Biology:Acacia ascendens
| Acacia ascendens | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. ascendens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia ascendens Maslin
| |
| |
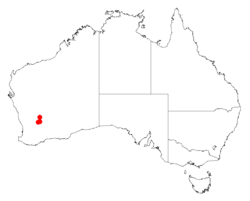
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Acacia ascendens is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to a small area in south western Australia .
Description
The erect shrub typically grows to a height of 1.3 to 3 metres (4 to 10 ft).[1] The glabrous shrub has resinous and slightly viscid new growth. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The evergreen phyllodes are inclined to erect and incurved to more or less straight with a length of 2 to 4 cm (0.79 to 1.57 in) and a width of 1 mm (0.039 in) with four impressed brownish nerves.[2] It blooms from June to September and produces yellow flowers.[1] The inflorescences occur singly or in pairs on terminal or axillary racemes with spherical flower-heads containing 20 to 25 densely packed golden flowers. Following flowering resinous seed pods form that have a narrowly oblong shape with a length that is up to 7 cm (2.8 in) and a width of around 5 mm (0.20 in) and contain longitudinally arranged seeds with an oblong-elliptic shape.[2]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist Bruce Maslin in 1990 as part of the work Acacia Miscellany. Three new Western Australian species with affinities to A. wilhelmiana (Leguminosae: Mimosoideae: Section Plurinerves) from Western Australia as published in the journal Nuytsia. It was reclassified as Racosperma ascendens by Leslie Pedley in 2003 and then transferred back to genus Acacia in 2014.[3] The shrub is closely related to Acacia abrupta and belongs to the Acacia wilhelmiana group.[2]
Distribution
It is native to a small area in the Wheatbelt and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia where it is often situated on scree slopes of breakaways composed of granite.[1] The range of the plant exists within the Chiddarcooping Nature Reserve, located approximately 70 km (43 mi) north east of Merredin as a part of low scrub or open woodland communities.[2]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Acacia ascendens". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/12248.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "Acacia ascendens". Wattle - Acacias of Australia. Lucid Central. https://apps.lucidcentral.org/wattle/text/entities/acacia_ascendens.htm. Retrieved 7 October 2020.
- ↑ "Acacia ascendens Maslin". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/https://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2921287#names. Retrieved 8 October 2020.
Wikidata ☰ Q9562347 entry
 |