Philosophy:Sefirot
This article needs additional citations for verification. (July 2022) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
Sefirot (/sfɪˈroʊt, ˈsfɪroʊt/; Hebrew: סְפִירוֹת, romanized: Səfīrōt, Tiberian: Săp̄īrōṯ),[1] meaning emanations, are the 10 attributes/emanations in Kabbalah,[2] through which Ein Sof (The Infinite) reveals itself and continuously creates both the physical realm and the chain of higher metaphysical realms (Seder hishtalshelus). The term is alternatively transliterated into English as sephirot/sephiroth, singular sefirah/sephirah, etc.
Alternative configurations of the sefirot are interpreted by various schools in the historical evolution of Kabbalah, with each articulating differing spiritual aspects. The tradition of enumerating 10 is stated in the Sefer Yetzirah, "Ten sefirot of nothingness, ten and not nine, ten and not eleven". As altogether 11 sefirot are listed across the various schemes, two (Keter and Da'at) are seen as unconscious and conscious manifestations of the same principle, conserving the 10 categories.[3] The sefirot are described as channels of divine creative life force or consciousness through which the unknowable divine essence is revealed to mankind.
The first sefirah, Keter, describes the divine superconscious Will that is beyond conscious intellect. The next three sefirot (Chokhmah, Binah and Da'at) describe three levels of conscious divine intellect. In particular, Da'at represents Keter in its knowable form, the concept of knowledge. Will and knowledge are corresponding somewhat dependent opposites. The seven subsequent sefirot (Chesed, Gevurah, Tiferet, Netzach, Hod, Yesod and Malkuth) describe the primary and secondary conscious divine emotions. The sefirot of the left side and the sefira of Malkuth are feminine, as the female principle in Kabbalah describes a vessel that receives the outward male light, then inwardly nurtures and gives birth to the sefirot below them. Kabbalah sees the human soul as mirroring the divine (after Genesis 1:27, "God created man in His own image, in the image of God He created him, male and female He created them"), and more widely, all creations as reflections of their life source in the sefirot. Therefore, the sefirot also describe the spiritual life of man, break down man's psychological processes, and constitute the conceptual paradigm in Kabbalah for understanding everything. This relationship between the soul of man and the divine gives Kabbalah one of its two central metaphors in describing divinity, alongside the other Ohr (light) metaphor. However, Kabbalah repeatedly stresses the need to avoid all corporeal interpretation. Through this, the sefirot are related to the structure of the body and are reformed into partzufim (personas). Underlying the structural purpose of each sefirah is a hidden motivational force which is understood best by comparison with a corresponding psychological state in human spiritual experience.[3]
In Hasidic philosophy, which has sought to internalise the experience of Jewish mysticism into daily inspiration (devekut), this inner life of the sefirot is explored, and the role they play in man's service of God in this world.
Ein Sof
The Ein Sof (lit: without end) is an important concept in Jewish Kabbalah. Generally translated as "infinity" and "endless", the Ein Sof represents the formless state of the universe before the self-materialization of God. In other words, the Ein Sof is God before he decided to become God as we now know him.[4]
The sefirot are divine emanations that come from the Ein Sof in a manner often described as a flame. The sefirot emanate from above to below. As the first Sefira is closest to Ein Sof, it is the least comprehensible to the human mind, while in turn the last is the best understood because it is closest to the material world that humanity dwells on.[4]
Ten sefirot
Sefirot (ספירות, sfirot, singular ספירה sfira), literally means "counting, enumeration", but early Kabbalists presented a number of other etymological possibilities from the same Hebrew root including: sefer ("text" - ספר), sippur ("recounting a story" - סיפור), sappir ("sapphire" - ספיר, "brilliance", "luminary"), sfar ("boundary" - ספר), and sofer, or safra ("scribe" - ספרא, סופר). The term sefirah thus has complex connotations within Kabbalah.[3]
The original reference to the sefirot is found in the ancient Kabbalistic text of Sefer Yetzirah, "The Book of Formation", attributed to the first Jewish patriarch, Abraham.[3] However, the names of the sefirot as given in later Kabbalah are not specified there, but rather are only identified by their attributes "forward", "backward", "right", "left", "down", "up", "light", "darkness", "good" and "evil". Further references to the sefirot, now with their later-accepted names, are elaborated on in the medieval Kabbalistic text of the Zohar, which is one of the core texts of Kabbalah.
The sefirot are 10 emanations, or illuminations of God's infinite light as it manifests in creation. As revelations of the creator's will (רצון rɔṣon),[5] the sefirot should not be understood as 10 different "gods", but rather as 10 different channels through which the one God reveals His will. In later Jewish literature, the 10 sefirot refer either to the 10 manifestations of God; the 10 powers or faculties of the soul; or the 10 structural forces of nature.[3]
In Cordoveran Kabbalah, the forces of creation are considered as autonomous forces that evolve independently of one another. By contrast, in Lurean or Lurianic Kabbalah (the Kabbalah of Isaac Luria), the sefirot are perceived as a constellation of forces in active dialogue with one another at every stage of that evolution. Luria described the sefirot as complex and dynamically interacting entities known as partzufim, or faces, each with its own symbolically human-like persona.[3]
Keter, the Crown, is the first sefirah. It is the superconscious intermediary between God and the other, conscious sefirot. Three different levels, or "heads", are identified within Keter. In some contexts, the highest level of Keter is called "The unknowable head",[6] The second level is "the head of nothingness" (reisha d'ayin) and the third level is "the long head" (reisha d'arich). These three heads correspond to the superconscious levels of faith, pleasure and will in the soul.[3]
In its early 12th-century dissemination, Kabbalah garnered criticism from some rabbis who adhered to Jewish philosophy, for its alleged introduction of multiplicity into Jewish monotheism. The seeming plurality of the One God is a result of the spiritual evolution of God's light, which introduced a multiplicity of emanations from the one infinite divine essence. This was necessary due to the inability of mankind to exist in God's infinite presence.[7][8] God does not change; rather, it is our ability to perceive his emanations that is modified. This is stressed in Kabbalah to avoid heretical notions of any plurality in the Godhead. One parable to explain this is the difference between the Ma'Ohr ("Luminary"-divine essence) and the Ohr ("Light") he emanates, like the difference between the single body of the sun and the multiple rays of sunlight that illuminate a room.[9]
Names in Cordoveran Kabbalah
In Kabbalah, there is a direct correspondence between the Hebrew name of any spiritual or physical phenomenon and its manifestations in the mundane world. The Hebrew name represents the unique essence of the object. This reflects the belief that the universe is created through the metaphorical speech of God, as stated in the first chapter of Genesis. Kabbalah expounds on the names of the sefirot and their nuances, including their gematria (numerical values), in order to reach an understanding of these emanations of God's essence.[3][10]
In the 16th-century rational synthesis of Moses ben Jacob Cordovero (Cordoveran Kabbalah), the first complete systemisation of Kabbalah, the sefirot are listed from highest to lowest:[10]
| Category: | Sefirah: |
|---|---|
| Super-conscious | 1 Keter - "Crown" |
| Conscious intellect | 2 Chokhmah - "Wisdom"
3 Binah - "Understanding" |
| Conscious emotions | (Primary emotions:)
4 Chesed - "Kindness"
|
Man-metaphor in Kabbalah
Describing the material world below in general, and humans in particular, as created in the "image" of the world above is not restricted in Rabbinic Judaism to Kabbalah, but abounds more widely in Biblical, Midrashic, Talmudic and philosophical literature.[11] Kabbalah extends the Man-metaphor more radically to anthropomorphise particular divine manifestations on high, while repeatedly stressing the need to divest analogies from impure materialistic corporality. Classical proof texts on which it bases its approach include, "From my flesh I envisage God",[12] and the rabbinic analogy "As the soul permeates the whole body...sees but is not seen...sustains the whole body...is pure...abides in the innermost precincts...is unique in the body...does not eat and drink...no man knows where its place is...so the Holy One, Blessed is He..."[13] Together with the metaphor of light, the Man-metaphor is central in Kabbalah. Nonetheless, it too has its limitations, needs qualification, and breaks down if taken as a literal, corporeal comparison. Its limitations include the effect of the body on the soul, while the World effects no change in God; and the distinct, separate origins of the soul and the body, while in relation to God's omnipresence, especially in its acosmic Hasidic development, all creation is nullified in its source.
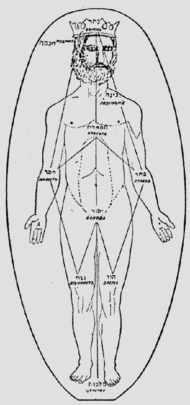
Configuration of the body
Despite the particular geometric depiction of the Yosher scheme, through each soul faculty in the body, physical human organs also reflect the supernal divine forces on high, as the scheme of Yosher underscores the inter-relationship of the sefirot as a unit or body. In this context, the physical upright standing of humans contrasts with the horizontal forms of animals. The correspondence of the sefirot with the physical organs of a human:
| Sefirah: | Organ: |
|---|---|
| Kether - Crown - כתר | Skull Encompassing crown Da'at elyon |
| Chochmah - Wisdom - חכמה | Right brain Brain |
| Binah - Understanding - בינה | Left brain Heart |
| Da'at - Knowledge - דעת | Central brain Da'at tachton |
| Chesed - Kindness - חסד | Right arm 10 fingers included |
| Gevurah - Strength - גבורה | Left arm 10 fingers included |
| Tiferet - Beauty - תפארת | Torso Front Pnimiut-Internality Back Hitzoniut-Externality |
| Netzach - Victory - נצח | Right leg 10 toes included Left kidney left testicle/ovary |
| Hod - Glory - הוד | Left leg 10 toes included Right kidney right testicle/ovary |
| Yesod - Foundation - יסוד | Sexual organ Holy covenant Female and male partzufim |
| Malkuth - Kingship - מלכות | Mouth Speech-revelation Feet |
The four worlds
These ten levels are associated with Kabbalah's four different "Worlds" or planes of existence, the main part from the perspective of the descending "chain of progression" (Seder hishtalshelut), that links the infinite divine Ein Sof with the finite, physical realm. In all Worlds, the 10 sefirot radiate, and are the divine channels through which every level is continuously created from nothing. Since they are the attributes through which the unknowable, infinite divine essence becomes revealed to the creations, all ten emanate in each World. Nonetheless, the structure of the Four Worlds arises because in each one, certain sefirot predominate. Each World is spiritual, apart from the lower aspect of the final World, which is the Asiyah Gashmi ("Physical Asiyah"), the physical Universe. Each World is progressively grosser and further removed from consciousness of the Divine.[14]
See also
References
- ↑ Khan, Geoffrey (2020). The Tiberian Pronunciation Tradition of Biblical Hebrew, Volume 1.. Open Book Publishers. ISBN 978-1783746767.
- ↑ Trachtenberg, Joshua (13 February 2004). "Glossary of Hebrew Terms". Jewish Magic and Superstition. Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press (published 2004). p. 333. ISBN 9780812218626. https://www.sacred-texts.com/jud/jms/jms43.htm. Retrieved Feb 22, 2023. "Sefirot—the ten creative attributes of God, according to the Kabbalah."
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Ginsburgh, Rabbi Yitzchak (2006). What You Need to Know about Kabbalah. Jerusalem: Gal Einai Institute. ISBN 965-7146-119.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Cohn-Sherbok, Dan. Kabbalah and Jewish Mysticism: An Introductory Anthology. One World Oxford. pp. 9.
- ↑ The Song of the Soul, Yechiel Bar-Lev, p. 73, cited on Kabbalah page.
- ↑ See the discourse "On the Essence of Chassidus", Kehot Publication Society, described on the Hasidic philosophy page. The acronym "RADLA" for this level is identified as the origin of the Torah of Hasidus.
- ↑ Ginsburgh, Rabbi Yitzchak (2007). Kabbalah and Meditation for the Nations. Canada and Israel: Gal Einai. ISBN 978-965-7146-125.
- ↑ See for example the classic passage from the Zohar beginning "Elijah opened his discourse.." that is read every Friday afternoon to prepare for the Sabbath, in the Habad Siddur "Tehillat HaShem".
- ↑ E.g., Tanya, Chapter 35
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Mystical Concepts in Chassidism by Jacob Immanuel Schochet. Kehot Publications. Chapter on the sefirot. Available separately, or printed at back of bilingual Hebrew-English edition Tanya
- ↑ Mystical Concepts in Chassidism, Jacob Immanuel Schochet, Kehot, Chaptor 1, "Anthropomorphism and Metaphors"
- ↑ Job 19:26
- ↑ Talmud Berachot 10a, Midrash Tehillim 103:4,5, Tikunei Zohar 13:28a and later Kabbalistic commentary. Cited in footnote 7, chapter 1, Mystical Concepts in Chassidism
- ↑ "Neohasid.org's Tu Bish'vat Haggadah". http://www.neohasid.org/pdf/flowchart%20haggadah%202018N.pdf.
Further reading
Early texts:
- Kaplan, Aryeh (ed. & tr.) (1995). The Bahir. Aronson. ISBN 1-56821-383-2.
- Kaplan, Aryeh (ed. & tr.) (1997). The Sefer Yetzirah: The Book of Creation. Samuel Weiser. ISBN 0-87728-855-0.
Modern guides:
- Fortune, Dion (2000). The Mystical Qabalah (Rev. ed.). Red Wheel/Weiser. ISBN 1-57863-150-5.
- Gray, William G. (1997). Qabalistic Concepts: Living the Tree. Samuel Weiser. ISBN 1-57863-000-2.
- Leitch, Aaron J. (Spring 2007). "The Decad of Creation: Sacred Geometry upon the Tree of Life". Journal of the Western Mystery Tradition 2 (13). http://www.jwmt.org/v2n13/doc.html.
Academic study:
- Schochet, Jacob Immanuel (1998). Mystical Concepts in Chassidism: An Introduction to Kabbalistic Concepts and Doctrines (3rd ed.). Kehot. ISBN 0826604129.
- Scholem, Gershom (1996). On The Kabbalah and its Symbolism. Schocken.. ISBN 0-8052-1051-2.
External links
- The Ten Sefirot: Introduction
- Kabbalah at Curlie
- Diagram of 10 Sefirot and Attributes
- Sefirotic Systems in the Sefer Yetsira, Bahir and Post-Zohar Kabbalah
 |