Array controller based encryption
Within a storage network, encryption of data may occur at different hardware levels. Array controller based encryption describes the encryption of data occurring at the disk array controller before being sent to the disk drives. This article will provide an overview of different implementation techniques to array controller based encryption. For cryptographic and encryption theory, see disk encryption theory.
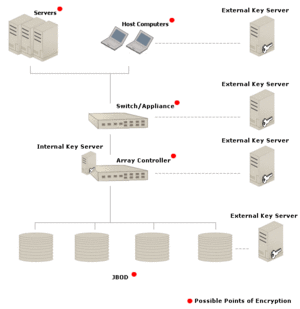
Possible points of encryption in SAN
The encryption of data can take place in many points in a storage network. The point of encryption may occur on the host computer, in the SAN infrastructure, the array controller or on each of the hard disks as shown on the diagram above. Each point of encryption has different merits and costs. Within the diagram, the key server components are also shown for each configuration of encryption. Designers of SANs and SAN components must take into consideration factors such as performance, deployment complexity, key server interoperability, strength of security, and cost when choosing where to implement encryption. But since the array controller is a natural central point of all data therefore encryption at this level is inherent and also reduces deployment complexity.
Array controller-based encryption
With different configurations of a hardware or software array controller, there are different types of solutions for this type of encryption. Each of these solutions can be built into existing infrastructures by replacing or upgrading certain components. Basic components include an encryption key server, key management client, and commonly an encryption unit which are all implemented into a storage network.
Internal array controller encryption
For an internal array controller configuration, the array controller is generally a PCI bus card situated inside the host computer. As shown in the diagram, the PCI array controller would contain an encryption unit where plaintext data is encrypted into ciphertext. This separate encryption unit is utilized to prevent and minimize performance reduction and maintain data throughput. Furthermore, the Key Management Client will generally be an additional service within the host computer applications where it will authenticate all keys retrieved from the Key Server. A major disadvantage to this type of implementation would be that encryption components are required to be integrated within each host computer and therefore is redundant on large networks with many host devices.
External array controller encryption
In the case of an external array controller setup, the array controller would be an independent hardware module connected to the network. Within the hardware array controller would be an Encryption unit for data encryption as well as a Key Management Client for authentication. Generally, there are few hardware array controllers to many host devices and storage disks. Therefore, it reduces deployment complexity to implement into fewer hardware components. Moreover, the lifecycle of an array controller is generally much longer than host computers and storage disks, therefore the encryption implementation will not need to be reimplemented as often as if encryption was done at another point in the storage network.
Encryption at the front-end or back-end side array controller
In an external array controller, the encryption unit can either be placed either on the front-end side or the back-end side of the array controller. There are different advantages and disadvantages in placing the encryption unit either on the front-end side or the back-end side:
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
|---|---|---|
| Front-end side | All data is first encrypted before it moves along the array controller, therefore data is encrypted before sending it through the replication link and or stored in internal array controller cache. | Since data is encrypted before it moves along the array controller, data de-duplication and data compression cannot be done when sending data through replication link. Therefore, huge costs can be incurred when sending huge amounts of data through the replication link. |
| Back-end side | Since all data is encrypted before leaving the array controller, data de-duplication and data compression can be done and therefore may save costs since only compressed and unique data is sent through the replication link. | Sensitive data may be compromised when sending through the replication link as well as cached data in the array controller compromised. |
The placement of the encryption unit may highly impact the secureness of your controller based encryption implementation. Therefore, this issue must be taken account for when designing your implementation to mitigate all security risks.
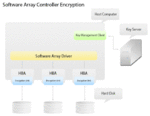
Software array controller encryption
For the software array controller encryption, a software array controller driver directs data into individual host bus adapters. In the adjacent diagram, there are multiple host bus adapters with hardware encryption units used for better performance requirements. In contrast, this type of encryption can be implemented with only 1 host bus adapter connected to a network of multiple hard drives and would still function. Performance will definitely be reduced since there will only be one encryption unit processing data. Key management will be done much like the internal array controller encryption mentioned before with the Key Management Client implemented as a service within the Host Computer.
External links
 |