Astronomy:Comet Swift–Tuttle
 Perseid meteor, originating from Comet Swift-Tuttle, from the ISS | |
| Discovery | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Lewis Swift Horace Parnell Tuttle |
| Discovery date | July 16, 1862 |
| Alternative designations | 1737 N1; 1737 II; 1862 O1; 1862 III; 1992 S2; 1992 XXVIII |
| Orbital characteristics A | |
| Epoch | October 10, 1995 (JD 2450000.5) |
| Observation arc | 257 yr |
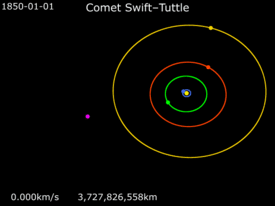
| Aphelion | 51.225 AU |
| Perihelion | 0.9595 AU |
| Semi-major axis | 26.092 AU |
| Eccentricity | 0.9632 |
| Orbital period | 133.28 yr 133y 7m (perihelion to perihelion) |
| Max. orbital speed | 42.6 km/s (26.5 mi/s)[lower-alpha 1] |
| Min. orbital speed | 0.8 km/s (0.50 mi/s) (2059-Dec-12) |
| Inclination | 113.45° |
| Earth MOID | 0.0009 AU (130,000 km; 84,000 mi) |
| Dimensions | 26 km (16 mi)[2] |
| Last perihelion | December 12, 1992[1] |
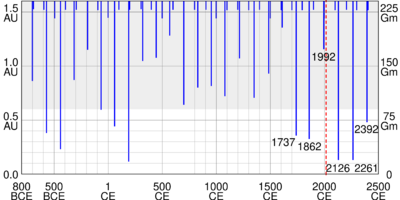
| Orbital period at different passages[1] | |||||||
| Perihelion date |
Orbital period (years) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2392-09-16 | 132.7 | ||||||
| 2261-08-10 | 134.6 | ||||||
| 2126-07-12 | 136.2 | ||||||
| 1992-12-12 | 135.0 | ||||||
| 1862-08-23 | 131.7 | ||||||
| 1737-06-15 | 127.8 | ||||||
| 1610-02-06 | 130.5 | ||||||
| 1479-10-18 | 133.4 | ||||||
| 1348-05-02 | 135.0 | ||||||
Comet Swift–Tuttle (formally designated 109P/Swift–Tuttle) is a large periodic comet with a 1995 (osculating) orbital period of 133 years that is in a 1:11 orbital resonance with Jupiter. It fits the classical definition of a Halley-type comet, which has an orbital period between 20 and 200 years.[2] The comet was independently discovered by Lewis Swift on July 16, 1862 and by Horace Parnell Tuttle on July 19, 1862.
Its nucleus is 26 km (16 mi) in diameter.[2] Swift–Tuttle is the parent body of the Perseid meteor shower, perhaps the best known shower and among the most reliable in performance.[3]
The comet made a return appearance in 1992, when it was rediscovered by Japanese astronomer Tsuruhiko Kiuchi and became visible with binoculars.[4] It was last observed in April 1995 when it was 8.6 astronomical unit|AU (1.3 billion km) from the Sun.[5] In 2126, it will be a bright naked-eye comet reaching an apparent magnitude of about 0.7.[6]
Historic observations
| Older passages[1] | |||||||
| CE/BCE | Date | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 188 CE | 188-07-10 | ||||||
| 69 BCE | –68-08-27 | ||||||
| 322 BCE | –321-09-27 | ||||||
Chinese records indicate that, in 188, the comet reached apparent magnitude 0.1.[6] Observation was also recorded in 69 BCE, and it was probably visible to the naked eye in 322 BCE.[7]
In the discovery year of 1862, the comet was as bright as Polaris.[8]
After the 1862 observations, it was thought that the comet would return between 1979 and 1983, but it didn't show up. However, it had been suggested in 1902 that this was the same comet as that observed by Ignatius Kegler on July 3, 1737,[9] and on this basis Brian Marsden calculated correctly that it would return in 1992.[7]
Orbit
The comet's perihelion is just under that of Earth, while its aphelion is just over that of Pluto. An unusual aspect of its orbit is that it was recently captured into a 1:11 orbital resonance with Jupiter; it completes one orbit for every 11 of Jupiter.[7] It was the first comet in a retrograde orbit to be found in a resonance.[7] In principle this would mean that its proper long-term average period would be 130.48 years, as it librates about the resonance. Over the short term, between epochs 1737 and 2126 the orbital period varies between 128 and 136 years.[5] However, it only entered this resonance about 1000 years ago, and will probably exit the resonance in several thousand years.[7]
Threat to Earth
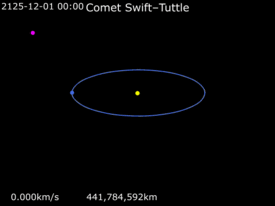
The comet is on an orbit that makes repeated close approaches to the Earth-Moon system,[7] and has an Earth-MOID (Minimum orbit intersection distance) of 0.0009 astronomical unit|AU (130,000 km; 84,000 mi).[2] Upon its September 1992 rediscovery, the comet's date of perihelion passage was off from the 1973 prediction by 17 days.[10] It was then noticed that if its next perihelion passage (July 2126) was also off by another 15 days (July 26), the comet could impact the Earth on August 14, 2126 (IAUC 5636: 1992t).[11]
Given the size of the nucleus of Swift–Tuttle, this was of some concern. This prompted amateur astronomer and writer Gary W. Kronk to search for previous apparitions of this comet. He found the comet was most likely observed by the Chinese at least twice, first in 69 BCE and later in 188 CE;[12] these two sightings were quickly confirmed by Brian Marsden and added to the list of perihelion passages at the Minor Planet Center.[5] Around 25 July 188 CE the comet passed about 0.129 astronomical unit|AU (19.3 million km) from Earth.[13]
This information and subsequent observations have led to recalculation of its orbit, which indicates the comet's orbit is sufficiently stable that there is absolutely no threat over the next two thousand years.[10] It is now known that the comet will pass 0.153 astronomical unit|AU (22.9 million km; 14.2 million mi) from Earth on August 5, 2126.[2][lower-alpha 2] and within 0.147 AU (22.0 million km; 13.7 million mi) from Earth on August 24, 2261.[13]
A close encounter with Earth is predicted for the comet's return to the inner Solar System in the year 3044, with the closest approach estimated to be one million miles (1,600,000 km; 0.011 AU).[14] Another close encounter is predicted for the year 4479, around Sept. 15; the close approach is estimated to be less than 0.05 AU, with a probability of impact of 1 in a million.[7] Subsequent to 4479, the orbital evolution of the comet is more difficult to predict; the probability of Earth impact per orbit is estimated as 2×10−8 (0.000002%).[7]
Comet Swift–Tuttle is by far the largest near-Earth object (Apollo or Aten asteroid or short-period comet) to cross Earth's orbit and make repeated close approaches to Earth.[15] With a relative velocity of 60 km/s,[16][17] an Earth impact would have an estimated energy of ~27 times that of the Cretaceous–Paleogene impactor.[18] The comet has been described as "the single most dangerous object known to humanity".[17] In 1996, the long-term possibility of Comet Swift–Tuttle impacting Earth was compared to 433 Eros and about 3000 other kilometer-sized objects of concern.[19]
| Date & time of closest approach |
Earth distance (AU) |
Sun distance (AU) |
Velocity wrt Earth (km/s) |
Velocity wrt Sun (km/s) |
Uncertainty region (3-sigma) |
Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2126-08-05 15:50 | 0.15337 astronomical unit|AU (22.944 million km; 14.257 million mi; 59.69 LD) | 1.04 AU (156 million km; 97 million mi; 400 LD) | 58.3 | 40.8 | ± 11000 km | Horizons |
See also
- Lists of comets
- List of interstellar comets
- List of comets by type
- List of non-periodic comets
- List of periodic comets
Notes
- ↑ v = 42.1219 √1/r − 0.5/a, where r is the distance from the Sun, and a is the semimajor axis.
- ↑ The 3-sigma uncertainty in the comet's closest approach to Earth on 5 August 2126 is about ±10 thousand km.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 The past and future motion of Comet P/Swift-Tuttle Orbital Elements on page 309
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 "JPL Small-Body Database Browser: 109P/Swift–Tuttle". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/tools/sbdb_lookup.html#/?sstr=109P%2FSwift-Tuttle&view=OPC.
- ↑ Bedient, John (20 June 2010). "Meteor Showers". American Meteor Society. http://www.amsmeteors.org/showers.html.
- ↑ Britt, Robert (2005-08-11). "Top 10 Perseid Meteor Shower Facts". Space.com. http://www.space.com/spacewatch/050811_perseid_facts.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedMPC - ↑ 6.0 6.1 Yau, K.; Yeomans, D.; Weissman, P. (1994). "The past and future motion of Comet P/Swift-Tuttle". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 266 (2): 305–16. doi:10.1093/mnras/266.2.305. Bibcode: 1994MNRAS.266..305Y.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 7.2 7.3 7.4 7.5 7.6 7.7 Chambers, J. E. (1995). "The long-term dynamical evolution of Comet Swift–Tuttle". Icarus (Academic Press) 114 (2): 372–386. doi:10.1006/icar.1995.1069. Bibcode: 1995Icar..114..372C.
- ↑ Levy, David H. (2008). David Levy's Guide to Observing Meteor Showers. Cambridge University Press. p. 12. ISBN 978-0-521-69691-3. https://books.google.com/books?id=jAr7HMnlPGUC&pg=PA12.
- ↑ Gary W. Kronk (1999). "109P/1737 N1". Cometography. 1. pp. 400–2.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Stephens, Sally (1993). "on Swift–Tuttle's possible collision". Astronomical Society of the Pacific. http://www.as.wvu.edu/~jel/skywatch/swfttle.html.
- ↑ Marsden, Brian G. (1992-10-15). "IAUC 5636: Periodic Comet Swift–Tuttle (1992t)". Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/05600/05636.html.
- ↑ Marsden, Brian G. (1992-12-05). "IAUC 5670: Periodic Comet Swift–Tuttle (1992t)". Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. http://www.cbat.eps.harvard.edu/iauc/05600/05670.html.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 The past and future motion of Comet P/Swift-Tuttle Close Approach Table on page 308
- ↑ "ASP: Cosmic Collisions". https://astrosociety.org/edu/publications/tnl/23/23.html.
- ↑ "JPL Small-Body Database Search Engine: q < 1 (au) and period < 200 (years)". JPL Solar System Dynamics. https://ssd.jpl.nasa.gov/sbdb_query.cgi?obj_group=all;obj_kind=all;obj_numbered=all;OBJ_field=0;ORB_field=0;combine_mode=AND;c1_group=ORB;c1_item=Bi;c1_op=%3C;c1_value=1;c2_group=ORB;c2_item=Bs;c2_op=%3C;c2_value=200;table_format=HTML;max_rows=100;format_option=comp;c_fields=AcBgBiBjBnBqBsCiCkAp;.cgifields=format_option;.cgifields=obj_kind;.cgifields=obj_group;.cgifields=obj_numbered;.cgifields=combine_mode;.cgifields=ast_orbit_class;.cgifields=table_format;.cgifields=com_orbit_class&query=1&c_sort=ApD.
- ↑ Weissman, Paul R. (August 2006), Milani, A.; Valsecchi, G.B.; Vokrouhlicky, D., eds., "The cometary impactor flux at the Earth", Proceedings of the International Astronomical Union, Near Earth Objects, our Celestial Neighbors: Opportunity and Risk; IAU Symposium No. 236 2 (s236): 441–450, doi:10.1017/S1743921307003559
- ↑ 17.0 17.1 Impact!: the threat of comets and asteroids. Oxford University Press. 1997. pp. 256 (see p. 116). ISBN 978-0-19-511919-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=4gnumbZdVqEC.
- ↑ This calculation can be carried out in the manner given by Weissman for Comet Hale–Bopp, as follows: A radius of 13.5 km and an estimated density of 0.6 g/cm3 gives a cometary mass of 6.2×1018 g. An encounter velocity of 60 km/s yields an impact velocity of 61 km/s, giving an impact energy of 1.15×1032 ergs, or 2.75×109 megatons, about 27.5 times the estimated energy of the K–T impact event.
- ↑ Browne, Malcolm W.. "Mathematicians Say Asteroid May Hit Earth in a Million Years" (in en). https://www.nytimes.com/1996/04/25/us/mathematicians-say-asteroid-may-hit-earth-in-a-million-years.html.
Bibliography
- Siegel, Ethan (2016-08-11). "The Most Dangerous Object Known To Humanity". https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2016/08/11/the-most-dangerous-object-known-to-humanity.
External links
- 109P/Swift-Tuttle at the Minor Planet Center's Database
- 109P/Swift–Tuttle at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory's Small-Body Database
- NASA Astronomy Picture of the Day: Periodic Comet Swift–Tuttle (19 February 1996)
| Numbered comets | ||
|---|---|---|
| Previous 108P/Ciffreo |
Comet Swift–Tuttle | Next 110P/Hartley |
 |