Engineering:Warsaw rectifier
From HandWiki
Short description: AC to DC conversion circuit
The Warsaw rectifier is a pulse-width modulation (PWM) rectifier, invented by Włodzimierz Koczara in 1992. [1] [2]
Features
The Warsaw Rectifier provides following features:
- Unity power factor [3]
- Three-wire input, does not require connection to the neutral wire
- Ohmic behaviour
- Controlled output voltage
- Simple control scheme
- Low power losses
Unique features of the Warsaw Rectifier:
- Short circuits do not cause current flow through switches
- No cross short circuit of switches possible
- Dead time not required
Topology
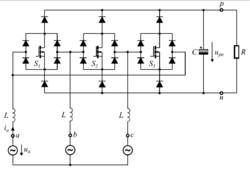
Warsaw Rectifier is a unidirectional, three-phase, three-switch two-level PWM rectifier. This topology uses three transistors and eighteen diodes. The bidirectional switches (made as four diodes and one transistor circuit) are connected in a delta topology. The rectifier output does not require a divided DC-link circuit as in the Vienna Rectifier topology.[4][5]
See also
References
- ↑ Koczara W., "Controlled Rectifier", Polish Patent PL 167855, Apr. 17, 1992.
- ↑ Koczara W., "Unity factor three phase rectifier", Power Quality ’92 Conference Europe, Münich, October 1992, 79–88, 14–15.
- ↑ Koczara W., Bialoskorki P., "Unity power factor three phase rectifiers" Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1993. PESC '93 Record., 24th Annual IEEE at [1]
- ↑ D. Carlton, W.G. Dunford, M. Edmunds, “Continuous conduction mode operation of a three-phase power-factor correction circuit with quasi tri-directional switches” Power Electronics Specialists Conference, 1999. PESC 99. 30th Annual IEEE [2]
- ↑ Bałkowiec T., “Three Phase Warsaw Boost Rectifier for High Power Variable Speed Power Generation” Prace Naukowe Instytutu Maszyn, Napędów i Pomiarów Elektrycznych Politechniki Wrocławskiej, Nr 71, 2015 at http://www.imnipe.pwr.wroc.pl
 |