Medicine:Trochanter
From HandWiki
Revision as of 03:51, 17 April 2022 by imported>Steve Marsio (url)
Short description: Protrusion of the femur (bone)
| Trochanter | |
|---|---|
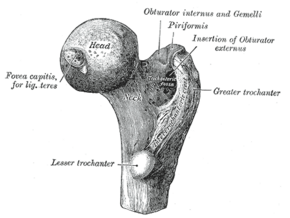 Upper part of right femur viewed from behind and above, showing greater and lesser trochanter | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Trochanter |
| Anatomical terminology | |
A trochanter is a tubercle of the femur near its joint with the hip bone. In humans and most mammals, the trochanters serve as important muscle attachment sites. Humans are known to have three trochanters, though the anatomic "normal" includes only the greater and lesser trochanters. (The third trochanter is not present in all specimens.)
Etymology
"Trokhos" (Greek) = "wheel", with reference to the spherical femoral head which was first named "trokhanter". Later usage came to include the femoral neck.[1]
Structure
In human anatomy, the trochanter is a part of the femur. It can refer to:
- Greater trochanter
- Lesser trochanter
- Third trochanter, which is occasionally present
Other animals
- Fourth trochanter, of archosaur leg bones
- Trochanter (arthropod leg), a segment of the arthropod leg
See also
- Intertrochanteric crest
- Intertrochanteric line
References
- ↑ O'Rahilly, Ronan, M.D.; Fabiola Müller, Dr. rer. nat., Stanley Carpenter, Ph.D., and Rand Swenson, D.C., M.D., Ph.D. (2004). "Etymology of Abdominal Visceral Terms". Basic Human Anatomy: A Regional Study of Human Structure. Rand Swenson, site ed.. Dartmouth Medical School. https://www.dartmouth.edu/~humananatomy/resources/etymology/Lower_limb.htm.
External links
 Media related to Trochanter at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Trochanter at Wikimedia Commons
 |

