Engineering:Zlín Z-50
| Zlin Z-50 | |
|---|---|

| |
| Z-50LX flown by The Flying Bulls Aerobatics Team | |
| Role | aerobatic aircraft |
| Manufacturer | Zlin Aircraft |
| First flight | 18 July 1975 |
| Introduction | 1975 |
The Zlin Z-50 is an aerobatic sports airplane built by the Czechoslovakian company Zlin Aircraft.
History
In the autumn of 1973 Zlín Aircraft decided to develop a new single seat aerobatic airplane. The design team was headed by Jan Mikula, a noted Czech designer. During the design phase, computer optimization was used to achieve the desired aerodynamic characteristics. The principal goal was to determine the optimum engine and propeller combination for this aircraft. Designers settled on the Lycoming AIO-540 D4B5 horizontally-opposed six-cylinder piston engine, rated at 194 kW (260 hp), driving a three-blade Hoffmann constant speed propeller.
The prototype Zlín Z-50L (L for its Lycoming engine), with civil registration OK-070, first flew 18 months after the start of design work, on 18 July 1975.[1][2] The first flights were successful.
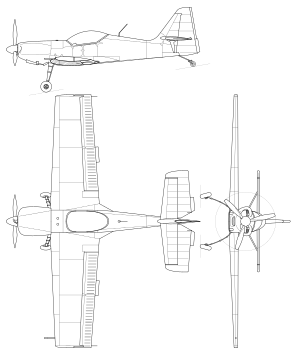
The Z-50L is a cantilever low-winged single-engined monoplane with a fixed tailwheel undercarriage. Unlike the Zlín Z 26 series which it replaced, the Z-50 was of all-metal construction, with limit maneuvering load factors of +9.0 and -6.0.[2] It does not incorporate landing flaps; in their place, two-section ailerons extend the full wingspan, providing an exceptional rate of roll. The designers made ample provision for trimming: automatic trim tabs are used on the inboard aileron sections; on one of the elevators and on the fabric-covered rudder; one outboard aileron has a ground-adjustable trim tab; the elevator has a trim tab which can be adjusted in-flight. The standard fuel capacity can be supplemented by wingtip auxiliary tanks for ferry flights. The full-vision bubble canopy can be jettisoned in-flight if necessary.[3]
The Zlín Z-50 made its competition debut at the 1976 World Aerobatic Championships, being flown by both the Czechoslovak and Polish teams, with a Czechoslovak Z-50 finishing in third place (behind two Soviet-flown Yakovlev Yak-50s), while the Czechoslovak team finished in second place in the team competition.[4] In the 1978 championships, the Zlín was more successful, with Czech-flown Z-50s finishing first and third in the individual competition, and a German-flown Zlín finishing fourth, with the Czechoslovak team winning the team competition.[5] Zlín Z-50s finished fourth in the 1980 championship,[6] and third in the 1982 competition.[7]
The Zlin Z-50LS, with a more powerful Lycoming AEIO-540 L1B5D engine of 224 kW (300 HP), was first flown by Zdenek Polasek on 29 July 1981. The more powerful engine enhanced vertical maneuvers. The Zlin Z-50LS can fly at 760 kg gross weight in the aerobatic category (+8g to –6g). Many Z-50L and LA versions were rebuilt to Z-50LS standard in the early 1980s.
A Z-50LS won the World Aerobatic Championships in 1984 and 1986,[8] but the debut of the Sukhoi Su-26 in the 1986 eventually edged out the Zlin from world-class competition.[9]
Another version derived from the Zlin Z-50 aircraft is a "baby fifty" – Z-50M with a LOM M137AZ engine of 134 kW (180 HP). This was introduced as a replacement for the Z-526, which was often converted to N (normal) category and used as a glider tug at aero clubs. The Z-50M has limit maneuvering load factors of +7 and -5,5. Only five Z-50M aircraft were built.
In April 1990 a Z-50LS received modified wings and was evaluated to determine if maneuvrability was improved. The plane was designated Z-50LE (Experimental). This unit remained as a prototype and is currently in Moravska Trebova, at the Czech air school.
The last version of Zlin 50 is the Z-50LX, which first flew in 1991, piloted by Zlin chief pilot Vladmir Peroutka. This version received additional fuel tanks in the wings and a robust smoke system for airshow routines; it was produced principally at the urging of show pilot Victor Norman. From 1992 to 1995 seven Z-50LX were built, and four of them are used by the Red Bull Flying Bulls Aerobatics Team led by Radka Máchová.
Z-50LS are still in use; the Polish Aerobatic Team Zelazny uses 3 of them.
Variants
- Z-50L
- First production variant with a Lycoming AEIO-540-D4B5 engine, certified in 1977, conversion to 50LA and 50LS variants, 25 built. (0001-0025)
- Z-50LA
- Variant certified in 1980, five built and 18 conversions from Z-50L.
- Z-50LS
- Variant certified in 1982 with a Lycoming AEIO-540-L1B5D engine, 34 built and 18 converted from Z-50, one aircraft was rebuilt as a Z-50M and two as Z-50LX.
- Z-50LX
- Variant certified in 1991 with a Lycoming AEIO-540-L1B5D engine, nine built with two converted from Z-50LS, two were rebuilt as Z-50LS.
- Z-50M
- Variant certified in 1989 with a LOM M 137 AZ engine, six built and one conversion.
Specifications (Z-50L)
Data from Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1976–77[2]
General characteristics
- Crew: 1
- Length: 6.62 m (21 ft 9 in) (tail down)
- Wingspan: 8.58 m (28 ft 2 in)
- Height: 1.86 m (6 ft 1 in)
- Wing area: 12.50 m2 (134.5 sq ft)
- Aspect ratio: 5.88:1
- Airfoil: NACA0018 at tip, NACA 0012 at tip
- Empty weight: 570 kg (1,257 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 720 kg (1,587 lb)
- Fuel capacity: 60 L (16 US gal; 13 imp gal) normal, provision for additional 100 L (26 US gal; 22 imp gal) in wingtip tanks for ferry flights
- Powerplant: 1 × Lycoming AEIO-540-D4B5 air-cooled flat-six engine, 190 kW (260 hp)
- Propellers: 3-bladed Hoffmann HO-V123/K/200AH constant-speed propeller
Performance
- Maximum speed: 293 km/h (182 mph, 158 kn) at 500 m (1,640 ft)
- Cruise speed: 240 km/h (150 mph, 130 kn) at 500 m (1,640 ft) (econ. cruise)
- Range: 640 km (400 mi, 350 nmi) (with wingtip tanks)
- Service ceiling: 6,000 m (20,000 ft)
- g limits: +9, -6
- Rate of climb: 12 m/s (2,400 ft/min)
- Takeoff distance to 15 m (50 ft): 220 m (720 ft)
- Landing distance from 15 m (50 ft): 500 m (1,640 ft)
References
- ↑ Flight International 9 October 1975, p. 540.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Taylor 1976, p. 33.
- ↑ Mondey, p. 248
- ↑ Smith Flight International 21 August 1976, pp. 437–438.
- ↑ Frazer Flight International 23 September 1978, pp. 1156–1157.
- ↑ Firth Flight International 20 September 1980, p. 1183.
- ↑ Flight International 11 September 1982, p. 776.
- ↑ Postlethwaite Flight International 2 July 1988, p. 34.
- ↑ Postlethwaite Flight International 2 July 1988, pp. 34–35.
- Firth, John. US wins world aerobatics". Flight International, 20 September 1980. p. 1183
- Frazer, Jeanne. "Czechs are world aerobatic champions". Flight International, 23 September 1978. pp. 1156–7
- Mondey, David. Encyclopedia of The World's Commercial and Private Aircraft, Zlin Z 50 L (p. 248). Crescent Books, New York NY (1981)
- Postlethwaite, Alan. "Czech flights". Flight International, 2 July 1988. pp. 33–6
- "Private Flight: New competition Zlin". Flight International, 9 October 1975. p. 540
- "Private Flight:Record entry in world aerobatics — USSR wins". Flight International, 11 September 1982. pp. 776–7
- Smith, Tony. "Lots of torque at Kiev". Flight International, 21 August 1976. pp. 437–440
- Taylor, John W. R. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1976–77. London:Jane's Yearbooks, 1976. ISBN:0-354-00538-3
External links
- Moravan Aeroplanes, Inc., The Czech Republic - manufacturer
- Zlin Z-50 Homepage - fan pages
- Zlín Z-50 in photos
 |