a leaf.
| Image | Term | Latin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100px | entire | Forma integra |
Even; with a smooth margin; without toothing |
| 100px | ciliate | ciliatus | Fringed with hairs |
| 100px | crenate | crenatus | Wavy-toothed; dentate with rounded teeth |
| crenulate | crenulatus | Finely crenate | |
| crisped | crispus | Curly | |
| 100px | dentate | dentatus | Toothed;
may be coarsely dentate, having large teeth or glandular dentate, having teeth which bear glands |
| 100px | denticulate | denticulatus | Finely toothed |
| 100px | doubly serrate | duplicato-dentatus | Each tooth bearing smaller teeth |
| 100px | serrate | serratus | Saw-toothed; with asymmetrical teeth pointing forward |
| 100px | serrulate | serrulatus | Finely serrate |
| 100px | sinuate | sinuosus | With deep, wave-like indentations; coarsely crenate |
| 100px | lobate | lobatus | Indented, with the indentations not reaching the center |
| 100px | undulate | undulatus | With a wavy edge, shallower than sinuate |
| 100px | spiny or pungent | spiculatus | With stiff, sharp points such as thistles |
Leaf folding
Leaves may also be folded, sculpted or rolled in various ways. If the leaves are initially folded in the bud, but later unrolls it is called vernation, ptyxis is the folding of an individual leaf in a bud.
| Image | Term | Latin | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| carinate or keeled | carinatus | With a longitudinal ridge, keel-shaped | |
 |
conduplicate | Folded upwards, with the surfaces close to parallel | |
 |
cucullate | Forming a hood, margins and tip curved downward | |
 |
involute | Rolled upwards (towards the adaxial surface) | |
 |
plicate | plicatus | With parallel folds |
| reduplicate | Folded downwards, with the surfaces close to parallel | ||
 |
revolute | Rolled downwards (towards the abaxial surface) | |
| supervolute | Opposing left and right halves of lamina folded along longitudinal axis, with one half rolled completely within the other |
Latin descriptions
The Latin word for 'leaf', folium, is neuter. In descriptions of a single leaf, the neuter singular ending of the adjective is used, e.g. folium lanceolatum 'lanceolate leaf', folium lineare 'linear leaf'. In descriptions of multiple leaves, the neuter plural is used, e.g. folia linearia 'linear leaves'. Descriptions commonly refer to the plant using the ablative singular or plural, e.g. foliis ovatis 'with ovate leaves'.[7]
See also
- Glossary of botanical terms
- Glossary of plant morphology
- Cladophylls are leaf-like petioles
- Leaf size
- Sinus
- Leaflet (botany) and Rachis
- Petiole (botany) and Plant stem
- Phylloclades are flattened stems that resemble leaves
- Pinnation
- Plant morphology
- Taxonomy
References
- ↑ Radford, A.E.; Dickison, W.C.; Massey, J.R.; Bell, C.R. (1976). "Phytography - Morphological Evidence". Vascular Plant Systematics. Harper and Row, New York. http://www.ibiblio.org/botnet/glossary/.
- ↑ Index of Garden Plants, Mark Griffiths, Timber Press, 1992
- ↑ Mucronate , Answers.com, from Roget's Thesaurus.
- ↑ "palmate (adj. palmately)". GardenWeb Glossary of Botanical Terms. iVillage GardenWeb. 2006. http://glossary.gardenweb.com/glossary/palmate.html.
- ↑ Nelson, Randal C. (2009). "Leaf description glossary". https://www.cs.rochester.edu/~nelson/wildflowers/glossaries/leaves/index.html#lobed.
- ↑ "Pedate leaf". http://dictionary.reference.com/browse/pedate+leaf.
- ↑ Stearn (2004), pp. 439–440.
Bibliography
- Stearn, W.T. (2004). Botanical Latin (4th (p/b) ed.). Portland, Oregon: Timber Press. ISBN 978-0-7153-1643-6.
- "Leaves". http://www.ibiblio.org/botnet/glossary/a_v.html., in (Massey Murphy)
- "Shapes". http://www.ibiblio.org/botnet/glossary/b_iii.html., in (Massey Murphy)
- Massey, Jimmy R.; Murphy, James C. (1996). "Vascular plant systematics". University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. http://www.ibiblio.org/botnet/glossary/.
External links
- The Description of Leaves, University of Rochester
- Fairchild Tropical Botanic Garden
- Vplants
- Botany 115
- The seed site
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Category:Leaf margins. |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Category:Leaf diagrams. |
 |