Astronomy:4MV
The 4MV planetary probe (short for 4th-generation Mars-Venus probe) is a designation for a common design used for Soviet unmanned probes to Mars and Venus.
It was an incremental improvement of earlier 3MV probes and was used for Mars missions 2 to 7 and Venera missions 9 to 16. Different versions of the bus exist, for example 4V-1, 4V-M and 4V-2.[1][2] The same base design was also used for earth-orbiting space observatories.[3]
Design
The spacecraft bus has a height of 2.8 meters (9 ft 2 in) and a solar panel span of 6.7 meters (22 ft). The central section of the bus has a diameter of about one meter (3 ft 3 in) and contained propellant. The main engine (KTDU-425) is encircled by a conical instrument compartment with the diameter of 2.35 meters (7 ft 9 in) at the base.[4] While Mars 2,3 and Kosmos 419 used the KTDU-425, 4MV buses after 1971 used the KTDU-425A).[5]
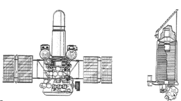
Variants
- Mars M-71|3MS: Kosmos 419 (M-71|3MS No.170), Mars 2 (M-71 No.171), Mars 3 (M-71 No.172)[6]
- Mars M-73|3MS|3MP: Mars 4 (M-73|3MS No.52S), Mars 5 (M-73|3MS No.53S), Mars 6 (M-73|3MP No.50P), Mars 7 (M-73|3MP No.51P)[7][8]
- Venera 4V-1: Venera 9 (4V-1 No.660), Venera 10 (4V-1 No.661), Venera 11 (4V-1 No.360), Venera 12 (4V-1 No.361), Venera 13 (4V-1M No.760), Venera 14 (4V-1M No.761)[1][2]
- Astron: Astron[9]
- Venera 4V-2: Venera 15 (4V-2 No.860), Venera 16 (4V-2 No.861)[10]
- Granat: Granat[11]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to 4MV. |
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Venera 9, 10, 11, 12 (4V1 #1, 2, 3, 4)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/venera-4v1.htm.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Venera 13, 14 (4V1M #1, 2)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/venera-4v1m.htm.
- ↑ "4MV". http://astronautix.com/4/4mv.html.
- ↑ "Venera-9 and 10". http://www.russianspaceweb.com/venera75.html.
- ↑ "KTDU-425". http://www.astronautix.com/k/ktdu-425.html.
- ↑ "Mars 2, 3 (Mars M71 #1, #2, #3)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/mars-71.htm.
- ↑ "Mars 4, 5 (Mars M73 Orbiter #1, #2)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/mars-73-orbiter.htm.
- ↑ "Mars 6, 7 (Mars M73 Lander #1, #2)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/mars-73-lander.htm.
- ↑ "Astron 1" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/astron.htm.
- ↑ "Venera 15, 16 (4V2 #1, 2)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/venera-4v2.htm.
- ↑ "Granat (Astron 2)" (in en). https://space.skyrocket.de/doc_sdat/granat.htm.
 |

