Biology:Animal trypanosomiasis
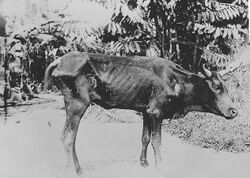
File:Parasite150045-fig1 Dog with Trypanosoma congolense.tif Animal trypanosomiasis, also known as nagana and nagana pest, or sleeping sickness, is a disease of vertebrates. The disease is caused by trypanosomes of several species in the genus Trypanosoma such as Trypanosoma brucei. Trypanosoma vivax causes nagana mainly in West Africa, although it has spread to South America.[1] The trypanosomes infect the blood of the vertebrate host, causing fever, weakness, and lethargy, which lead to weight loss and anemia; in some animals the disease is fatal unless treated. The trypanosomes are transmitted by tsetse flies.[2]
An interesting feature is the remarkable tolerance to nagana pathology shown by some breeds of cattle, notably the N'Dama – a West African Bos taurus breed. This contrasts with the susceptibility shown by East African Bos indicus cattle such as the zebu.[3]
Transmission
Most trypanosomes develop in tsetse flies (Glossina spp.), its biological vector, in about one to a few weeks. When an infected tsetse fly bites an animal, the parasites are transmitted through its saliva. It can also be spread by fomites such as surgical instruments, needles, and syringes. The most important vectors are thought to be horseflies (Tabanidae spp.) and stable flies (Stomoxys spp.).
The immune response of animals may be unable to eliminate trypanosomes completely, and the host may become an inapparent carrier. These inapparent infections can be reactivated if the animal is stressed. Transplacental transmission can also occur.[4]
Signs and symptoms
The incubation period ranges from 4 days to approximately 8 weeks. The infection leads to significant weight loss and anemia. Various symptoms are observed, including fever, oedema, adenitis, dermatitis and nervous disorders. The disease cannot be diagnosed with certainty except physically detecting parasites by blood microscopic examination or various serological reactions.[4][5]
Vectors
| Disease | Species affected | Trypanosoma agents | Distribution | Glossina vectors |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nagana — acute form | antelope
cattle camels horses |
T. brucei brucei | Africa | G. morsitans
G. swynnertoni G. pallidipes G. palpalis G. tachinoides |
| Nagana — chronic form | cattle
camels horses |
T. congolense | Africa | G. palpalis
G. morsitans G. austeni G. swynnertoni G. pallidipes G. longipalpis G. tachinoides G. brevipalpis |
| Nagana — acute form | domestic pigs
cattle camels horses |
T. simiae | Africa | G. palpalis
G. fuscipes G. morsitans G. tachinoides G. longipalpis G. fusca G. tabaniformis G. brevipalpis G. vanhoofi G. austeni |
| Nagana — acute form | cattle
camels horses |
T. vivax | Africa | G. morsitans
G. palpalis G. tachinoides G. swynnertoni G. pallidipes G. austeni G. vanhoofi G. longipalpis |
Control measures
If the outbreak is detected early, the organism can be destroyed by quarantines, movement controls, and the euthanasia of infected animals. Tsetse fly populations can be reduced or eliminated by traps, insecticides, and by treating infected animals with antiparasitic drugs. The tsetse habitat can be destroyed by alteration of vegetation. Some drugs can prevent trypanosomiasis, and are called prophylactic drugs. These are very effective in protecting animals during the times they are exposed to diseases. Historically, these drugs were not used properly, leading to some resistance.
Economic impact
Although the loss of direct livestock products (meat, milk, and blood) is problematic, the greatest impact of livestock trypanosomiasis is the loss of crop productivity due to loss of the animals' draught power in the field.[6][7]
References
- ↑ "Association of Trypanosoma vivax in extracellular sites with central nervous system lesions and changes in cerebrospinal fluid in experimentally infected goats". Veterinary Research 42 (63): 1–7. 2011. doi:10.1186/1297-9716-42-63. PMID 21569364.
- ↑ "Human African trypanosomiasis (sleeping sickness)". WHO. https://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs259/en/.
- ↑ "Host genetics in African trypanosomiasis". Infect. Genet. Evol. 8 (3): 229–38. May 2008. doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2008.02.007. PMID 18394971.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "African Animal Trypanosomiasis". October 2018. http://www.cfsph.iastate.edu/Factsheets/pdfs/trypanosomiasis_african.pdf.
- ↑ Finelle, P.. "African animal trypanosomiasis". Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. http://www.fao.org/docrep/010/ah809e/AH809E02.htm. Retrieved 19 April 2017.
- ↑ Swallow, Brent M.; Animal Production and Health Division, International Livestock Research Institute, Nairobi, Kenya. (2000). Impacts of trypanosomiasis on African agriculture. PAAT Technical and Scientific Series. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. p. vii+52. ISBN 92-5-104413-9. OCLC 45185699. AGRIS id XF2001396009. CABD 20003010139.
- ↑ Giordani, Federica; Morrison, Liam J.; Rowan, Timothy G.; De Koning, Harry P.; Barrett, Michael P. (2016-10-10). "The animal trypanosomiases and their chemotherapy: a review". Parasitology (Cambridge University Press (CUP)) 143 (14): 1862–1889. doi:10.1017/s0031182016001268. ISSN 0031-1820. PMID 27719692.
Further reading
- WHO fact sheet on Trypanosomiasis
- "A step closer to treating nagana". 2017-01-17. http://www.galvmed.org/step-closer-treating-nagana/.
 |