Engineering:Image Share
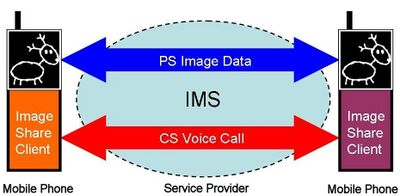
Image Share is a service for sharing images between users during a mobile phone call. It has been specified for use in a 3GPP-compliant cellular network by the GSM Association in the PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification.[1]
According to the specification, "The terminal interoperable Image Share service allows users to share Images between them over PS connection with ongoing CS call, thus enhancing and enriching end-users voice communication."
An Image Share session begins by end-users setting up a normal circuit switched (CS) voice call. After the voice call is set up, terminals perform a registration to an IMS core system with a packet switched (PS) connection. Then based on successful capability negotiation between the terminals, the end-user will be presented with an option in terminal UI offering the possibility of sharing one or several images. If this is selected, then these images are transferred between the Image Share software clients located in the mobile phones using the PS connection and the recipient is able to see the images. During this process the normal CS voice session has been ongoing continuously.
Image Share can be seen as a kind of spin-off from the Video Share mobile phone service. Video Share is commercially launched for example by AT&T in USA, but Image Share is not yet available from any mobile operator/service provider.
Technical features
- Interoperable multi-vendor compliant service, i.e. Image Share works across different mobile phones from various vendors (as long as they have the necessary software client installed)
- IMS service, i.e. 3GPP compliant IMS core system required for the service provider/operator offering Image Share
- CSI (CS and IMS combinational) service compliant to 3GPP specifications TS 22.279, TS 23.279 and TS 24.279, i.e. CS voice call set up required prior to sharing the images
- SIP used for signaling via IMS, i.e. registration for the service is performed using the capabilities offered by IMS platform with SIP protocol
- MSRP (Message Session Relay Protocol, RFC 4975) used for transporting media between the mobile phones
- IETF File transfer mechanisms [2] utilized for negotiating shared images between offerer and answerer via SIP/SDP offer/answer model
- Capability query performed using SIP OPTIONS method between the mobile phones to find out whether the recipient is Image Share capable
- Peer-to-peer service, i.e. no server required in the network for sharing the images
- Both live and pre-stored images can be shared between the participating mobile phones
- Requires 3G or EDGE DTM (Dual Transfer Mode) mobile network
Usage
According to GSMA press release [3] interoperability between different Image Share clients was successfully tested in a multi-vendor trial in May 2007, including interworking between multiple networks.
No mobile operator has launched Image Share so far (as of March 2008).
See also
- Video Share, which (re)uses similar basic architecture
- IM, especially OMA SIMPLE IM [4] which also utilizes MSRP for transporting media
- MMS, which also provides the means for users to exchange images between mobile phones
- Multiple different file/image sharing applications & services available from various companies
References
- GSM Association PRD IR.79 Image Share Interoperability Specification [5]
- IETF RFC 4975 Message Session Relay Protocol
- 3GPP TS 22.279 Combinied Circuit Switched (CS) and IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) sessions; Stage 1
- 3GPP TS 23.279 Combining Circuit Switched (CS) and IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) services; Stage 2
- 3GPP TS 24.279 Combining Circuit Switched (CS) and IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS) services; Stage 3

