Biology:Isopogon trilobus
| Barrel coneflower | |
|---|---|

| |
| Flower head of Isopogon trilobus | |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Order: | Proteales |
| Family: | Proteaceae |
| Genus: | Isopogon |
| Species: | I. trilobus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Isopogon trilobus | |
| |
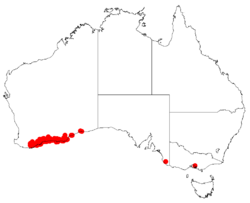
| Occurrence data from Australasian Virtual Herbarium | |
| Synonyms[1] | |
| |
Isopogon trilobus, commonly known as barrel coneflower,[2] is a species of flowering plant in the family Proteaceae and is endemic to South Coast Western Australia. It is a shrub with wedge-shaped leaves with lobed or toothed leaves, and oval, spherical or barrel-shaped heads of cream-coloured to yellow flowers.
Description
Isopogon trilobus grows as a shrub anywhere from 30 to 2 m (98.4 to 6.6 ft) in height. The new stems are pale to reddish brown, and initially covered with small fine hairs before becoming smooth. The leaves are 40–70 mm (1.6–2.8 in) long and have three to nine teeth or three to five lobes deep lobes, the teeth or lobes with a sharp point on the end. The flowers are arranged on the ends of branchlets in sessile, oval, spherical or barrel-shaped heads 25–30 mm (0.98–1.18 in) wide with hairy, broadly egg-shaped involucral bracts at the base. The flowers are silky-hairy, cream-coloured to yellow, and 8–10 mm (0.31–0.39 in) long. Flowering occurs from September to December and the fruit is a hairy oval nut, fused with others in a barrel-shaped head about 28 mm (1.1 in) in diameter.[2][3][4][5]
Taxonomy
Isopogon trilobus was first formally described in 1810 by botanist Robert Brown in Transactions of the Linnean Society.[6][7] Isopogon tripartitus R.Br., that Brown described in 1830 in the Supplementum to his Prodromus Florae Novae Hollandiae et Insulae Van Diemen,[8][9] is now considered a synonym of the older name.[1] The specific epithet (trilobus) is derived from the Latin tri- "three", and lobus "lobe", and relates to the leaves.[10] The epithet tripartitus means "divided into three parts".[11]
Distribution and habitat
Barrel coneflower is widespread from the Stirling Range east to Israelite Bay along the south coast of Western Australia where it grows on sandplains, dunes or rocky outcrops, on sandy soils, sometimes over laterite, in heathland or shrubland communities.[2]
Ecology
The colletid bee Hylaeus sanguinipictus and halictid bee Lasioglossum caesium have been recorded visiting the flowerheads of Isopogon trilobus.[12]
Use in horticulture
Sensitive to Phytophthora cinnamomi dieback,[13] I. trilobus requires excellent drainage and full sun. It will likely not tolerate humid climates. Grafting onto eastern species such as I.anethifolius or I.dawsonii could render it more adaptable to a wider climatic range.[10] Its dense habit and large fruit give it its horticultural potential.[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Isopogon trilobus". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/101547.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Isopogon trilobus". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/2240.
- ↑ "Isopogon trilobus R.Br.". Flora of Australia Online. Department of the Environment and Heritage, Australian Government. http://www.anbg.gov.au/abrs/online-resources/flora/stddisplay.xsql?pnid=44818.
- ↑ Foreman, David B.. "Isopogon trilobus". Australian Biological Resources Study, Department of Agriculture, Water and the Environment: Canberra. https://profiles.ala.org.au/opus/foa/profile/Isopogon%20trilobus.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Wrigley, John; Fagg, Murray (1991). Banksias, Waratahs and Grevilleas. Sydney: Angus & Robertson. p. 436. ISBN 0-207-17277-3.
- ↑ "Isopogon trilobus". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/529206.
- ↑ Brown, Robert (1810). "On the Proteaceae of Jussieu". Transactions of the Linnean Society 10: 72. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/757236#page/80/mode/1up.
- ↑ "Isopogon tripartitus". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/529273.
- ↑ Brown, Robert (1830). Supplementum primum prodromi florae Novae Hollandiae. London. p. 8. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/77294#page/522/mode/1up. Retrieved 29 November 2020.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Walters, Brian (November 2007). "Isopogon trilobus". Australian Native Plants Society (Australia) website. Australian Native Plants Society (Australia). http://anpsa.org.au/i-tri.html.
- ↑ Sharr, Francis Aubi; George, Alex (2019). Western Australian Plant Names and Their Meanings (3rd ed.). Kardinya, WA: Four Gables Press. p. 328. ISBN 9780958034180.
- ↑ "Plant Search Taxon: Isopogon trilobus". Bioinformatics. Melbourne: Museum Victoria. http://flyaqis.museum.vic.gov.au/cgi-bin/texhtml.
- ↑ "Western Australian natives susceptible to Phytophthora cinnamomi.". Dieback Working Group. http://www.dwg.org.au/files/Western%20Australian%20natives%20susceptible.pdf.
Wikidata ☰ Q6086251 entry
 |


