Biology:Acacia maconochieana
| Mullan wattle | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Fabales |
| Family: | Fabaceae |
| Subfamily: | Caesalpinioideae |
| Clade: | Mimosoid clade |
| Genus: | Acacia |
| Species: | A. maconochieana
|
| Binomial name | |
| Acacia maconochieana Pedley
| |
| |
Acacia maconochieana, also known as Mullan wattle,[1] is a shrub or tree of the genus Acacia and the subgenus Plurinerves that is endemic to an arid area of central Australia .
Description
The shrub or tree typically grows to a height of 2.5 to 12 metres (8 to 39 ft)[2] and has longitudinally fissured, grey coloured bark and densely haired branchlets. Like most species of Acacia it has phyllodes rather than true leaves. The hairy, evergreen phyllodes have a linear shape with a length of 8 to 18 cm (3.1 to 7.1 in) and a width of 2 to 5 mm (0.079 to 0.197 in) with many fine and closely parallel nerves.[1] It blooms in October and produces yellow flowers.[2]
Taxonomy
The species was first formally described by the botanist Leslie Pedley in 1986 as a part of the work Acacia maconochieana (Mimosaceae), a new species from semi-arid Australia as described in the journal Austrobaileya. It was reclassified by Pedley as Racosperma maconochieanum in 2003 then returned to genus Acacia in 2006.[3]
Distribution
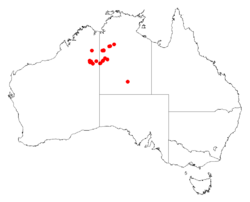
It is native to an area in the Northern Territory and the Kimberley and Goldfields-Esperance regions of Western Australia and is commonly situated along the margins of lakes that are periodically flooded growing in sandy or loamy soils.[2] The range of the plant extends from around Gregory Salt Lake in the west through to around Nongra Lake in the Tanami Desert in the east where it is usually a part of low open forest or woodland or open scrubland communities.[1]
Aboriginal names
The Walmajarri people of the Paruku IPA in the Kimberley call this wattle Wirimangurru.[4] Other Aboriginal names are:Jaru: gunanduru, wirrimangurru and Ngarinyman: Gunadurr.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "Acacia maconochieana". World Wide Wattle. Western Australian Herbarium. http://worldwidewattle.com/speciesgallery/maconochieana.php. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "Acacia maconochieana". FloraBase. Western Australian Government Department of Parks and Wildlife. https://florabase.dpaw.wa.gov.au/browse/profile/3433.
- ↑ "Acacia maconochieana Pedley". Atlas of Living Australia. Global Biodiversity Information Facility. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/https://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2886748#names. Retrieved 8 December 2020.
- ↑ , Wikidata Q106088428
- ↑ "NT Flora: Acacia Maconochieana". http://eflora.nt.gov.au/factsheet?id=3489.
Wikidata ☰ Q15287697 entry
 |

