Biology:Aegidae
From HandWiki
Short description: Family of crustaceans
| Aegidae | |
|---|---|
| |
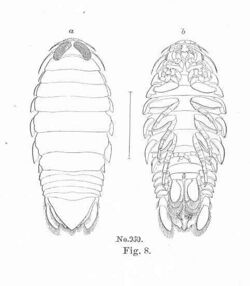
| Aega psora | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Superorder: | Peracarida |
| Order: | Isopoda |
| Suborder: | Cymothoida |
| Superfamily: | Cymothooidea |
| Family: | Aegidae White, 1850 |
The Aegidae are a family of isopod crustaceans. The adults are temporary parasites of fish, feeding on their hosts' blood before dropping off to digest the meal.[1] They differ from members of the family Cirolanidae in having only three pairs of hook-like pereiopods, whereas in Cirolanidae all seven pairs of pereiopods are hooked.[2] The family was first described by Adam White in 1850.[3]
The family contains the following genera:[4]
- Aega Leach, 1815
- Aegapheles Bruce, 2009
- Aegiochus Bovallius, 1885
- Alitropus H. Milne-Edwards, 1840
- Epulaega Bruce, 2009
- Rocinela Leach, 1818
- Syscenus Harger, 1880
- Xenuraega Tattersall, 1909
References
- ↑ Richard C. Brusca, Vánia R. Coelho & Stefano Taiti (2007). "Isopoda". The Light and Smith Manual: Intertidal Invertebrates from Central California to Oregon (4th ed.). University of California Press. pp. 503–542. ISBN 9780520239395. https://books.google.com/books?id=64jgZ1CfmB8C&pg=PA513.
- ↑ Roger Tory Peterson; Kenneth L. Gosner (1999). A Field Guide to the Atlantic Seashore: from the Bay of Fundy to Cape Hatteras. Peterson Field Guide. 24. Houghton Mifflin Harcourt. p. 225. ISBN 9780618002092. https://books.google.com/books?id=E1UQ9VEX7qAC&pg=PA225.
- ↑ White, A. (1850), https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/49050355, Wikidata Q115584173
- ↑ "Aegidae". World Marine, Freshwater and Terrestrial Isopod Crustaceans database. World Register of Marine Species. 2011. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=118272.
Wikidata ☰ Q3916255 entry
 |

