Medicine:Koch's triangle
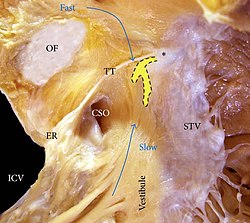
Koch's triangle, also known as the Triangle of Koch, is named after the German pathologist Walter Koch.[1] It is an anatomical area located at the base of the right atrium, and its boundaries are the coronary sinus orifice, tendon of Todaro, and the septal leaflet of the right atrioventricular valve (also known as the tricuspid valve).[2] It is anatomically significant because the atrioventricular node is located at the apex of the triangle. The base is formed by the coronary sinus orifice and the vestibule of the right atrium, and the hypotenuse is formed by the tendon of Todaro, which is often a continuation off the Eustachian valve. Other structures near to it are the membranous septum and the Eustachian ridge. Variations in the size of Koch's triangle are common.
The Triangle of Koch is an important landmark for atrioventricular catheter ablation procedures for the localization of the atrioventricular node.[3]
References
- ↑ Conti, Andrea A. (2011). "Calling the Heart by Name: Distinguished Eponyms in the History of Cardiac Anatomy". The Heart Surgery Forum 14 (3): 183. doi:10.1532/HSF98.20101047. https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/d1a2/47c7a80df61b8d9ada78f940be727daa6b7b.pdf.
- ↑ Catheter ablation of cardiac arrhythmias. Huang, Shoei K.,, Miller, John M. (John Michael), 1954- (Third ed.). Philadelphia, PA. pp. Figure 6-6. ISBN 9780323244299. OCLC 892338420. https://www.worldcat.org/oclc/892338420.
- ↑ Feger, Joachim. "Triangle of Koch | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org" (in en-US). https://radiopaedia.org/articles/triangle-of-koch?lang=us.
Further reading
- Sumitomo, Naokata; Tateno, Shigeru; Nakamura, Yoshihide; Ushinohama, Hiroya; Taniguchi, Kazuo; Ichikawa, Rie; Fukuhara, Junji; Abe, Osamu et al. (2007). "Clinical Importance of Koch's Triangle Size in Children". Circulation Journal 71 (12): 1918–21. doi:10.1253/circj.71.1918. PMID 18037746.
- Francalanci, Paola; Drago, Fabrizio; Agostino, Domenico Antonio; Liso, Gaetano; Giommo, Vincenzo; Boldrini, Renata; Ragonese, Pietro; Bosman, Cesare (1998). "Koch's Triangle in Pediatric Age: Correlation with Extra- and Intracardiac Parameters". Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 21 (8): 1576–9. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.1998.tb00245.x. PMID 9725156.
- Inoue, Shin; Becker, Anton E. (1998). "Koch's Triangle Sized Up: Anatomical Landmarks in Perspective of Catheter Ablation Procedures". Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology 21 (8): 1553–8. doi:10.1111/j.1540-8159.1998.tb00242.x. PMID 9725153.
- Sánchez-Quintana, Damián; Picazo-Angelín, Beatriz; Cabrera, Alberto; Murillo, Margarita; Cabrera, José Ángel (2010). "Koch's Triangle and the Atrioventricular Node in Ebstein's Anomaly: Implications for Catheter Ablation". Revista Española de Cardiología 63 (6): 660–7. doi:10.1016/S1885-5857(10)70140-7. PMID 20515623.
- Anderson, R. H.; Cook, A. C. (2007). "The structure and components of the atrial chambers". Europace 9 (Suppl 6): vi3–9. doi:10.1093/europace/eum200. PMID 17959691.
External links
- "Triangle of Koch". University of Minnesota. http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/right-atrium/triangle-of-koch/index.shtml.
 |

