Biology:Caryosyntrips
| Caryosyntrips | |
|---|---|
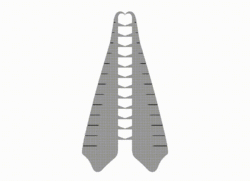
| |
| Frontal appendages of Caryosyntrips | |

| |
| Speculative life restoration as a radiodont | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Stem group: | Arthropoda |
| Genus: | †Caryosyntrips Daley & Budd, 2010 |
| Type species | |
| Caryosyntrips serratus Daley & Budd, 2010
| |
| species | |
Caryosyntrips ("nutcracker") is an extinct genus of stem-arthropod which known from Canada , United States and Spain during the middle Cambrian.[1]
Description

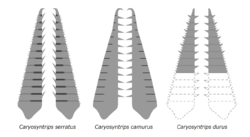
Caryosyntrips was first named by Allison C. Daley, Graham E. Budd in 2010 and the type species is Caryosyntrips serratus.[3] Multiple species had been recovered from the Burgess Shale Formation, Canada, Wheeler Shale and Marjum Formation, United States, and Valdemiedes Formation, Spain.[1][4] The latter contain a large specimen, which was initially misidentified as a body remain of lobopodian ("Mureropodia apae").[5][1][6][2]
Caryosyntrips is known only from its 14-segmented frontal appendages, which resemble nutcrackers, with the endite (ventral spine)-bearing margin facing each other. the bell-shaped bases might represent movable articulations with the animal's head. Details of endites, terminal spines, segmental boundaries and outer margins differ between species.[1] Other structures remain unknown, although a specimen with paired appendages possibly contain other fragmental head sclerites as well.[3][4]
Caryosyntrips is thought to have used their frontal appendages in a scissor-like grasping or slicing motion, and were probably durophagous, feeding on hard-shelled organisms.[1]
Taxonomic affinities
As of 2010s, Caryosyntrips was long considered to be a basal radiodont of uncertain position, usually resolved in a polytomy between euarthropod and radiodont branches.[7][8][9][2][10][11] however more recent papers have found that it may sit outside of the monophyletic Radiodonta all together.[11][12] Due to the unusual morphology of the frontal appendages and the limited extent of known remains, its position within the arthropod stem-group remains uncertain.[1][12]
| Panarthropoda |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
See also
- Cucumericrus, another stem-arthropod with similar uncertainties.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Stephen Pates; Allison C. Daley (2017). "Caryosyntrips: a radiodontan from the Cambrian of Spain, USA and Canada". Papers in Palaeontology 3 (3): 461–470. doi:10.1002/spp2.1084. Bibcode: 2017PPal....3..461P. http://osf.io/5avkg/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Pates, Stephen (2018-09-14). "New suspension-feeding radiodont suggests evolution of microplanktivory in Cambrian macronekton" (in en). Nature Communications 9 (1): 3774. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06229-7. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 30218075. Bibcode: 2018NatCo...9.3774L.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Allison C. Daley, Graham E. Budd (2010). "New anomalocaridid appendages from the Burgess Shale, Canada". Palaeontology 53 (4): 721–738. doi:10.1111/j.1475-4983.2010.00955.x. Bibcode: 2010Palgy..53..721D.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Pates, Stephen; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Daley, Allison C.; Kier, Carlo; Bonino, Enrico; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2021-01-19). "The diverse radiodont fauna from the Marjum Formation of Utah, USA (Cambrian: Drumian)" (in en). PeerJ 9: e10509. doi:10.7717/peerj.10509. ISSN 2167-8359. PMID 33552709.
- ↑ Gámez Vintaned, José Antonio; Liñán, Eladio; Yu. Zhuravlev, Andrey (2011), Pontarotti, Pierre, ed., "A New Early Cambrian Lobopod-Bearing Animal (Murero, Spain) and the Problem of the Ecdysozoan Early Diversification" (in en), Evolutionary Biology – Concepts, Biodiversity, Macroevolution and Genome Evolution (Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer): pp. 193–219, doi:10.1007/978-3-642-20763-1_12, ISBN 978-3-642-20763-1, https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-20763-1_12, retrieved 2024-01-05
- ↑ Pates, Stephen; Daley, Allison; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2018). "Response to Comment on "Aysheaia prolata from the Utah Wheeler Formation (Drumian, Cambrian) is a frontal appendage of the radiodontan Stanleycaris" with the formal description of Stanleycaris" (in en). Acta Palaeontologica Polonica 63. doi:10.4202/app.00443.2017. ISSN 0567-7920. https://doi.org/10.4202/app.00443.2017.
- ↑ Jakob Vinther; Martin Stein; Nicholas R. Longrich; David A. T. Harper (2014). "A suspension-feeding anomalocarid from the Early Cambrian". Nature 507 (7493): 496–499. doi:10.1038/nature13010. PMID 24670770. Bibcode: 2014Natur.507..496V. http://dro.dur.ac.uk/21270/1/21270.pdf.
- ↑ Cong, Peiyun; Ma, Xiaoya; Hou, Xianguang; Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Strausfeld, Nicholas J. (September 2014). "Brain structure resolves the segmental affinity of anomalocaridid appendages" (in en). Nature 513 (7519): 538–542. doi:10.1038/nature13486. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 25043032. Bibcode: 2014Natur.513..538C. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature13486.
- ↑ Van Roy, Peter; Daley, Allison C.; Briggs, Derek E. G. (June 2015). "Anomalocaridid trunk limb homology revealed by a giant filter-feeder with paired flaps" (in en). Nature 522 (7554): 77–80. doi:10.1038/nature14256. ISSN 1476-4687. PMID 25762145. Bibcode: 2015Natur.522...77V. https://www.nature.com/articles/nature14256.
- ↑ Liu, Jianni; Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Steiner, Michael; Dunlop, Jason A; Shu, Degan; Paterson, John R (2018-06-01). "Origin of raptorial feeding in juvenile euarthropods revealed by a Cambrian radiodontan". National Science Review 5 (6): 863–869. doi:10.1093/nsr/nwy057. ISSN 2095-5138. https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwy057.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Moysiuk, J.; Caron, J.-B. (2019-08-14). "A new hurdiid radiodont from the Burgess Shale evinces the exploitation of Cambrian infaunal food sources" (in en). Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 286 (1908): 20191079. doi:10.1098/rspb.2019.1079. ISSN 0962-8452. PMID 31362637.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 McCall, Christian (13 December 2023). "A large pelagic lobopodian from the Cambrian Pioche Shale of Nevada". Journal of Paleontology: 1–16. doi:10.1017/jpa.2023.63. https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-paleontology/article/abs/large-pelagic-lobopodian-from-the-cambrian-pioche-shale-of-nevada/11B0704C49A7730AA3E8F46EB2CA1C95?utm_campaign=shareaholic&utm_medium=copy_link&utm_source=bookmark#article. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
External links
- "Caryosyntrips serratus". Burgess Shale Fossil Gallery. Virtual Museum of Canada. 2011. https://burgess-shale.rom.on.ca/fossils/caryosyntrips-serratus/.
Wikidata ☰ {{{from}}} entry
 |