Biology:Acacia extensa
| Acacia extensa | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. extensa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia extensa Lindl.
| |
| |
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
| Synonyms | |
Acacia extensa, commonly known as wiry wattle, is an erect shrub that is native to the South West corner of Western Australia. This particular species is resistant to dieback.[3]
Description
The wiry wattle is a perennial evergreen shrub that grows to a height of 2 metres (7 ft) tall,[4] although it can grow taller under cultivation. This occasionally weeping bush produces angled glabrous branchlets that are green with yellowish ribs.[5] The foliage are light green filiform pyllodites that are scattered along the branchlets that they resemble, they are typically 6 centimetres (2.4 in) to 24 centimetres (9 in) in length and 0.75 millimetres (0.03 in) to 2 millimetres (0.08 in) in width. A. extensa typically flowers in spring (between August and October) and produces yellow ball shaped blossoms that are generally less than 1 centimetre (0.39 in) in diameter off short stem stalks called racemes.[6]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist John Lindley in 1839 as part of the work A Sketch of the Vegetation of the Swan River Colony. Synonyms include Acacia graminea as described by Johann Georg Christian Lehmann, Acacia pentaedra by Eduard August von Regel, Acacia calamistrata by Nikolaus Joseph von Jacquin and Racosperma extensum by Leslie Pedley.[2]
The type specimen was collected in the Swan River Colony by James Drummond.[5]
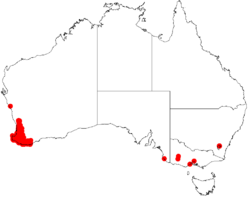
Distribution
A. extensa is found in the South West corner of Western Australia. The species is found as far east as Albany and as far north as Leeman. This species prefers sandy or sandy lateritic soils generally in damp areas such as along water courses or near lakes and swamps.[6]
See also
References
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Acacia extensa. |
- ↑ "Western Australian Natives Resistant to Phytophthora cinnamomi". 2006. http://www.ildis.org/LegumeWeb?version~10.01&LegumeWeb&tno~23023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Acacia extensa Lindl.". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2904648#names.
- ↑ "ILDIS Legumeweb - Acacia extensa". 2005. http://www.cpsm.murdoch.edu.au/downloads/resources/natives_resistant.pdf.
- ↑ "Australian National Botanic Garden - Acacia extensa". 2007. http://www.anbg.gov.au/acacia/species/A-extensa.html.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "World Wide Wattle - Acacia extensa". 2005. http://www.worldwidewattle.com/speciesgallery/extensa.php?id=3331.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 "Acacia extensa". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/3331.
Wikidata ☰ Q4670931 entry
 |
