Homotopy category of chain complexes
In homological algebra in mathematics, the homotopy category K(A) of chain complexes in an additive category A is a framework for working with chain homotopies and homotopy equivalences. It lies intermediate between the category of chain complexes Kom(A) of A and the derived category D(A) of A when A is abelian; unlike the former it is a triangulated category, and unlike the latter its formation does not require that A is abelian. Philosophically, while D(A) turns into isomorphisms any maps of complexes that are quasi-isomorphisms in Kom(A), K(A) does so only for those that are quasi-isomorphisms for a "good reason", namely actually having an inverse up to homotopy equivalence. Thus, K(A) is more understandable than D(A).
Definitions
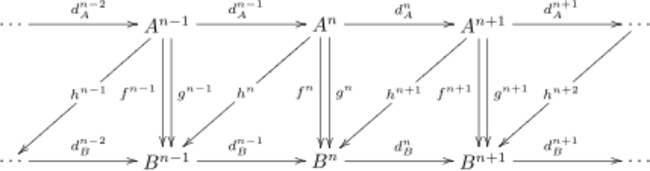
Let A be an additive category. The homotopy category K(A) is based on the following definition: if we have complexes A, B and maps f, g from A to B, a chain homotopy from f to g is a collection of maps [math]\displaystyle{ h^n \colon A^n \to B^{n - 1} }[/math] (not a map of complexes) such that
- [math]\displaystyle{ f^n - g^n = d_B^{n - 1} h^n + h^{n + 1} d_A^n, }[/math] or simply [math]\displaystyle{ f - g = d_B h + h d_A. }[/math]
This can be depicted as:
We also say that f and g are chain homotopic, or that [math]\displaystyle{ f - g }[/math] is null-homotopic or homotopic to 0. It is clear from the definition that the maps of complexes which are null-homotopic form a group under addition.
The homotopy category of chain complexes K(A) is then defined as follows: its objects are the same as the objects of Kom(A), namely chain complexes. Its morphisms are "maps of complexes modulo homotopy": that is, we define an equivalence relation
- [math]\displaystyle{ f \sim g\ }[/math] if f is homotopic to g
and define
- [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{Hom}_{K(A)}(A, B) = \operatorname{Hom}_{Kom(A)}(A,B)/\sim }[/math]
to be the quotient by this relation. It is clear that this results in an additive category if one notes that this is the same as taking the quotient by the subgroup of null-homotopic maps.
The following variants of the definition are also widely used: if one takes only bounded-below (An=0 for n<<0), bounded-above (An=0 for n>>0), or bounded (An=0 for |n|>>0) complexes instead of unbounded ones, one speaks of the bounded-below homotopy category etc. They are denoted by K+(A), K−(A) and Kb(A), respectively.
A morphism [math]\displaystyle{ f : A \rightarrow B }[/math] which is an isomorphism in K(A) is called a homotopy equivalence. In detail, this means there is another map [math]\displaystyle{ g : B \rightarrow A }[/math], such that the two compositions are homotopic to the identities: [math]\displaystyle{ f \circ g \sim Id_B }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ g \circ f \sim Id_A }[/math].
The name "homotopy" comes from the fact that homotopic maps of topological spaces induce homotopic (in the above sense) maps of singular chains.
Remarks
Two chain homotopic maps f and g induce the same maps on homology because (f − g) sends cycles to boundaries, which are zero in homology. In particular a homotopy equivalence is a quasi-isomorphism. (The converse is false in general.) This shows that there is a canonical functor [math]\displaystyle{ K(A) \rightarrow D(A) }[/math] to the derived category (if A is abelian).
The triangulated structure
The shift A[1] of a complex A is the following complex
- [math]\displaystyle{ A[1]: ... \to A^{n+1} \xrightarrow{d_{A[1]}^n} A^{n+2} \to ... }[/math] (note that [math]\displaystyle{ (A[1])^n = A^{n + 1} }[/math]),
where the differential is [math]\displaystyle{ d_{A[1]}^n := - d_A^{n+1} }[/math].
For the cone of a morphism f we take the mapping cone. There are natural maps
- [math]\displaystyle{ A \xrightarrow{f} B \to C(f) \to A[1] }[/math]
This diagram is called a triangle. The homotopy category K(A) is a triangulated category, if one defines distinguished triangles to be isomorphic (in K(A), i.e. homotopy equivalent) to the triangles above, for arbitrary A, B and f. The same is true for the bounded variants K+(A), K−(A) and Kb(A). Although triangles make sense in Kom(A) as well, that category is not triangulated with respect to these distinguished triangles; for example,
- [math]\displaystyle{ X \xrightarrow{id} X \to 0 \to }[/math]
is not distinguished since the cone of the identity map is not isomorphic to the complex 0 (however, the zero map [math]\displaystyle{ C(id) \to 0 }[/math] is a homotopy equivalence, so that this triangle is distinguished in K(A)). Furthermore, the rotation of a distinguished triangle is obviously not distinguished in Kom(A), but (less obviously) is distinguished in K(A). See the references for details.
Generalization
More generally, the homotopy category Ho(C) of a differential graded category C is defined to have the same objects as C, but morphisms are defined by [math]\displaystyle{ \operatorname{Hom}_{Ho(C)}(X, Y) = H^0 \operatorname{Hom}_C (X, Y) }[/math]. (This boils down to the homotopy of chain complexes if C is the category of complexes whose morphisms do not have to respect the differentials). If C has cones and shifts in a suitable sense, then Ho(C) is a triangulated category, too.
References
- Manin, Yuri Ivanovich; Gelfand, Sergei I. (2003), Methods of Homological Algebra, Berlin, New York: Springer-Verlag, ISBN 978-3-540-43583-9
- Weibel, Charles A. (1994). An introduction to homological algebra. Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics. 38. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-55987-4. OCLC 36131259.
 |