Engineering:Cable blowing machine
From HandWiki
Revision as of 15:46, 15 February 2021 by imported>WikiEditor (linkage)
This article includes a list of references, related reading or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations. (September 2015) (Learn how and when to remove this template message) |
A cable blowing machine (also known as a fiber blowing machine) is a machine designed to fit fiber optic cables into telecommunication ducts and microducts with the use of compressed air or water.
Blowing machine design
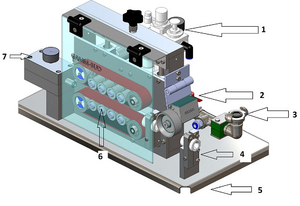
A cable blowing machine (fiber blowing machine) consists of the following components:
- a head that ensures secure fitting of the duct into which the cable will be blown and supplying the medium (air or water) to the duct. The cable inserted into the duct via the head goes through a sealing system preventing the medium from getting into the machine;
- a belt feeder that moves the cable towards the head;
- a base plate or a frame onto which the blowing machine’s subsystems are mounted;
- cable guidance, that is a system of bushes or rolls guiding the cable towards the blowing head;
- air or water connections that supply the medium securely to the blowing machine;
- a meter counter that shows the length (sometimes also the velocity) of the blown cable;
- a control unit that allows to control the speed of cable insertion and the propelling power of the feeder.
Types of blowing machines
Blowing machines are classified with regard to the diameter of the cable they can handle and the type of drive system (track feeder, roller feeder, belt feeder or blowing heads without feeders). The optical fiber cable blowing machine are of 2 types.
- Hydraulically powered
- Pneumatically powered.
The hydraulically blowing machine consists of 2 parts.
- Cable feeding unit: - This is the main component of blowing machine and it pushes the cable into the HDPE duct with the help of compressed air.
- Hydraulic Power pack: - This unit provides the power to cable feeding unit and it is because of hydraulic power pack, the cable feeding unit operates.
The commonly used is hydraulically powered one.
References
- Andrzejewski M. "Wdmuchiwarki kabli, mikrokabli i mikrorurek" Inżynieria Bezwykopowa 6/2012 [48]
- Andrzejewski M, Szeląg B. "Metody układania kabli telekomunikacyjnych w obiektach podziemnej infrastruktury miejskiej" Wydawnictwo INŻYNIERIA sp. z o.o. Kraków 2011
- Andrzejewski M. "Wdmuchiwanie światłowodów" Inżynieria Bezwykopowa 1/2008 [21]
- Andrzejewski M. "Technika wdmuchiwania mikrokabli dla potrzeb telekomunikacji"Inżynieria Bezwykopowa 2/2008 [22]
- Andrzejewski M. "Narodziny niebieskiego smoka - Blue Dragon Jet" Paliwa i Energetyka 3/2014 [10]
- "Maszyny do układania kabli" Forum Budowlane 3(214)/2014(ISSN 1425-8773) page 31
- Wolfgang Hagemann: Architecture and construction dictionary. Beuth Verlag, 2014, ISBN:978-3-410-16645-0, S. 131 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Dietrich Stein: Grabenloser Leitungsbau. John Wiley & Sons, 2003, ISBN:978-3-433-01778-4, S. 83–84 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Barry J. Elliott: Cable Engineering for Local Area Networks. Woodhead Publishing, 2000, ISBN:978-1-85573-488-3, S. 205 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- B. J. Elliott: Designing a Structured Cabling System to ISO 11801: Cross-referenced to European CENELEC and American Standards. Woodhead Publishing, 2002, ISBN:978-1-85573-612-2, S. 52 (eingeschränkte Vorschau in der Google-Buchsuche).
- Griffioen, W., "Installation of optical cables in ducts", Plumettaz, PTT Research 1993 (ISBN:90-72125-37-1)
- Griffioen, W., Nijstad, H., Grooten, A.T.M., Van Wingerden, A., Brown, G., Hawkins, D.F., Plumettaz, G., "JETnet: versatile access network solutions" Proc. ANCIT Workshop (Eurescom), Torino, 30-31 March 1998
- Griffioen, W., Van Wingerden, A., Van 't Hul, C., "Versatile outside plant solution for optical access networks", Proc. 48th IWCS, November 1999, page 152-156
- Griffioen, W., Van Wingerden, A., Van 't Hul, C., Lock, P., Van der Tuuk, A., "Innovative solutions for optical access networks", CANTO conference, Willemstad (Curaçao), 28 June - 1 July 2000
- Griffioen, W., Van Wingerden, A., Van 't Hul, C., Lock, P., Van der Tuuk, A., "Innovative solutions for access networks", Proc. 49th IWCS, November 2000, page 538-542
- Griffioen, W., Greven, W., Pothof, T. "A new fiber optic life for old ducts", Proc. 51st IWCS, November 2002, page 244-250
- Griffioen, W., Greven, W., Pothof, T, "Upgrading old ducts for new optical connections", ITG Factagung "Kommunikationskabelnetze", 10-11 December 2002, Köln, Germany
- Griffioen, W., Van Wingerden, A., Van 't Hul, C., Keijzer, M., "Microduct cabling: Fiber to the Home", Proc 52nd IWCS, November 2003, page 431-437
- Erkan GOK, Equipments:, "How to use fiber optic cable blowing machines: Fttx", , November 2016, Web: Fttx User Manual.
 |