Biology:Gowardia
| Gowardia | |
|---|---|
| |
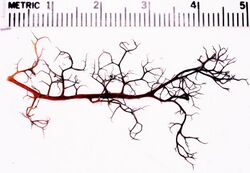
| Herbarium specimen of Gowardia nigricans collected near Meade River, Alaska | |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Fungi |
| Division: | Ascomycota |
| Class: | Lecanoromycetes |
| Order: | Lecanorales |
| Family: | Parmeliaceae |
| Genus: | Gowardia Halonen, Myllys, Velmala & Hyvärinen (2009) |
| Type species | |
| Gowardia nigricans (Ach.) Halonen et al. (2009)
| |
| Species | |
Gowardia is a genus of medium-sized, greyish hair lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. It is a circumpolar genus, mainly restricted to arctic-alpine habitats in northern Canada, Europe, and Russia.[1]
Taxonomy and naming
Gowardia was previously included within the genus Alectoria, but is now differentiated from this genus on the basis of its chemistry and colour, as well as by molecular phylogenetics.[1] Gowardia was named after Trevor Goward, a lichenologist in British Columbia, Canada, in recognition of his "remarkable and ongoing work on North American lichens".[1] This genus currently contains three species, Gowardia arctica, Gowardia nigricans,[1] and Gowardia zebrina, the last of which was described in 2020. Examination of North American herbarium specimens filed under A. nigricans suggests that there are several additional species of Gowardia that have yet to be described.[2] The species G. nigricans was previously called Alectoria nigricans (Ach.) Nyl.,[3] while G. arctica was not differentiated as a species until the creation of this genus.
Description
Gowardia are shrubby to decumbent hair lichens that are greyish to blackish in colour. They look similar to Alectoria, but Alectoria contains usnic acid, which gives it a yellowish to greenish-yellow hue, while Gowardia lacks this chemical and instead contains melanic pigments which make it greyish to blackish in colour. The pseudocyphellae of Gowardia are always white.[1]
The species of Gowardia could be confused with several other hair lichens. Bryoria nitidula looks similar but contains fumarprotocetraric acid and has dark-coloured pseudocyphellae.[1] Bryocaulon divergens is red-brown in colour instead of greyish.[1] Alectoria ochroleuca also looks similar, but contains usnic acid and always has some yellow parts to its thallus, while Gowardia does not.[4]
Habitat and Distribution
Gowardia is found in arctic and alpine tundra in northern Canada, Europe, and Russia. G. arctica grows on dry to moist tundra soil in northern regions of Canada and Russia, along the Arctic Ocean coast and islands.[1] G. nigricans has a wider distribution, and is found in arctic and alpine tundra habitat in northern and northwestern North America, as well as in northern Europe and Asia.[4] Although G. nigricans normally grows on tundra heath, it is occasionally found on low branches of trees or shrubs.[4]
Traditional use by people
Gowardia nigricans, along with A. ochroleuca, B. divergens, and B. nitidula, is called tingaujaq by the Inuit. It is known to be a favorite food of caribou, and is used by children to lure fawns close enough to touch them.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 1.7 Halonen, P. L. Myllys, S. Velmala, & H. Hyvärinen. 2009. Gowardia (Parmeliaceae)-a new alectorioid lichen genus with two species. The Bryologist 112(1): 138–146.
- ↑ Goward, Trevor; Myllys, Leena (2020). "Gowardia zebrina sp. nov., a new species in a little-known genus of arctic-alpine lichens (Parmeliaceae)". Plant and Fungal Systematics 65: 219–226. doi:10.35535/pfsyst-2020-0017.
- ↑ Alectoria and allied genera in North America. Opera Botanica. 42. Stockholm: Swedish Natural Science Research Council. 1977. pp. 1–164.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Lichens of North America. New Haven, Connecticut: Yale University Press. 2001. ISBN 0-300-08249-5.
- ↑ Wilson, M. R. 1979. Notes on ethnobotany in Inuktitut. The Western Canadian Journal of Anthropology 8(2,3,4): 180–196.
External links
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Gowardia nigricans. |
- Pictures of Gowardia nigricans from Alaska
- Picture of Gowardia nigricans from Iceland
Wikidata ☰ Q127189 entry
 |

