Finance:Sacrifice zone
A sacrifice zone or sacrifice area (often termed a national sacrifice zone or national sacrifice area) is a geographic area that has been permanently changed by heavy environmental alterations (often to a negative degree) or economic disinvestment, often through locally unwanted land use (LULU). Commentators including Chris Hedges, Joe Sacco, and Steve Lerner have argued that corporate business practices contribute to producing sacrifice zones.[1][2][3] A 2022 report by the United Nations highlighted that millions of people globally are in pollution sacrifice zones, particularly in zones used for heavy industry and mining.[4]
Definition
A sacrifice zone or sacrifice area is a geographic area that has been permanently impaired by environmental damage or economic disinvestment.[5]
Another definition states that sacrifice zones are places damaged through locally unwanted land use causing "chemical pollution where residents live immediately adjacent to heavily polluted industries or military bases."[1]
Etymology
According to Helen Huntington Smith,[6] the term was first used in the U.S. discussing the long-term effects of strip-mining coal in the American West in the 1970s. The National Academy of Sciences/National Academy of Engineering Study Committee on the Potential for Rehabilitating Lands Surface Mined for Coal in the Western United States produced a 1973 report that introduced the term, finding:
In each zone the probability of rehabilitating an area depends upon the land use objectives, the characteristics of the site, the technology available, and the skill with which this technology is applied. At the extremes, if surface mined lands are declared national sacrifice areas, all ecological zones have a high probability of being successfully rehabilitated. If, however, complete restoration is the objective, rehabilitation in each zone has no probability of success.[7]
Similarly in 1975, Genevieve Atwood wrote in Scientific American:
Surface mining without reclamation removes the land forever from productive use; such land can best be classified as a national sacrifice area. With successful reclamation, however, surface mining can become just one of a series of land uses that merely interrupt a current use and then return the land to an equivalent potential productivity or an even higher one.[8]
Huntington Smith wrote in 1975, "The Panel that issued the cautious and scholarly National Academy of Sciences report unwitting touched off a verbal bombshell" with the phrase National Sacrifice Area; "The words exploded in the Western press overnight. Seized upon by a people who felt themselves being served up as 'national sacrifices,' they became a watchword and a rallying cry."[6] The term sparked public debate, including among environmentalists and politicians such as future Colorado governor Richard Lamm.[9][10]
The term continued to be used in the context of strip mining until at least 1999: "West Virginia has become an environmental sacrifice zone".[11]
Use of the term
Chile
Reportedly, in 2011 Terram introduced the term sacrifice zone to the Chilean political discourse.[12]
The Chilean port of Quintero and adjacent Puchuncaví have been pointed out as a sacrifice zone.[12] The zone hosts the coal-fired Ventanas Power Plant, an oil refinery, a cement storage, Fundición Ventanas, a copper foundry and refinery, a lubricant factory and a chemical terminal.[12] In total 15 polluting companies operate in the area.[13] In 2011, Escuela La Greda located in Puchuncaví, was engulfed in a chemical cloud from the Ventanas Industrial Complex. The sulfur cloud poisoned an estimated 33 children and 9 teachers, resulting in the relocation of the school. The old location of the school is now abandoned.[14] In August and September 2018 there was a public health crisis in Quintero and Puchuncaví, where over 300 people experienced illness from toxic substances in the air, coming from the polluting industries.[15]
United States
The US EPA affirmed in a 2004 report in response to the Office of Inspector General, that "the solution to unequal protection lies in the realm of environmental justice for all Americans. No community, rich or poor, black or white, should be allowed to become a 'sacrifice zone'."[16]:28
Commentators including Chris Hedges,[2] Joe Sacco, Robert Bullard[1] and Stephen Lerner have argued that corporate business practices contribute to producing sacrifice zones and that these zones most commonly exist in low-income and minority, usually African-American communities.[17] Sacrifice zones are a central topic for the graphic novel Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt, written by Hedges and illustrated by Sacco.[3]
In 2012, Hedges stated that examples of sacrifice zones included Pine Ridge, South Dakota and Camden, New Jersey[2] In 2017 a West Calumet public housing project in East Chicago, Indiana built at the former site of a lead smelter needed to be demolished and soil replaced to bring the area up to residential standards, displacing 1000 residents.[18] In 2014, Naomi Klein wrote that "running an economy on energy sources that release poisons as an unavoidable part of their extraction and refining has always required sacrifice zones."[19]
Space industry
The human-environment interactions that lie at the heart of environmental justice, including sacrifice zones, have been proposed to also include the environmental sacrifice of regions beyond Earth.[20] Klinger states that "the environmental geopolitics of Earth and outer space are inextricably linked by the spatial politics of privilege and sacrifice - among people, places and institutions".[20] Dunnett has called outer space the 'ultimate sacrifice zone' that exemplifies a colonially framed pursuit of infinite opportunities for accumulation, exploitation, and pollution. This manifests in both terrestrial and space-based sacrifice zones related to launch infrastructure, waste, and orbital debris.[21]
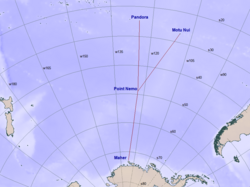
Point Nemo is an oceanic point of inaccessibility located inside the South Pacific Gyre. It is selected as the most remote location in the world and serves as a "spacecraft cemetery" for space infrastructure and vessels.[22] Since 1971, 273 spacecraft and satellites have been directed to Point Nemo; this number includes the Mir Space Station (142 tonnes) and will include the International Space Station (240 tonnes).
See also
- Agroextractivism
- Chernobyl disaster
- Ecocide
- Environmental dumping
- Environmental justice
- Environmental racism
- Eutrophication
- Exclusion zone
- Global environmental inequality
- Global waste trade
- Pollution is Colonialism
- Toxic colonialism
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Bullard, Robert D. (June 2011). "Sacrifice Zones: The Front Lines of Toxic Chemical Exposure in the United States by Steve Lerner . Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2010. 346 pp., $29.95 ISBN: 978-0-262-01440-3". Environmental Health Perspectives 119 (6): A266. doi:10.1289/ehp.119-a266. ISSN 0091-6765. PMC 3114843. https://archive.org/details/sacrificezonesfr00stev.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Kane, Muriel (2012-07-20). "Chris Hedges: America's devastated 'sacrifice zones' are the future for all of us". https://www.rawstory.com/2012/07/chris-hedges-americas-sacrifice-zones-being-destroyed-for-profit/.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Neal Conan (2 August 2012). "Drive For Profit Wreaks 'Days Of Destruction'". https://www.npr.org/2012/08/02/157813661/drive-for-profit-wreaks-days-of-destruction.
- ↑ "Millions suffering in deadly pollution 'sacrifice zones', warns UN expert". 2022-03-10. https://www.theguardian.com/environment/2022/mar/10/millions-suffering-in-deadly-pollution-sacrifice-zones-warns-un-expert.
- ↑ "How are hazards / risks distributed among different groups?". https://disaster-sts-network.org/content/peceannotation1524569139.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Huntington Smith, Helena (1975-02-16). "The Wringing of the West". The Washington Post (Washington, DC): p. 1–B4. ProQuest 146405625. ISSN 0190-8286.
- ↑ National Research Council (U. S.) Study Committee on the Potential for Rehabilitating Lands Surface Mined for Coal in the Western United States (1974). Rehabilitation potential of western coal lands. Cambridge, MA: Ford Foundation Energy Policy Project / Ballinger Pub. Co.. pp. 85–86. ISBN 978-0-88410-331-8. https://archive.org/details/rehabilitationpo0000nati.
- ↑ Atwood, Genevieve (1975-12-01). "The Strip-Mining of Western Coal". Scientific American 233 (6): 23–29. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1275-23. ISSN 0036-8733. Bibcode: 1975SciAm.233f..23A.
- ↑ "Lamm explained his view that Colorado must begin to control its own future, rather than succumbing to Washington's plea that the state should be "a national sacrifice area" to provide for the nation's energy needs." Griffith, Winthrop (1974-10-27). "An eco‐freak for governor?". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1974/10/27/archives/an-ecofreak-for-governor.html. Retrieved 2017-05-10.
- ↑ Sterba, James P. (1974-09-26). "Worry Rises That Rockies Face Pollution and Crowds". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. https://www.nytimes.com/1974/09/26/archives/worry-rises-that-rockies-face-pollution-and-crowds-no-exaggeration.html. Retrieved 2017-05-10.
- ↑ Fox, Julia (June 1999). "Mountaintop Removal in West Virginia". Organization & Environment 12 (2): 163–183. doi:10.1177/1086026699122002. ISSN 1086-0266.
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 "¿Qué son las zonas de sacrificio de Chile?" (in Spanish). El Diario. 2019-12-05. https://www.eldiario.es/ballenablanca/365_dias/zonas-sacrificio-chile-cumbre-clima_1_1205027.html.
- ↑ "Quintero y Puchuncaví: La zona de sacrificio" (in Spanish). La Tercera. 25 August 2018. https://www.latercera.com/nacional/noticia/quintero-puchuncavi-la-zona-sacrificio/295044/.
- ↑ "La olvidada escuela la Greda". 7 April 2019. https://www.latercera.com/nacional/noticia/la-olvidada-escuela-la-greda/603939/.
- ↑ "Chile: Supreme Court Hears Massive Air Pollution Case". 11 April 2019. https://www.hrw.org/news/2019/04/11/chile-supreme-court-hears-massive-air-pollution-case.
- ↑ US EPA (7 June 2004). "Agency Response to Recommendations Provided in the OIGEvaluation Report entitled, "EPA Needs to Consistently Implement the Intent of the Executive Order on Environmental Justice"". https://www.epa.gov/sites/production/files/2015-02/documents/oig-report-ej-cover-memo-response-6-8-04.pdf.
- ↑ Jessica Roake. "Think Globally, Act Locally: Steve Lerner, 'Sacrifice Zones,' at Politics and Prose". Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/express/wp/2010/09/23/steve-lerner-book-sacrifice-zones/.
- ↑ Bamberger, Kaela (2017-07-11). "Not Your Sacrifice Zone: In Lead-Poisoned East Chicago, Residents Fight for Their Health and Homes". In These Times. ISSN 0160-5992. http://inthesetimes.com/article/20320/lead-contamination-east-chicago-pollution-environmental-racism.
- ↑ "From Rethinking Schools: Sacrifice Zones". 2016. https://www.rethinkingschools.org/articles/sacrifice-zones.
- ↑ 20.0 20.1 Klinger, Julie Michelle (2021). "Environmental geopolitics and outer space". Geopolitics 26 (3): 666–703. doi:10.1080/14650045.2019.1590340. https://www.bu.edu/pardeeschool/files/2019/03/Environmental-Geopolitics-and-Outer-Space.pdf.
- ↑ Dunnett, Oliver; Klinger, Julie; Maclaren, Andrew; Lane, Maria; Sage, Daniel (2019). "Geographies of Outer Space: Progress and New Opportunities". Progress in Human Geography 43 (2): 314–366. doi:10.1177/0309132517747727. https://pure.qub.ac.uk/en/publications/geographies-of-outer-space-progress-and-new-opportunities(40ba81c0-2b24-498d-a94b-5ace7b48d3b0).html.
- ↑ Fernandes, Joao (2021). "8 facts about Point Nemo". History of Yesterday. https://historyofyesterday.com/8-facts-about-point-nemo-5ea0ca844795.
Further reading
- Dumping in Dixie by Robert Bullard. Routledge, 1990, 302 pp. ISBN:0-8133-6792-1
- Sacrifice Zones: The Front Lines of Toxic Chemical Exposure in the United States by Steve Lerner. Cambridge, MA:MIT Press, 2010. 346 pp. ISBN:978-0-262-01440-3
- Days of Destruction, Days of Revolt By Chris Hedges and Joe Sacco. Illustrated. 302 pp. Nation Books, 2012. 302pp. ISBN:978-1-56858-824-7
 |


