Biology:Acacia lasiocarpa
| Panjang | |
|---|---|

| |
| A. lasiocarpa flowers. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. lasiocarpa
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia lasiocarpa Benth.
| |
| |
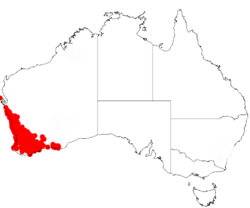
| Occurrence data from AVH | |
Acacia lasiocarpa, commonly known as Panjang or Pajang[1] or glow wattle,[2] is a shrub of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Pulchellae that is endemic to Western Australia.
Description
The shrub typically grows to a height of 0.15 to 0.5 metres (0.5 to 1.6 ft)[3] and 1 m (3 ft) across.[2] The branchlets are covered in spines. The pinnae occur in pairs and have a length of 1 to 10 millimetres (0.039 to 0.394 in) with two to eight pairs of pinnules that are 1 to 5 mm (0.039 to 0.197 in) long and 0.5 to 1 mm (0.020 to 0.039 in) wide.[4] The foliage is lime green in colour.[2] It blooms from May to October and produces yellow flowers.[3] The rudimentary inflorescences have globular flowerheads containing 16 to 50 golden flowers. Following flowering flat or undulate brown seed pods form that are 10 to 40 mm (0.4 to 1.6 in) in length and 3 to 5 mm (0.12 to 0.20 in) wide. The sometimes mottled seeds inside have an oblong to elliptic or circular shape and are 1.5 to 2.5 mm (0.06 to 0.10 in) in length.[4]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist George Bentham in 1837 as part of the Bentham, Stephan Endlicher, Eduard Fenzl and Heinrich Wilhelm Schott work Enumeratio plantarum quas in Novae Hollandiae ora austro-occidentali ad fluvium Cygnorum et in Sinu Regis Georgii collegit Carolus liber baro de Hügel. It was reclassified as Racosperma lasiocarpum in 2003 but transferred back to the genus Acacia in 2006.[5]
There are three varieties:
- Acacia lasiocarpa var. bracteolata
- Acacia lasiocarpa var. lasiocarpa[6]
- Acacia lasiocarpa var. sedifolia
Distribution
It is native to an area in the Wheatbelt, Goldfields-Esperance and Great Southern regions of Western Australia[3] with the bulk of the population found south west of a line from Kalbarri to Esperance.[4] The plant is found in a range of habitat including in seasonally damp areas, in and around swamps, on flats and coastal dunes an can grow in a variety of soils.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ "Noongar names for plants". kippleonline.net. http://www.kippleonline.net/bobhoward/plantsframe.html. Retrieved 20 November 2016.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Acacia lasiocarpa Glow wattle (prostrate form)". Lullfitz Nursery. http://www.lullfitz.com.au/acacia-lasiocarpa/. Retrieved 23 September 2018.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Acacia lasiocarpa". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/3409.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Acacia lasiocarpa". World Wide Wattle. Western Australian Herbarium. 24 September 2018. http://worldwidewattle.com/speciesgallery/lasiocarpa.php.
- ↑ "Acacia lasiocarpa Benth.". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/http://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2893109#names. Retrieved 24 September 2018.
- ↑ "Acacia lasiocarpa var. lasiocarpa". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/11611.
Wikidata ☰ Q15287570 entry
 |

