Biology:Symphyotrichum subulatum
| Symphyotrichum subulatum | |
|---|---|

| |
| Symphyotrichum subulatum var. subulatum | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Asterids |
| Order: | Asterales |
| Family: | Asteraceae |
| Tribe: | Astereae |
| Subtribe: | Symphyotrichinae |
| Genus: | Symphyotrichum |
| Subgenus: | Symphyotrichum subg. Astropolium |
| Species: | S. subulatum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Symphyotrichum subulatum | |
| Varieties[3] | |
|
List
| |
| |
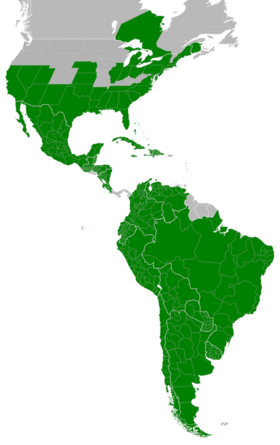
| Combined native distribution[3] | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Basionym
Varieties
| |
Symphyotrichum subulatum (formerly Aster subulatus), commonly known as eastern annual saltmarsh aster or, in Britain and Ireland where it is naturalized, annual saltmarsh aster,[7] is an annual plant in the family Asteraceae native to the eastern United States and the Gulf Coast to Texas .[8] The species grows primarily in coastal salt marshes, although in the Ozarks it occurs as a non-marine weedy variety.[9]
Description
Symphyotrichum subulatum is an annual forb that possesses a single erect stem that can reach up to 1 meter (3 feet 3 inches) in height. The stem, along with its thin green to dark green leaves, are both hairless. The sheathing base-blades of the leaves are ovulate, and the margins are entire.[10]
The top of the stem extends into a raceme inflorescence. The heads open up into bright yellow disc florets that are surrounded by ray florets that vary in color from white to lavender.[11]
Taxonomy
The species' full scientific name is Symphyotrichum subulatum (Michx.) G.L.Nesom. (As of December 2021), three varieties of S. subulatum were accepted by Plants of the World Online (POWO), with S. subulatum var. subulatum as the autonym:[3]
- S. subulatum var. subulatum[4]
- S. subulatum var. elongatum (Boss. ex A.G.Jones & Lowry) S.D.Sundb.[5]
- S. subulatum var. squamatum (Spreng.) S.D.Sundb.[6]
The varieties S. subulatum var. ligulatum (Shinners) S.D.Sundb. and S. s. var. parviflorum (Nees) S.D.Sundb., (As of December 2021), are accepted at the species level by POWO as Symphyotrichum divaricatum (Nutt.) G.L.Nesom[12] and Symphyotrichum expansum (Poepp. ex Spreng.) G.L.Nesom,[13] respectively. (As of December 2021), S. s. var. parviflorum (Nees) S.D.Sundb. is accepted at the species level by Catalogue of Life (COL) as Symphyotrichum parviflorum.[14]
Distribution and habitat
Symphyotrichum subulatum is a terrestrial species that will typically grow among grasses of any kind.[10] It is found in salt marshes, pond margins, sloughs, swamps, crop field margins, lawns, and roadsides. It is thought to be especially prevalent in these areas because of a tolerance to saline soils and mowing.[15] It is native to the eastern and Gulf Coast areas of the United States. It is also common across Mexico, the West Indies, Bermuda, Central America, and South America, depending on variety.[11]
Uses
According to the Lady Bird Johnson Wildflower Center, eastern annual saltmarsh aster can be planted to attract butterflies and has value for native bees.[16]
Citations
- ↑ NatureServe 2021.
- ↑ Maiz-Tome 2016.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 POWO 2021a.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 POWO 2021d.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 POWO 2021e.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 POWO 2021f.
- ↑ BSBI 2007.
- ↑ USDA 2021.
- ↑ Gleason & Cronquist 1991.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Sharma, Bhattacharjee & Lakshminarasimhan 2012.
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 Brouillet et al. 2006.
- ↑ POWO 2021b.
- ↑ POWO 2021c.
- ↑ Hassler 2021.
- ↑ Missouri Native Plant Society 2018.
- ↑ TWC Staff 2018.
References
- Flora of North America Editorial Committee, ed. (2006), "Symphyotrichum subulatum", Flora of North America North of Mexico (FNA), 20, New York and Oxford, http://www.efloras.org/florataxon.aspx?flora_id=1&taxon_id=250049273, retrieved 7 July 2021
- Template:Cite BSBI 2007
- Manual of Vascular Plants of Northeastern United States and Adjacent Canada. Bronx, New York: New York Botanical Garden. 1991. p. 590. ISBN 0-89327-365-1.
- Hassler, M. (8 December 2021). "Symphyotrichum parviflorum (Nees) Greuter – World Plants: Synonymic Checklists of the Vascular Plants of the World". in Bánki, O.; Roskov, Y.; Döring, M. et al.. Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life, 18 December 2021. Leiden, Netherlands: Naturalis Biodiversity Center. https://www.catalogueoflife.org/data/taxon/8S8YZ. Retrieved 30 December 2021.
- Maiz-Tome, L. (2016). "Aster subulatus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (Gland, Switzerland: International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN)). doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-1.RLTS.T19035773A78457022.en. ISSN 2307-8235. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/19035773/78457022. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- "Symphyotrichum subulatum (Michx.) G.L.Nesom — Inland Saltmarsh Aster". 19 November 2018. http://www.missouriplants.com/Symphyotrichum_subulatum_page.html.
- "Symphyotrichum subulatum Annual Saltmarsh Aster". Arlington, Virginia. 2 July 2021. https://explorer.natureserve.org/Taxon/ELEMENT_GLOBAL.2.153812/Symphyotrichum_subulatum.
- POWO (2021a). "Symphyotrichum subulatum (Michx.) G.L.Nesom" (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/981909-1.
- POWO (2021b). "Symphyotrichum divaricatum (Nutt.) G.L.Nesom" (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/981800-1.
- POWO (2021c). "Symphyotrichum expansum (Poepp. ex Spreng.) G.L.Nesom" (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/981816-1.
- POWO (2021d). "Symphyotrichum subulatum var. subulatum" (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/77232740-1.
- POWO (2021e). "Symphyotrichum subulatum var. elongatum (Boss. ex A.G.Jones & Lowry) S.D.Sundb." (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/60437846-2.
- POWO (2021f). "Symphyotrichum subulatum var. squamatum (Spreng.) S.D.Sundb." (in en). Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. http://www.plantsoftheworldonline.org/taxon/60437849-2.
- Sharma, M.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Lakshminarasimhan, P. (December 2012). "Symphyotrichum subulatum (Asteraceae) — a first report of an alien weed in India". Nelumbo (Salt Lake City, Kolkata: Botanical Survey of India) 54 (December 2012): 252–254. ISSN 0976-5069. http://www.nelumbo-bsi.in/index.php/nlmbo/article/view/57445/44822. Retrieved 7 July 2021.
- "Symphyotrichum subulatum". University of Texas at Austin. 19 September 2018. https://www.wildflower.org/plants/result.php?id_plant=sysu5.
- "Symphyotrichum subulatum". Natural Resources Conservation Service PLANTS Database. USDA. 2021. https://plants.usda.gov/core/profile?symbol=SYSU5.
Wikidata ☰ {{{from}}} entry
 |






