Biology:Palaeoglomus
| Palaeoglomus | |
|---|---|
| |
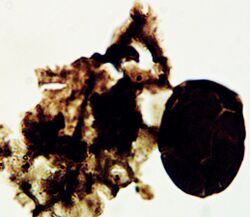
| Spore and arbuscle of Palaeoglomus strotheri, from Douglas Lake Member of Lenoir Limestone, at Douglas Dam, Tennessee[1] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | Palaeoglomus Redecker et al. (2002)[2]
|
| Type species | |
| Palaeoglomus grayi Redecker et al. (2002)
| |
Palaeoglomus ("ancient ball") is a genus of microscopic mycorrhizal fossil, found in palynological preparations of rocks which separate out organic remains by acid dissolution.
Description
Palaeoglomus has large spherical to ellipsoidal spores with multilayered walls, as well as irregularly shaped vesicles, attached to aseptate hyphae.
Species
Palaeoglomus grayi type species from the Middle Ordovician Guttenberg Formation near Platteville, Wisconsin.[2]
Palaeoglomus boullardi from the Early Devonian Rhynie Chert bear Rhynie, Scotland.[3]
Palaeoglomus strotheri from the Middle Ordovician (Darriwilian, 460 million years old) Douglas Lake Member of the Lenoir Limestone from Douglas Dam, Tennessee.[1]
Biological affinities
Palaeoglomus is similar to modern mycorrhizae such as Glomus.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Retallack, G.J. (2019). "Ordovician land plants and fungi from Douglas Dam, Tennessee". The Palaeobotanist 68: 1–33.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Redecker, D.; Kodner,R.; Graham, L.E. (2002). "Palaeoglomus grayi from the Ordovician.". Mycotaxon 84: 33–37.
- ↑ Strullu-Derrien, C.; Kenrick,P.; Pressel,S.; Duckett, J.G.; Rioult, J.P.; Strullu,D.G. (2014). "Fungal associations in Horneophyton ligneri from the Rhynie Chert (c. 407 million year old) closely resemble those in extant lower land plants: novel insights into ancestral plant–fungus symbioses". New Phytologist 203 (3): 964–9797. doi:10.1111/nph.12805. PMID 24750009.
Wikidata ☰ Q28210813 entry
 |

